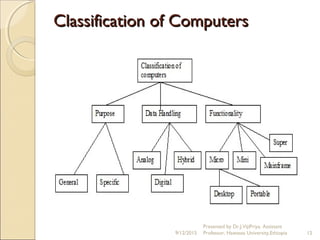
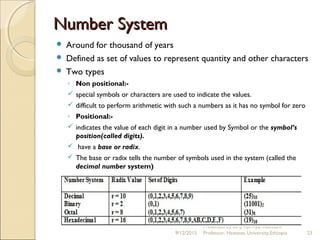
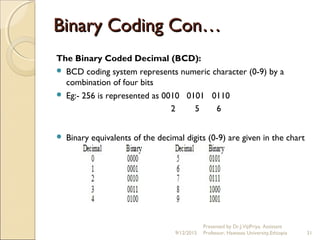
This document provides an introduction to computers and information and communication technology. It discusses the definition of a computer as an electronic device that can perform calculations and logical operations by processing input and outputting results. Computers are used in many fields including medicine, education, science, engineering, government, entertainment, and agriculture. The document then discusses data representation in computers, including number systems, binary and decimal conversions, and basic units of representation like bits and bytes.