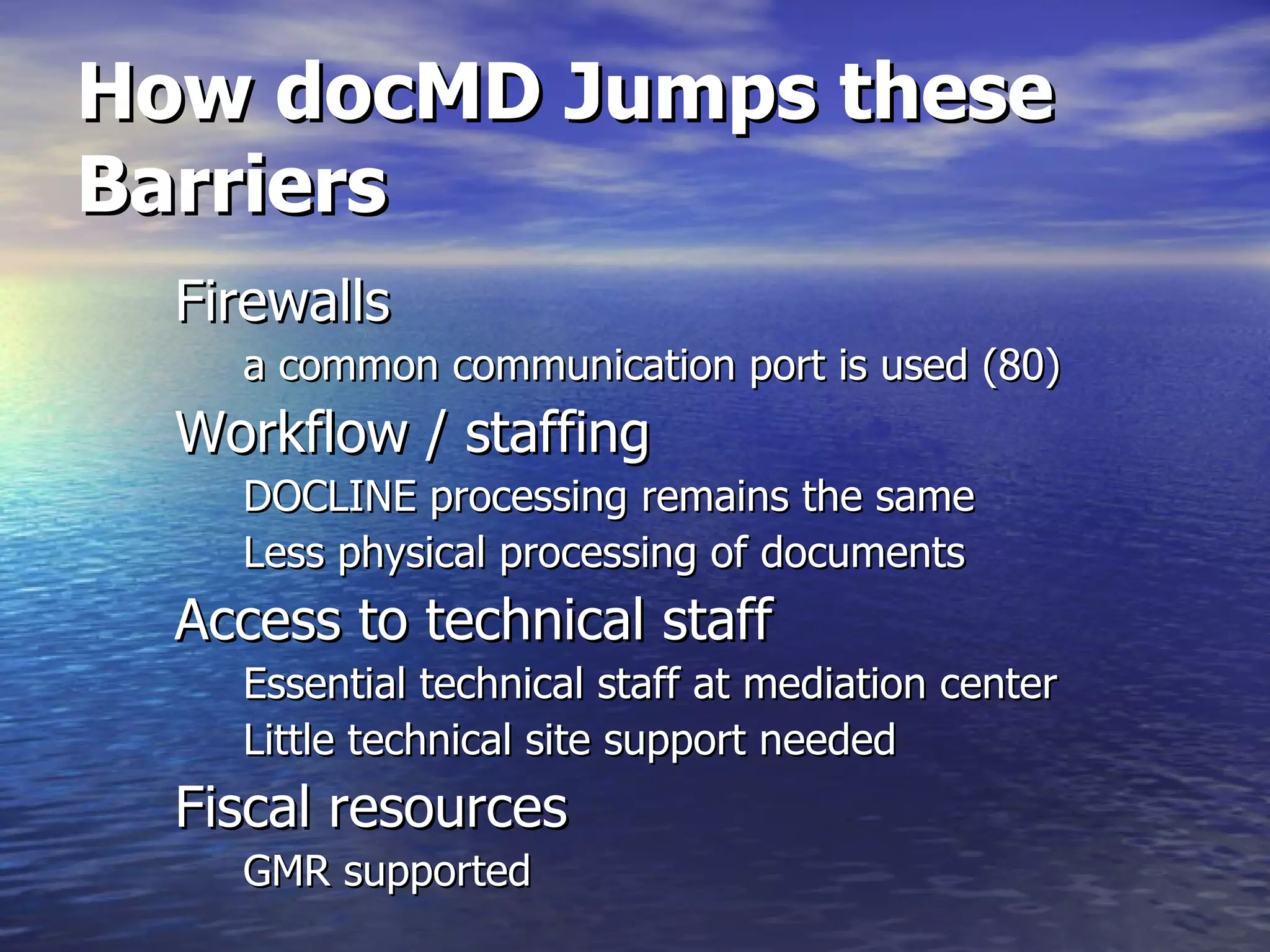
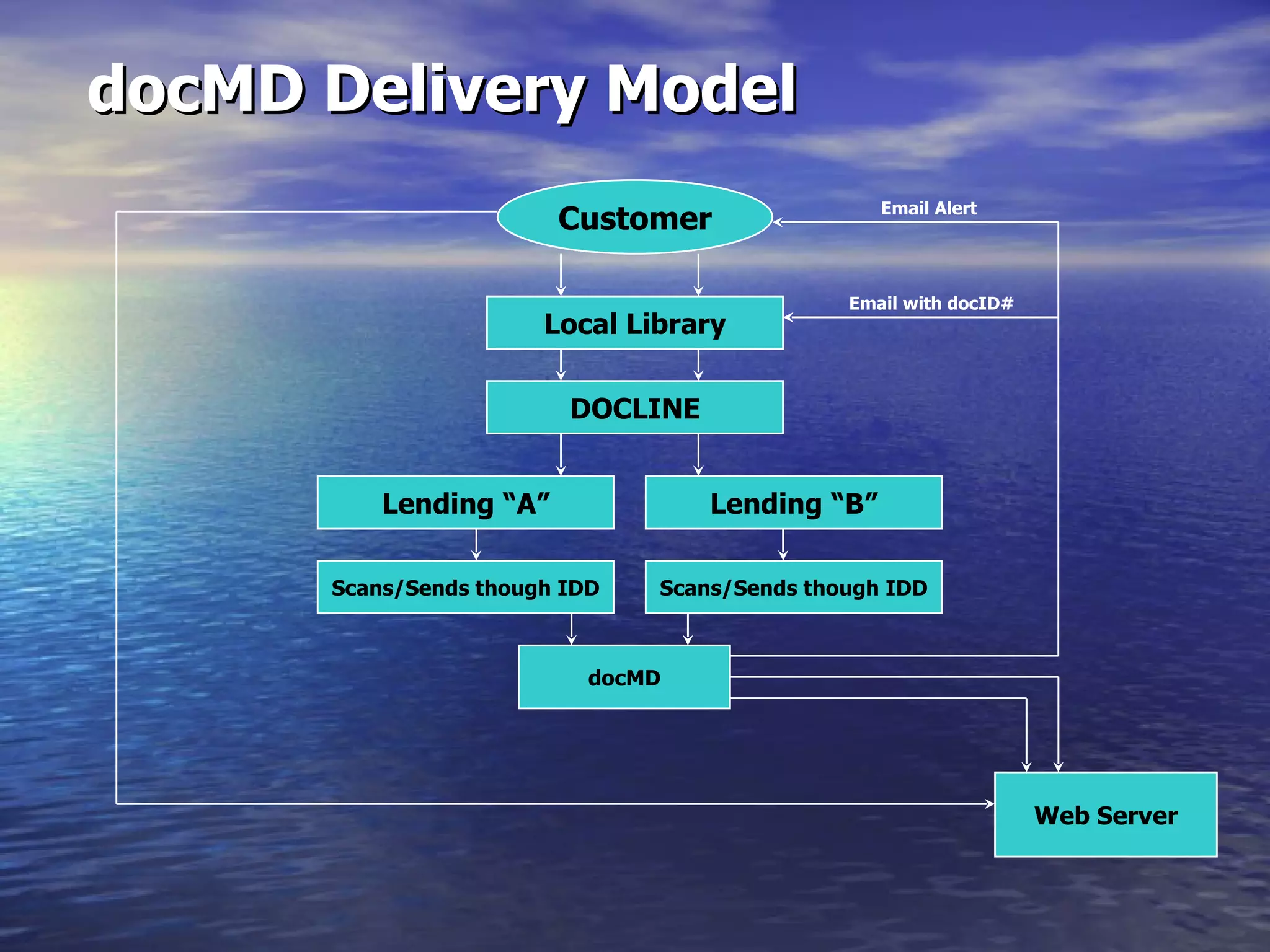
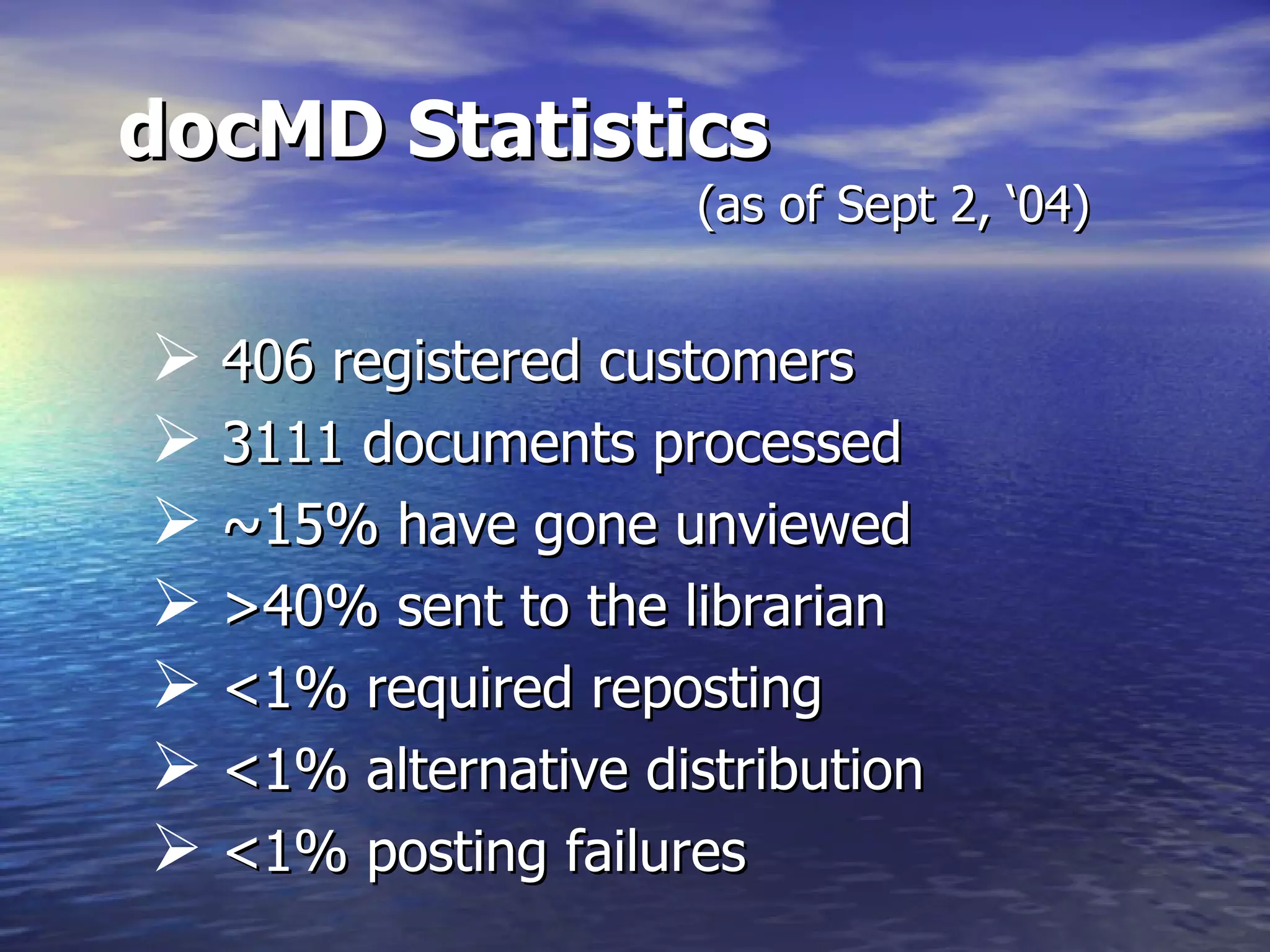
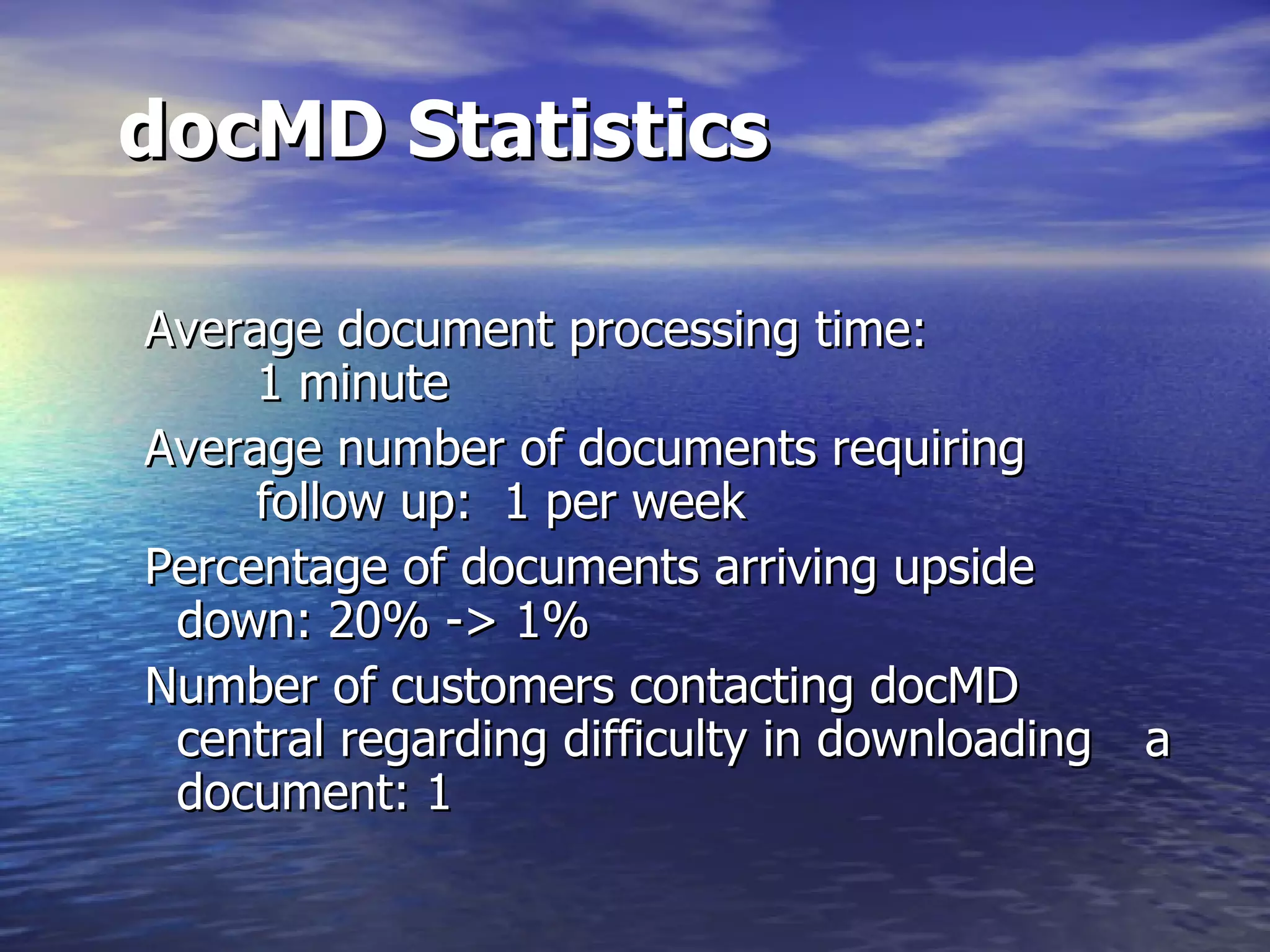
