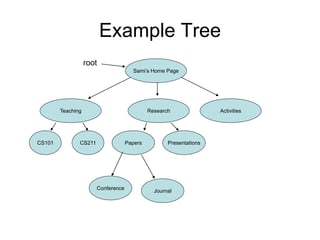
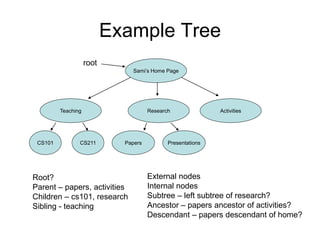
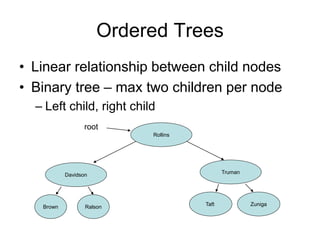
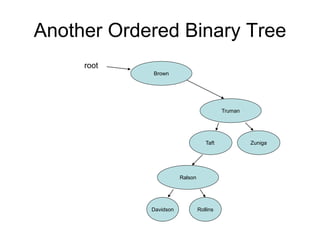
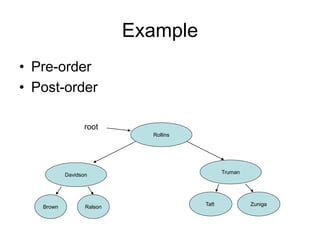
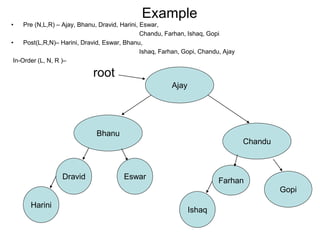
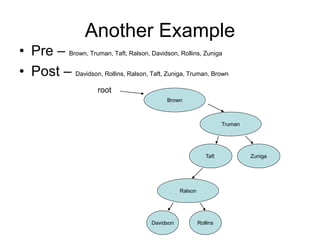
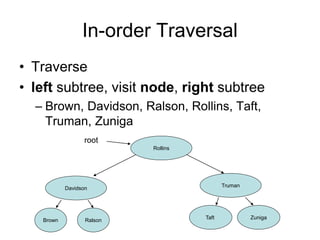
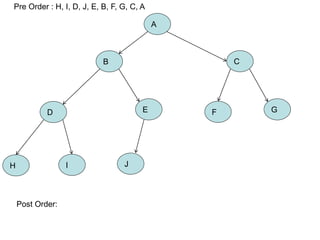
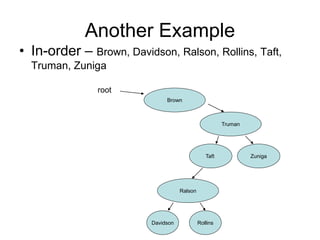
The document discusses trees as data structures and tree traversal methods. It provides examples of binary trees and describes tree terminology like root, parent, child, and subtree. It also explains different tree traversal orders like pre-order, post-order, and in-order traversal, which involve visiting nodes in different sequences. Examples are given to demonstrate how nodes would be visited using each traversal method on sample trees.