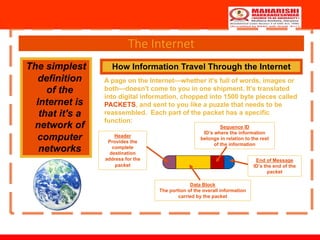
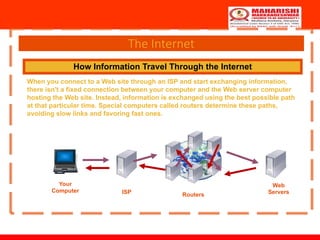
The document discusses the history and development of the Internet and World Wide Web. It explains that the Internet began as a US Department of Defense research project called ARPANET in the 1960s to connect government computers. Over time, other networks were connected to ARPANET to share information, leading to the commercialization of the Internet in the 1990s. The World Wide Web was created in the late 1980s to share information over the Internet through hyperlinked documents that could be accessed using a web browser. Today, the Internet and World Wide Web enable global communication, commerce, education and more.