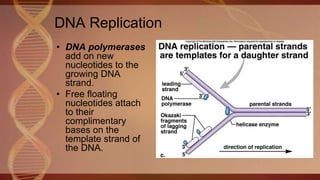
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division. It involves unwinding the DNA double helix at the replication fork, using DNA polymerases to add complementary nucleotides to each single strand, resulting in two identical DNA molecules each with one original and one new strand (semi-conservative replication). The leading strand is replicated continuously while the lagging strand replication occurs discontinuously in fragments joined by DNA ligase. Telomeres and the telomerase enzyme prevent DNA loss during replication.