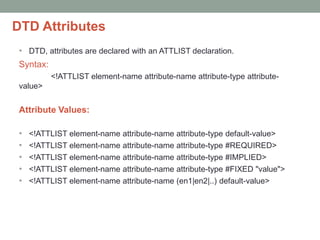
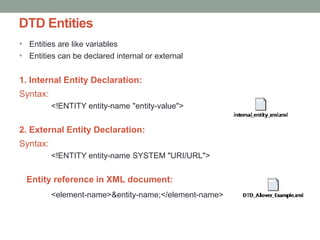
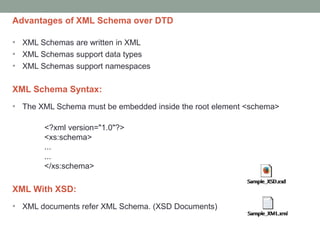
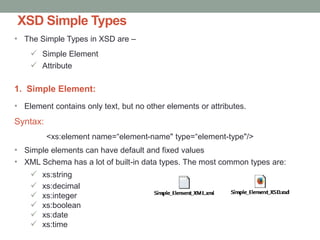
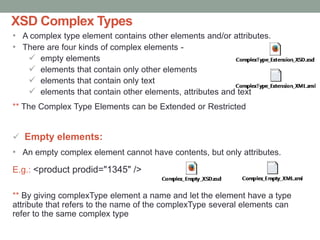
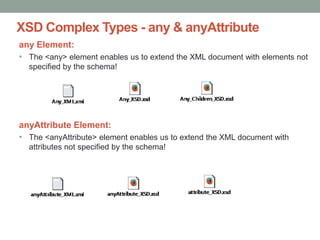
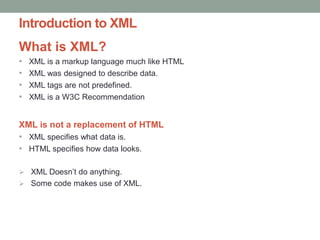
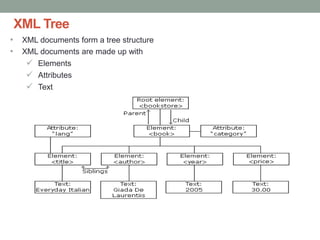
The document provides a comprehensive overview of XML, including its syntax, structure, and advantages over HTML, as well as an introduction to DTD (Document Type Definition) and XML Schema. It explains important concepts like XML elements, attributes, and namespaces, along with the structure definition provided by DTD and the more advanced schema capabilities offered by XML Schema with data types. Additionally, it covers the different ways to define document formats, emphasizing the importance of validation in XML standards.










![1. Internal DTD Declaration:
• The DTD is declared inside the XML file
Syntax:
<!DOCTYPE root-element [element-declarations]>
2. External DTD Declaration
• The DTD is declared in an external file
• The DTD document is referred to xml document
Syntax:
<!DOCTYPE root-element SYSTEM "filename">](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xmldtdxsd-141018015700-conversion-gate02/85/XML-DTD-XSD-Overview-15-320.jpg)