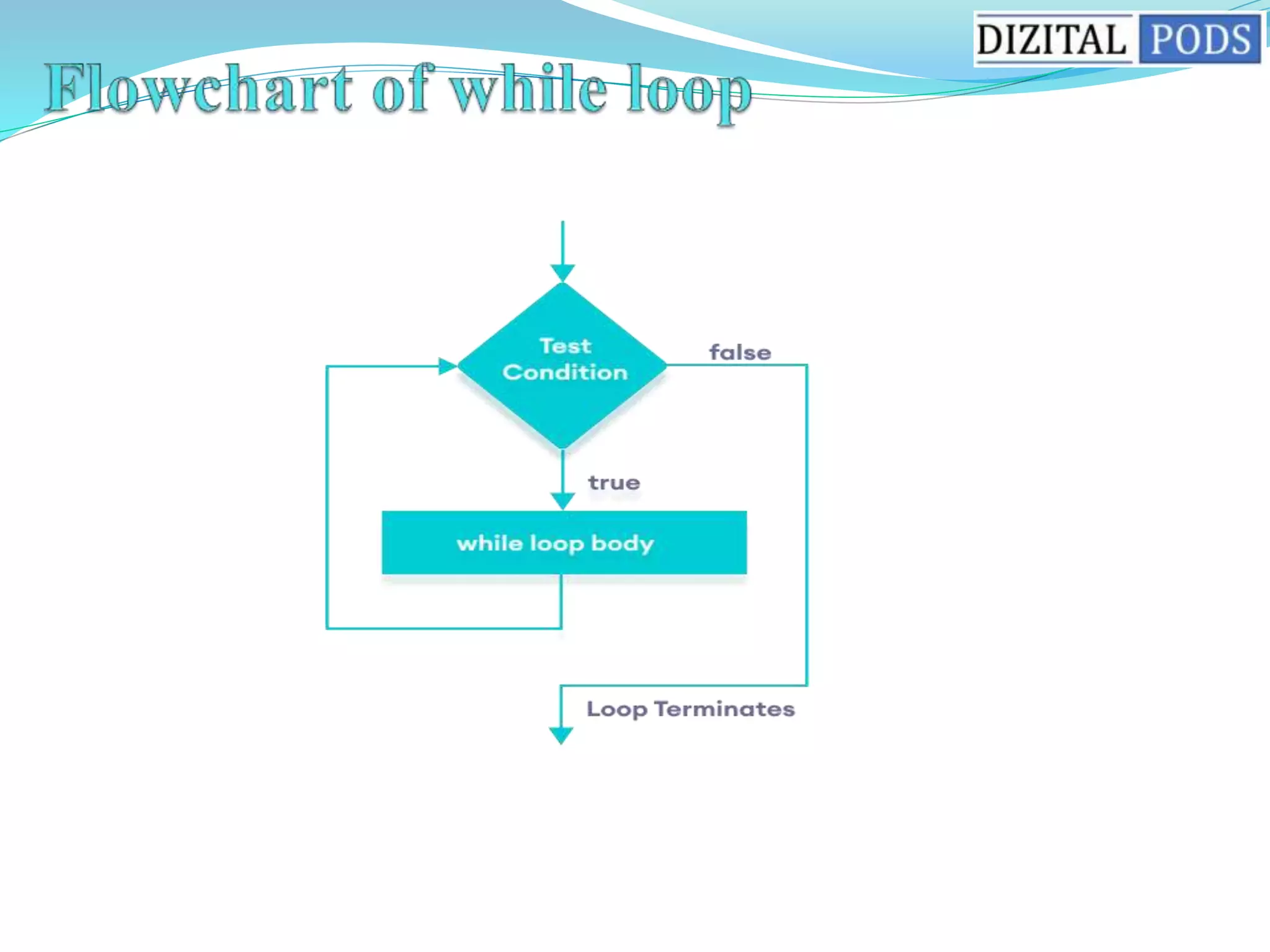
The document discusses different types of loops in Java including for, while, and do-while loops. It provides the syntax for each loop and examples of how to use them to iterate through a range of numbers. It also covers the break and continue statements that can be used to control the flow of loops, such as breaking out of a loop entirely or skipping the current iteration.




![// Program to print numbers from 1 to 5
class Main {
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
int n = 5;
// for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-5-2048.jpg)



![// Program to display numbers from 1 to 5
class Main
{ public static void main(String[ ] args) {
// declare variables
int i = 1, n = 5;
// while loop from 1 to 5
while(i <= n) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-10-2048.jpg)




![import java.util.Scanner;
// Program to find the sum of natural numbers from 1 to 100.
class Main{
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
int i = 1, n = 5;
// do...while loop from 1 to 5
do {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while(i <= n);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-15-2048.jpg)



![public class BreakExample {
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
//using for loop
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
//breaking the loop
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-19-2048.jpg)
![public class BreakExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//outer loop
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++){
//inner loop
for(int j=1;j<=3;j++){
if(i==2&&j==2){
//using break statement inside the inner loop
break;
}
System.out.println(i+" "+j);
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-20-2048.jpg)


![//inside the for loop.
public class ContinueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//for loop
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
if(i==5){
//using continue statement
continue;//it will skip the rest statement
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-23-2048.jpg)
![//Java Program to demonstrate the use of continue statement
//inside the while loop.
public class ContinueWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//while loop
int i=1;
while(i<=10){
if(i==5){
//using continue statement
i++;
continue;//it will skip the rest statement
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-24-2048.jpg)
![//Java Program to demonstrate the use of continue statement
//inside the Java do-while loop.
public class ContinueDoWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//declaring variable
int i=1;
//do-while loop
do{
if(i==5){
//using continue statement
i++;
continue;//it will skip the rest statement
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}while(i<=10);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-25-2048.jpg)
![//Java Program to demonstrate the use of continue statement
//inside the Java do-while loop.
public class ContinueDoWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//declaring variable
int i=1;
//do-while loop
do{
if(i==5){
//using continue statement
i++;
continue;//it will skip the rest statement
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}while(i<=10);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dizitalpodssession5-loops-220721033512-9405e265/75/dizital-pods-session-5-loops-pptx-26-2048.jpg)