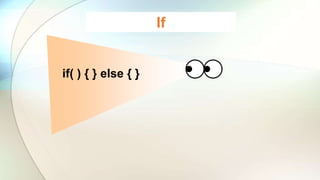
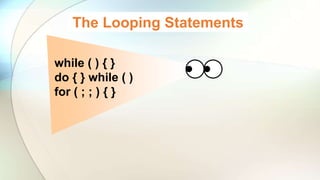
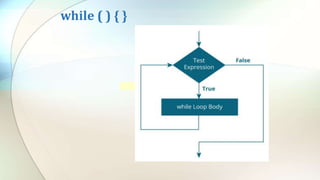
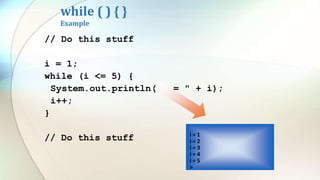
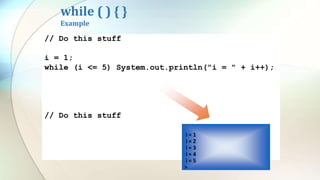
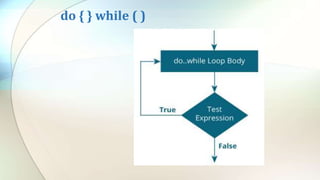
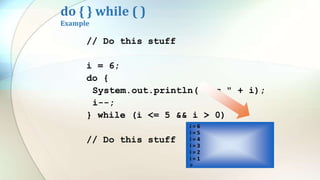
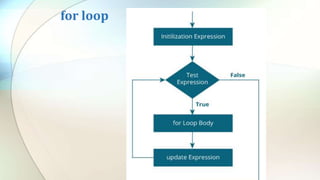
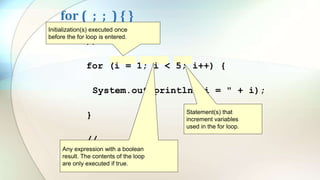
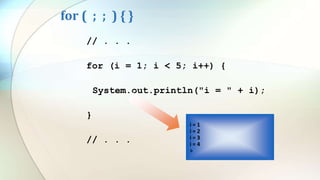
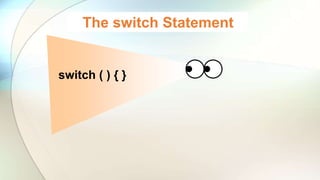
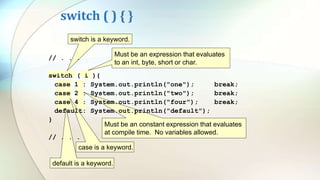
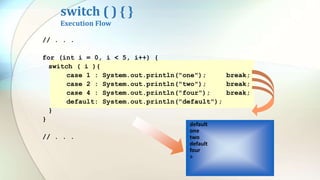
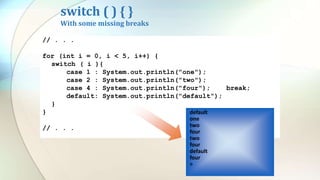
The document discusses various flow control statements in Java including if-else statements, while loops, do-while loops, for loops, break and continue statements, return statements, and switch statements. It provides examples of how to use each statement and explains their functionality such as only executing the contents of an if block if the condition is true or always executing the do block once in a do-while loop.