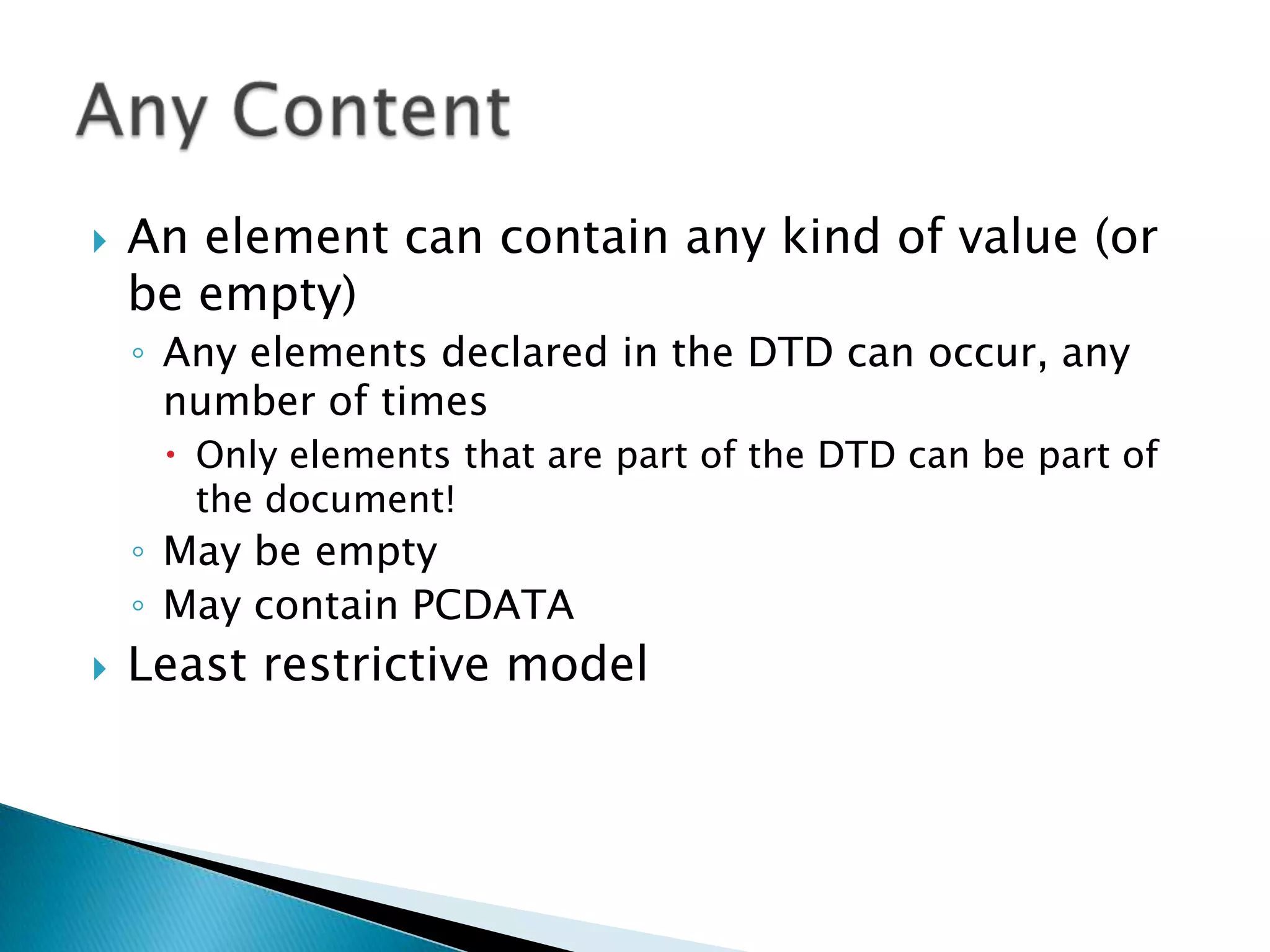
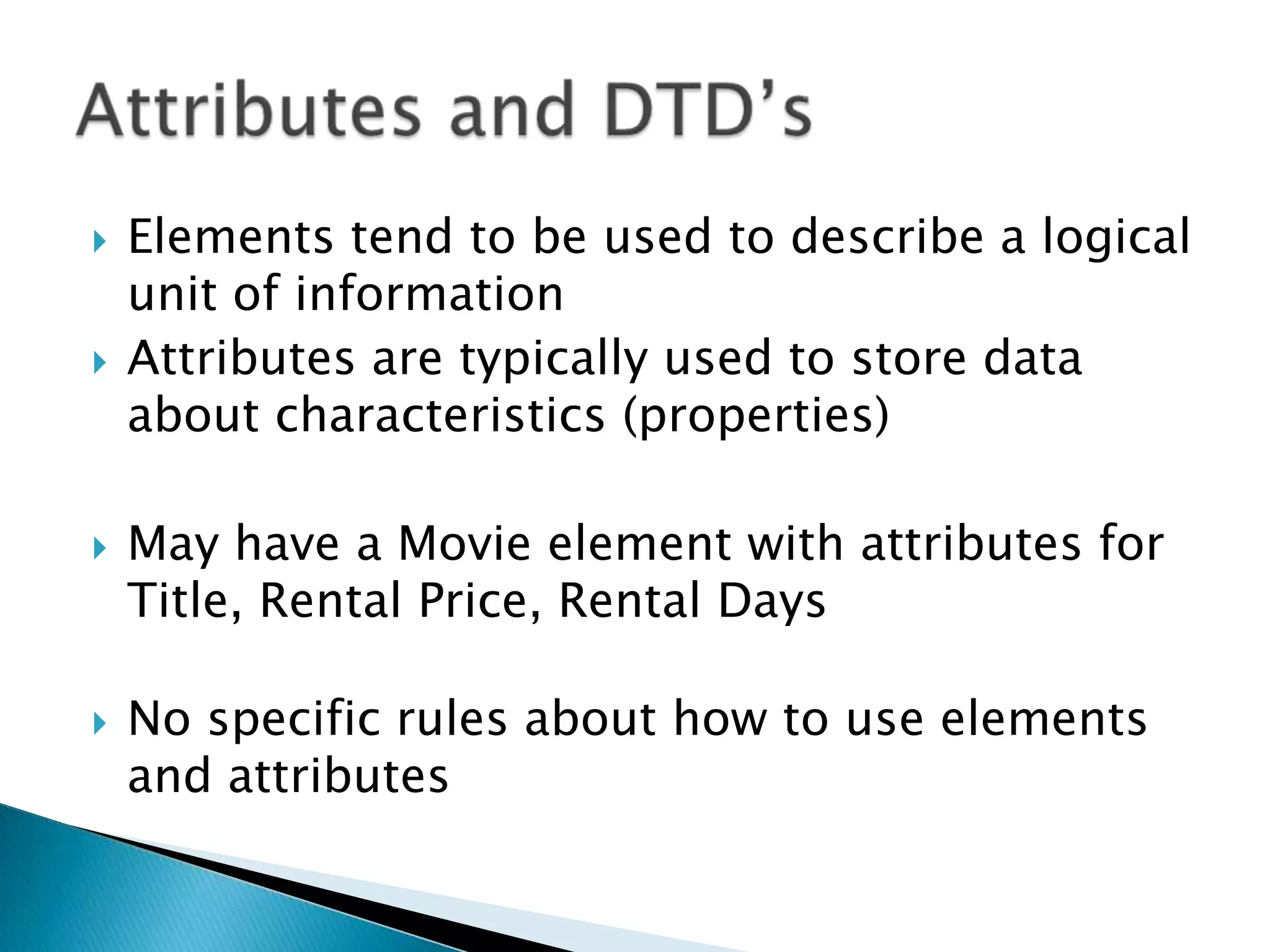
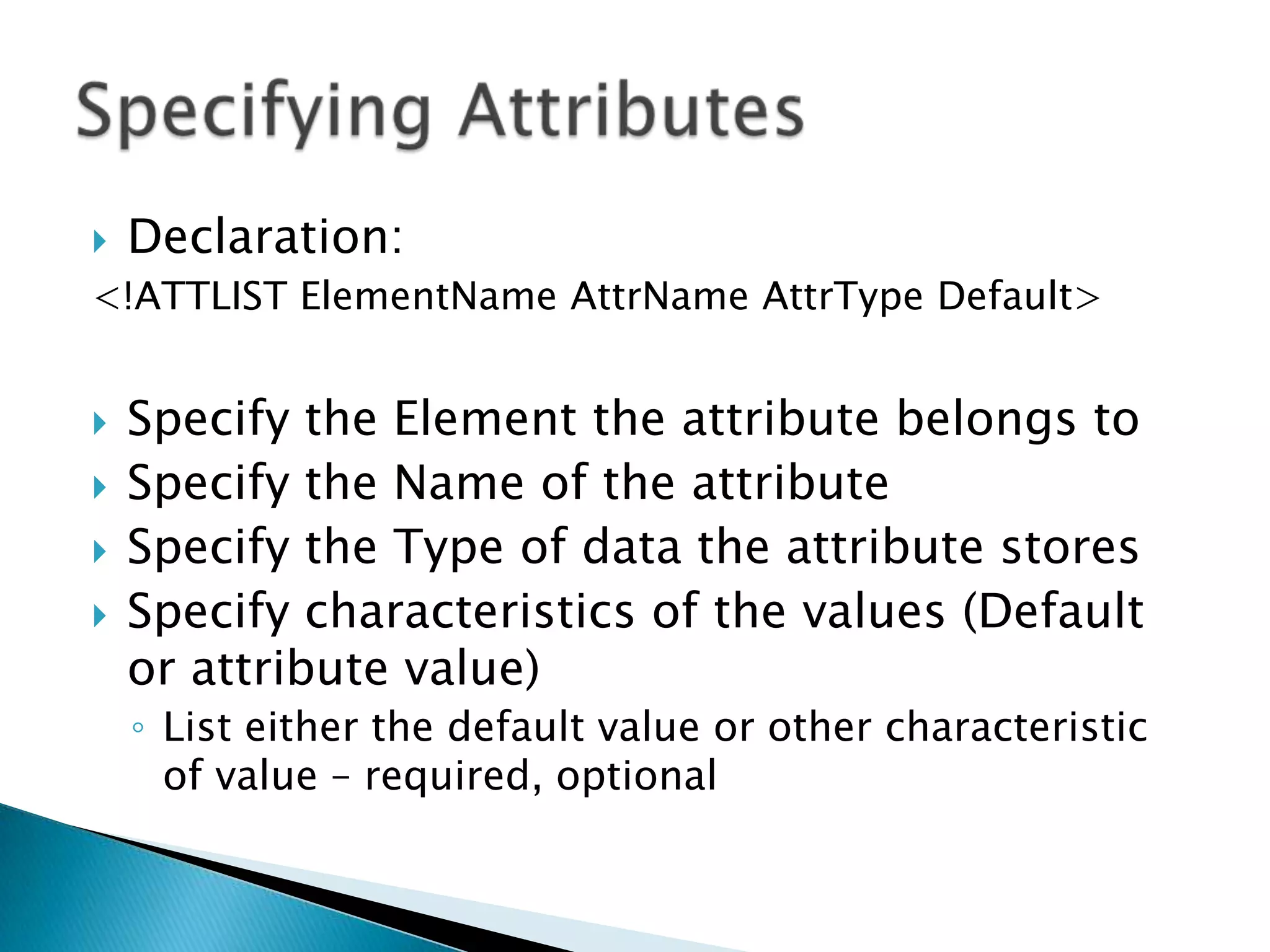
DTD stands for Document Type Definition and allows an XML document to specify requirements to be valid. It declares elements, attributes, and other components that can be used in an XML document. Validation ensures an XML document matches the DTD specifications by checking elements, attributes, and structure. DTDs can be embedded locally in an XML file or referenced externally from another file.






![DTD included in XML documentDefinition of a student:<!DOCTYPE student[<!ELEMENT student(first, last, studentID)><!ELEMENT first (#PCDATA)><!ELEMENT last(#PCDATA)><ELEMENT studentID(#PCDATA)>]>LocalDTDDocument Type DeclarationElement DeclarationA student element is made up of first name, last name, and student id elements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/documenttypedefinitions-091021130825-phpapp01/75/Document-Type-Definitions-7-2048.jpg)

![Reference in XML file:<!DOCTYPE student SYSTEM “student.dtd”>External file:<!ELEMENT student(first, last, studentID)><!ELEMENT first (#PCDATA)><!ELEMENT last(#PCDATA)><ELEMENT studentID(#PCDATA)>]>Sample External DefinitionDocument Type DeclarationElement Declaration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/documenttypedefinitions-091021130825-phpapp01/75/Document-Type-Definitions-9-2048.jpg)