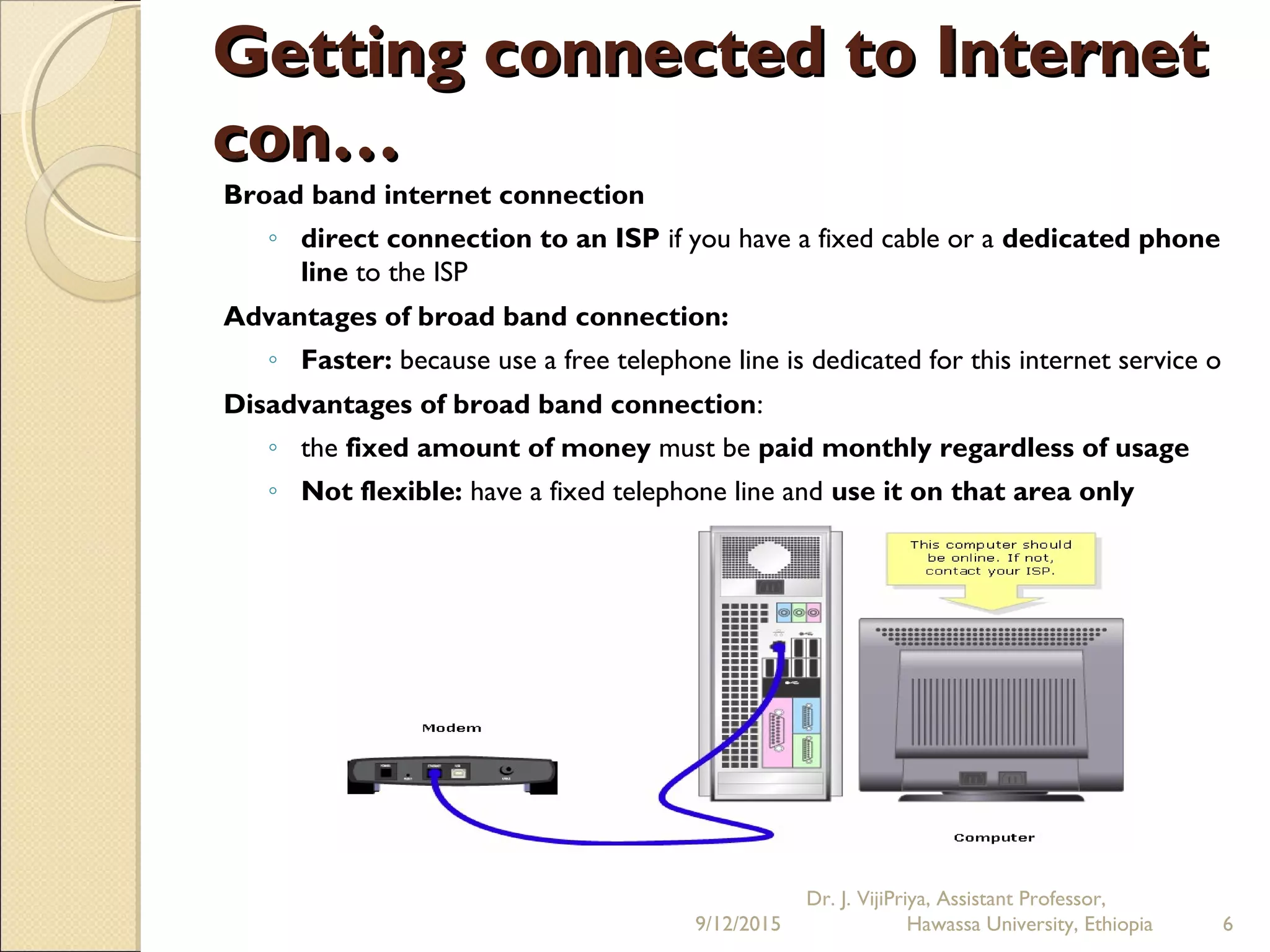
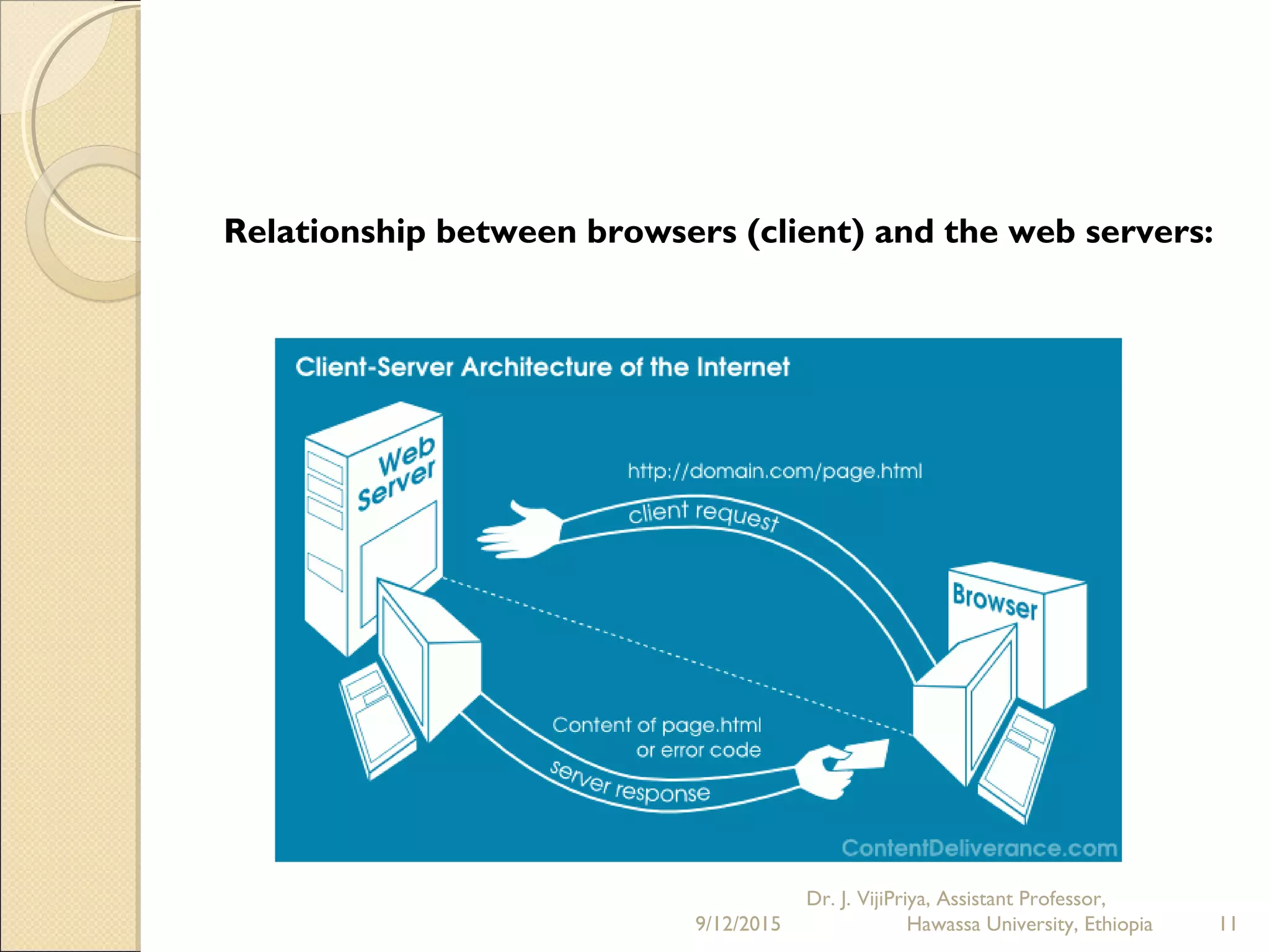
The document discusses the Internet and social networking services. It begins by defining the Internet as a network of networks that connects computers globally using TCP/IP protocols. It describes how users can connect to the Internet via dial-up or broadband connections using modems. Common Internet applications are discussed, including the World Wide Web, email, file transfer, and social networking services. Social networks allow users to create profiles, make connections with friends, and share content. Emerging trends include businesses using social networks for branding and recruitment. Issues with privacy and oversharing personal information on social platforms are also noted.