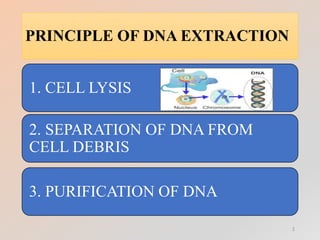
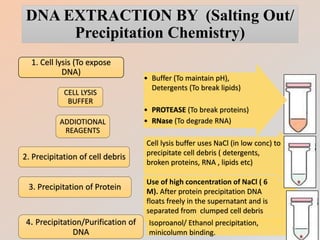
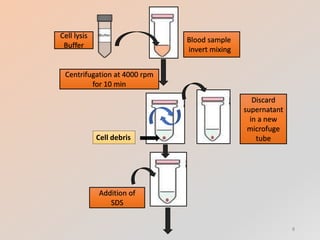
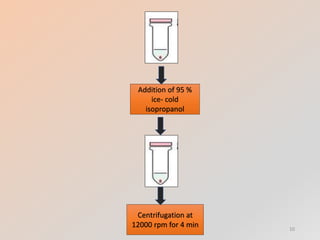
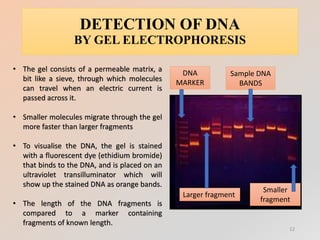
The document outlines the principles and methods of DNA extraction, highlighting techniques such as phenol-chloroform extraction and salting out, which is noted for its cost-effectiveness and minimal contamination. It details the procedures involved, including cell lysis, purification, and the subsequent detection of DNA through gel electrophoresis, along with applications ranging from medical diagnostics to forensic science. Additionally, it provides specific methodologies and necessary reagents used in the extraction process, with references for further reading.