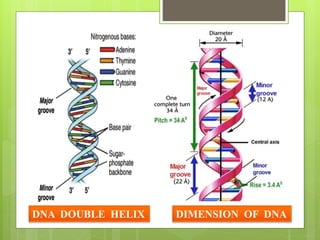
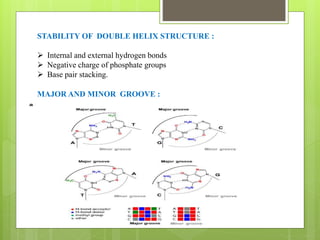
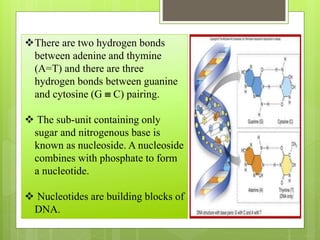
This document summarizes the DNA double helix structure proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. They discovered that DNA exists as two intertwined strands that coil around each other to form a double helix. Each strand is made up of alternating sugar and phosphate groups with nitrogenous bases protruding inward. The bases on one strand form hydrogen bonds with complementary bases on the other strand according to Chargaff's rules - adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. Watson and Crick received the Nobel Prize in 1962 for their discovery of the DNA double helix structure.





![ Erwin Chargaff in 1949 showed that
(i) The bases pair in specific manner. Adenine always pairs with
thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine.
(ii) Total amount of purine nucleotides is always equal to the total
amount of pyrimidine nucleotides i.e.[A] + [G] = [T] + [C].
(iii) The proportion of adenine is equal to thymine and so also of
guanine is equal to cytosine. But the [A] + [T] need not necessarily
be equal to [G] + [C].
These empirical rules regarding the composition of bases in DNA is
collectively known as Chargaff’s law or Base pair rules.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doublehelicaldna-210519075743/85/Double-helical-DNA-Structure-and-Definition-9-320.jpg)