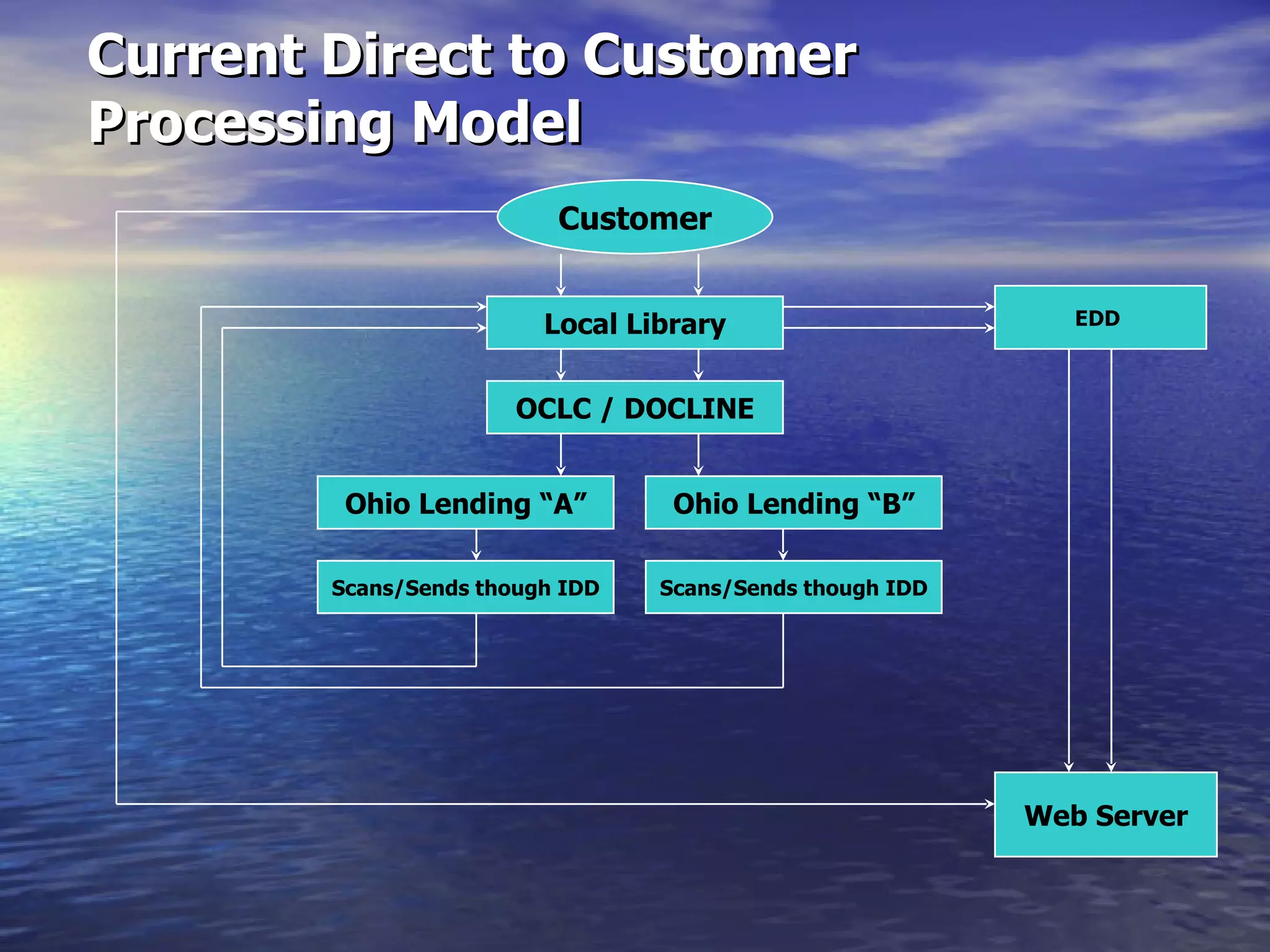
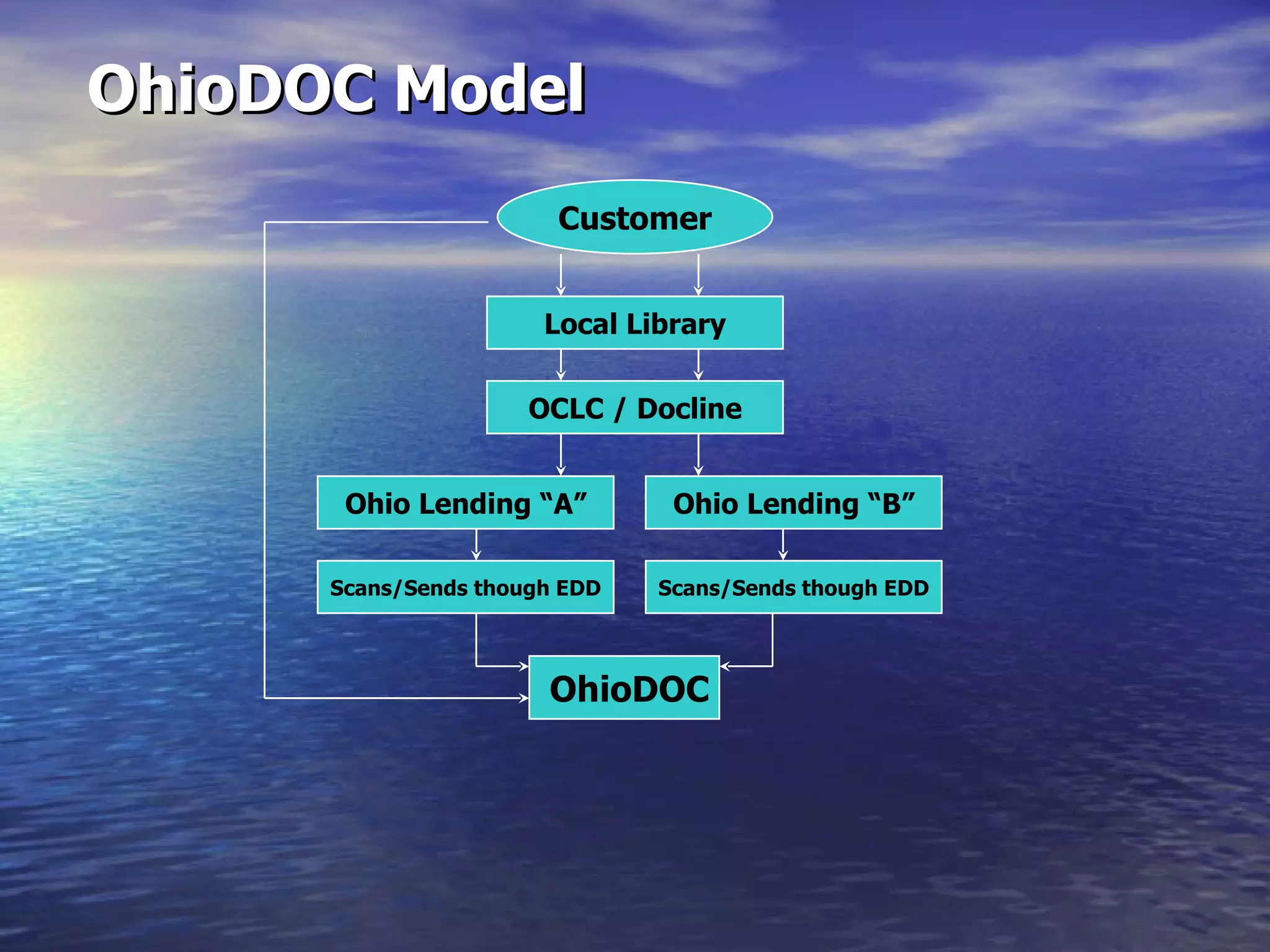
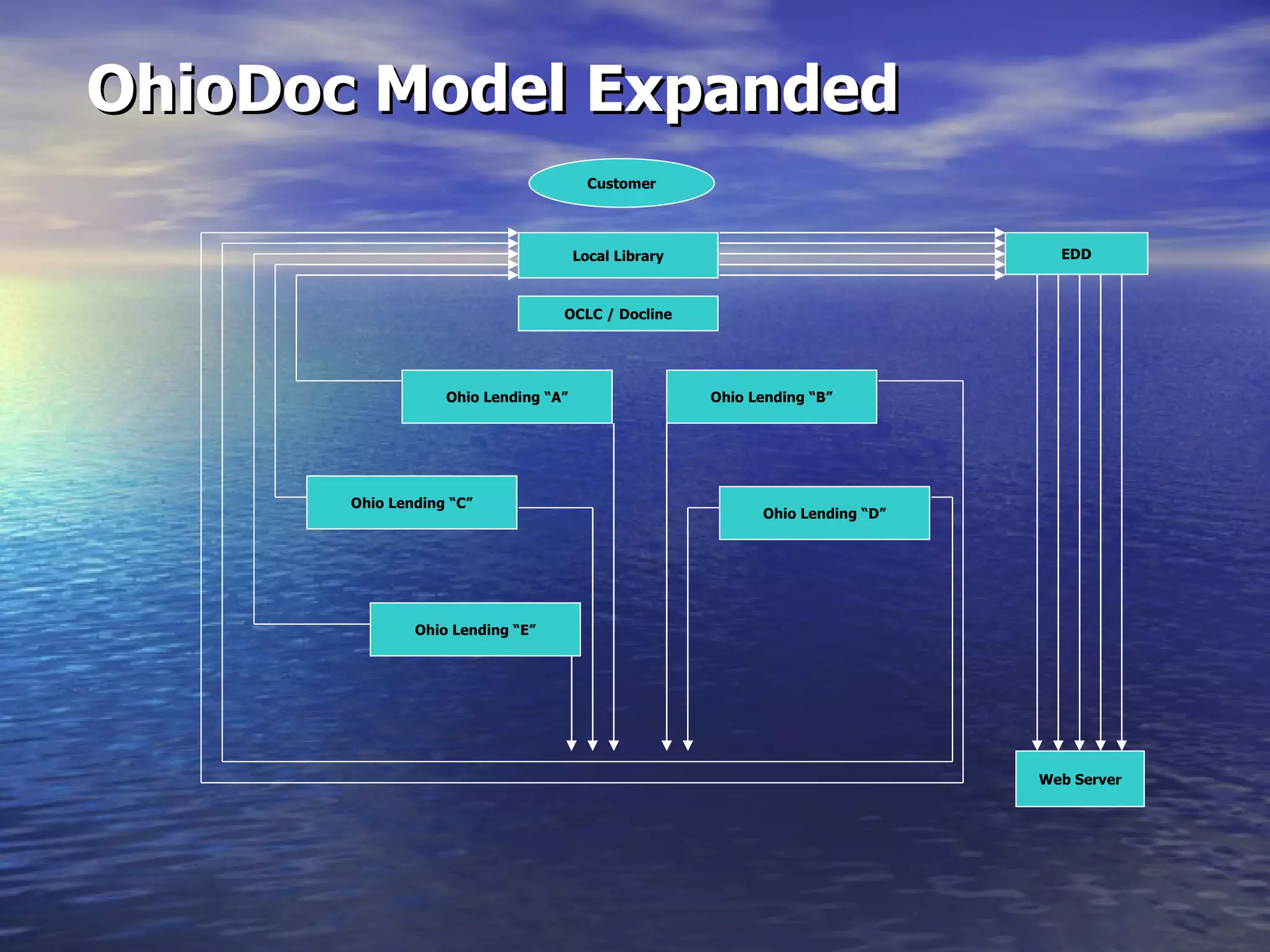
