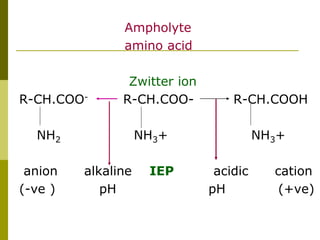
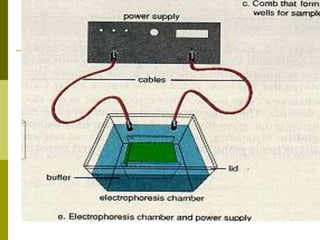
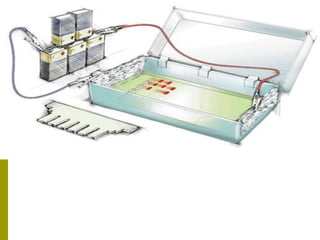
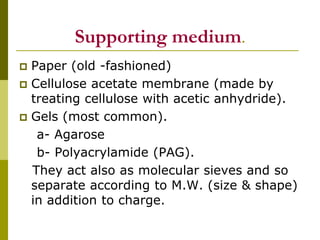
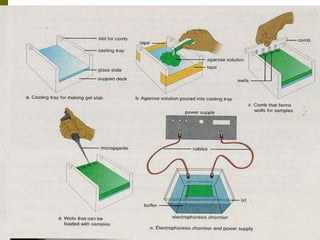
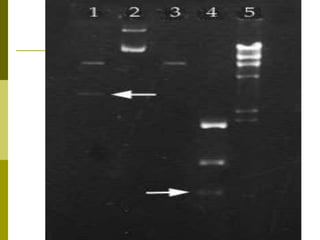
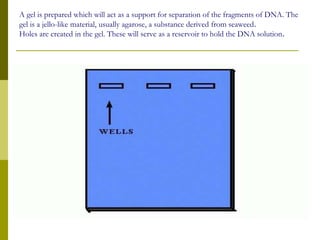
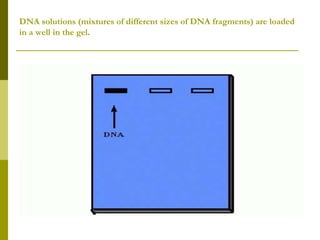
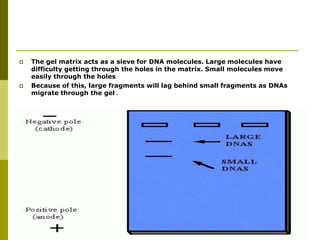
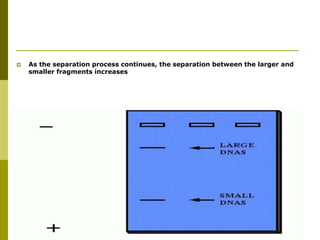
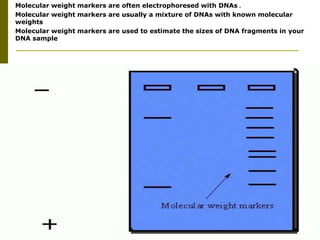
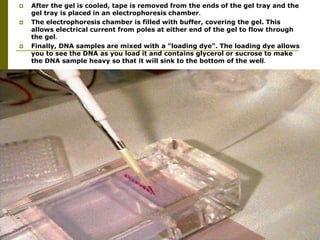
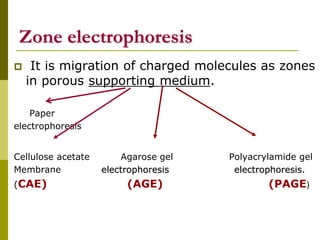
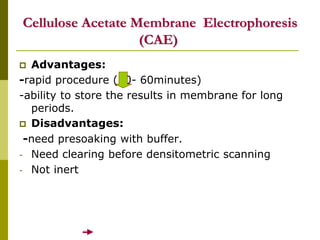
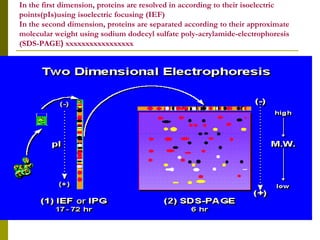
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate charged molecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and amino acids. It works by migrating the molecules through a supportive medium like agarose gel or polyacrylamide gel under the influence of an electric field. Larger molecules migrate more slowly than smaller ones. Factors like electric field strength, net charge on the molecule, and temperature influence migration velocity. Electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments by size. DNA samples are loaded into wells and electrophoresed, with smaller fragments migrating farther than larger ones. The separated fragments can then be visualized under UV light after ethidium bromide staining. Two-dimensional electrophoresis separately resolves proteins by their isoelectric point and