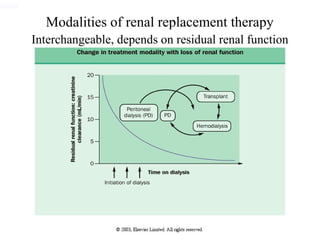
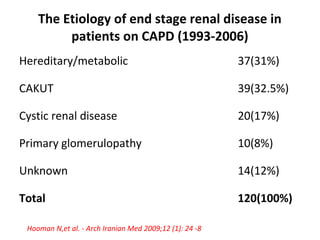
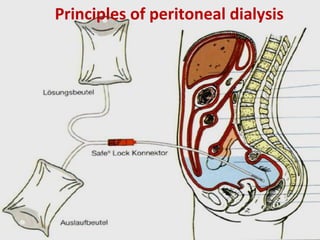
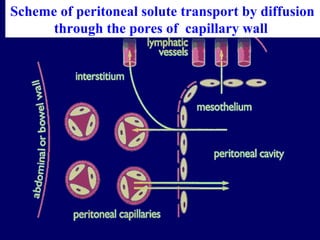
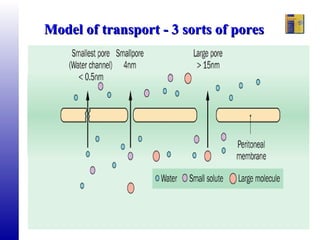
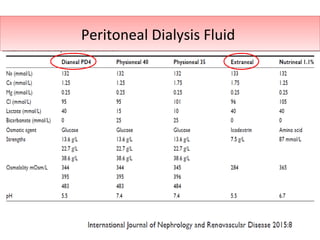
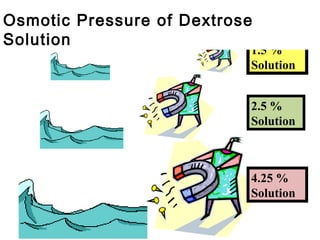
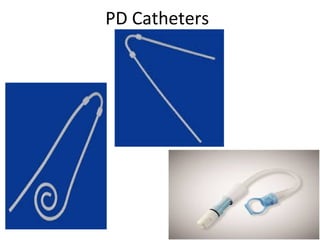
The document outlines the principles and processes of peritoneal dialysis (PD) in children, including various modalities, indications, contraindications, and assessment of adequacy. It emphasizes the importance of patient-specific adjustments to PD prescriptions and highlights potential complications. Nutrition considerations and the role of residual renal function in therapy are also discussed.