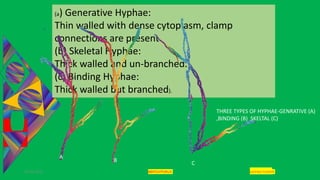
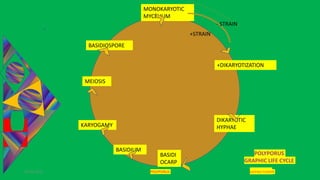
Polyporus is a genus of wood-rotting fungi that causes decay in trees. It has a vegetative mycelial stage that exists in two phases - a primary monokaryotic mycelium and a secondary dikaryotic mycelium. The secondary mycelium develops underground and secretes enzymes to digest wood. Fruiting bodies called basidiocarps form above ground on wood surfaces. Basidiocarps are shelf-like or bracket-shaped structures with pores on their undersides containing basidia that undergo karyogamy and meiosis to produce haploid basidiospores for reproduction.