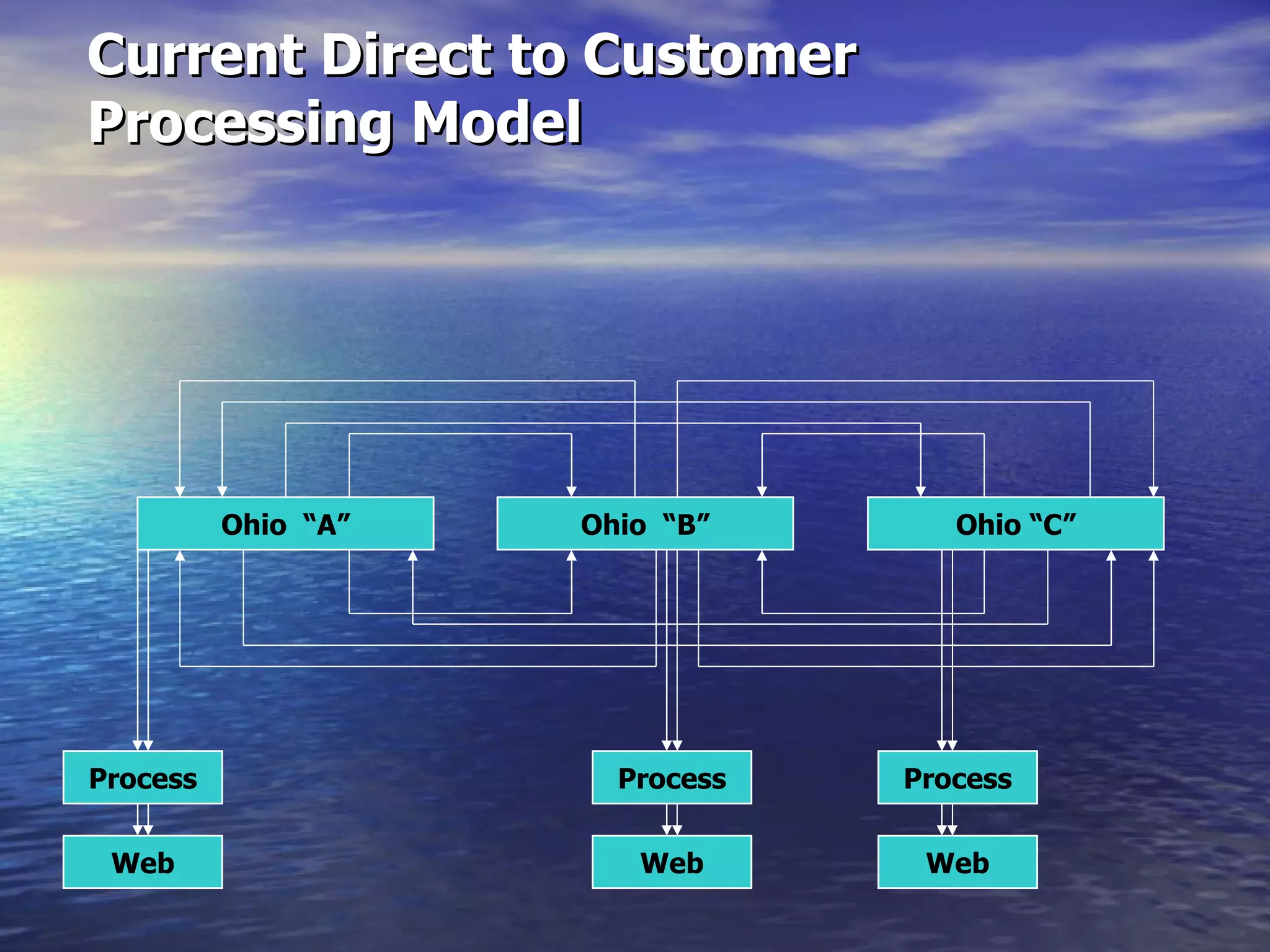
The document describes docMD, an electronic document delivery service established by the Ohio State University to provide access to articles for hospital libraries. DocMD aims to reduce costs and turnaround times for document delivery. It establishes a centralized mediation service to handle delivery between participating libraries in order to overcome barriers hospitals face in directly implementing interlibrary loan delivery services, such as firewalls, workflow issues, and lack of technical support. The summary provides statistics on docMD's usage and effectiveness in reducing turnaround times after its establishment.


















![Thanks! E-mail: [email_address] Project: docmd.med.ohio-state.edu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docmd_portland-090223114737-phpapp01/75/docMD-DOCument-Mediated-Delivery-28-2048.jpg)