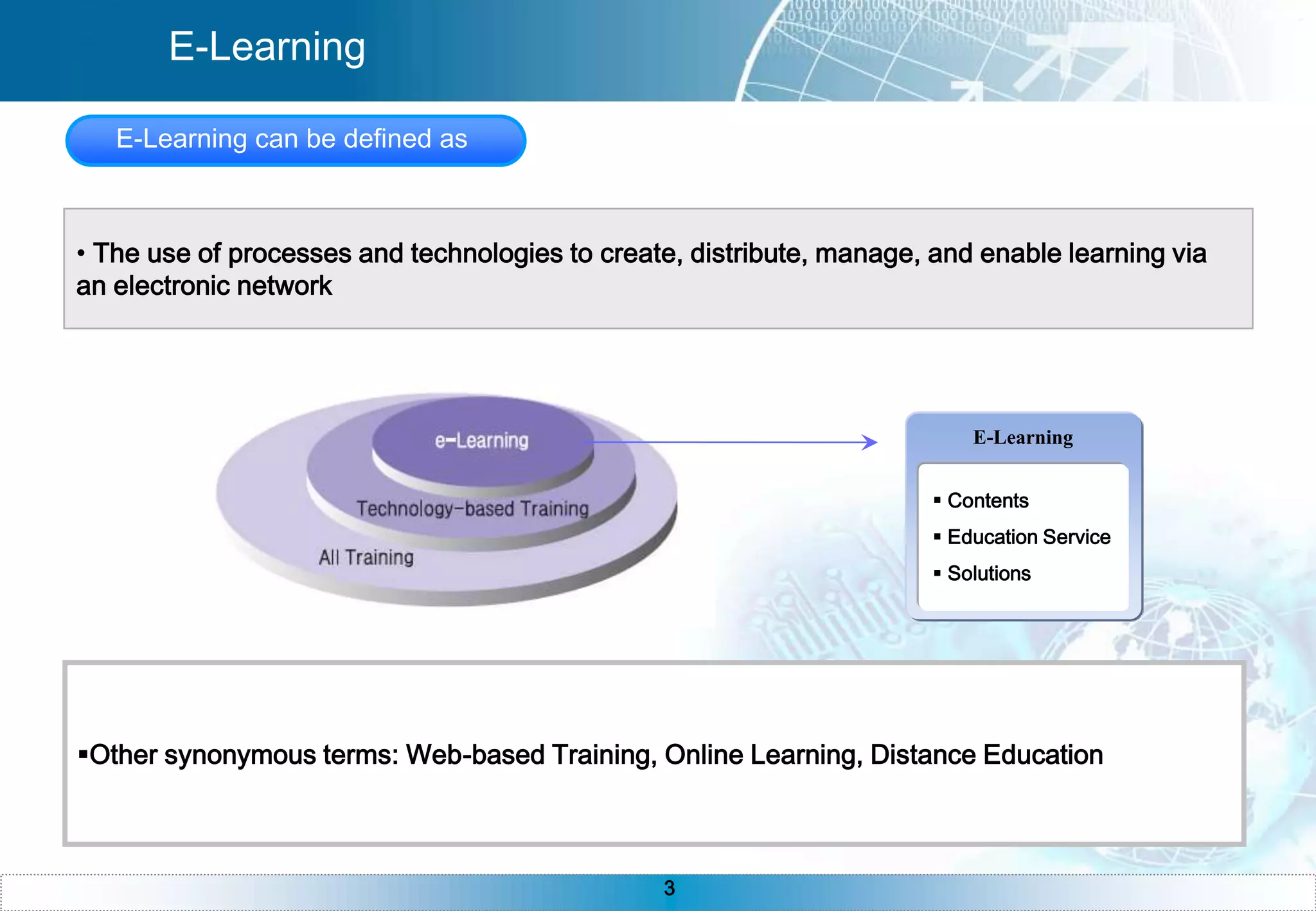
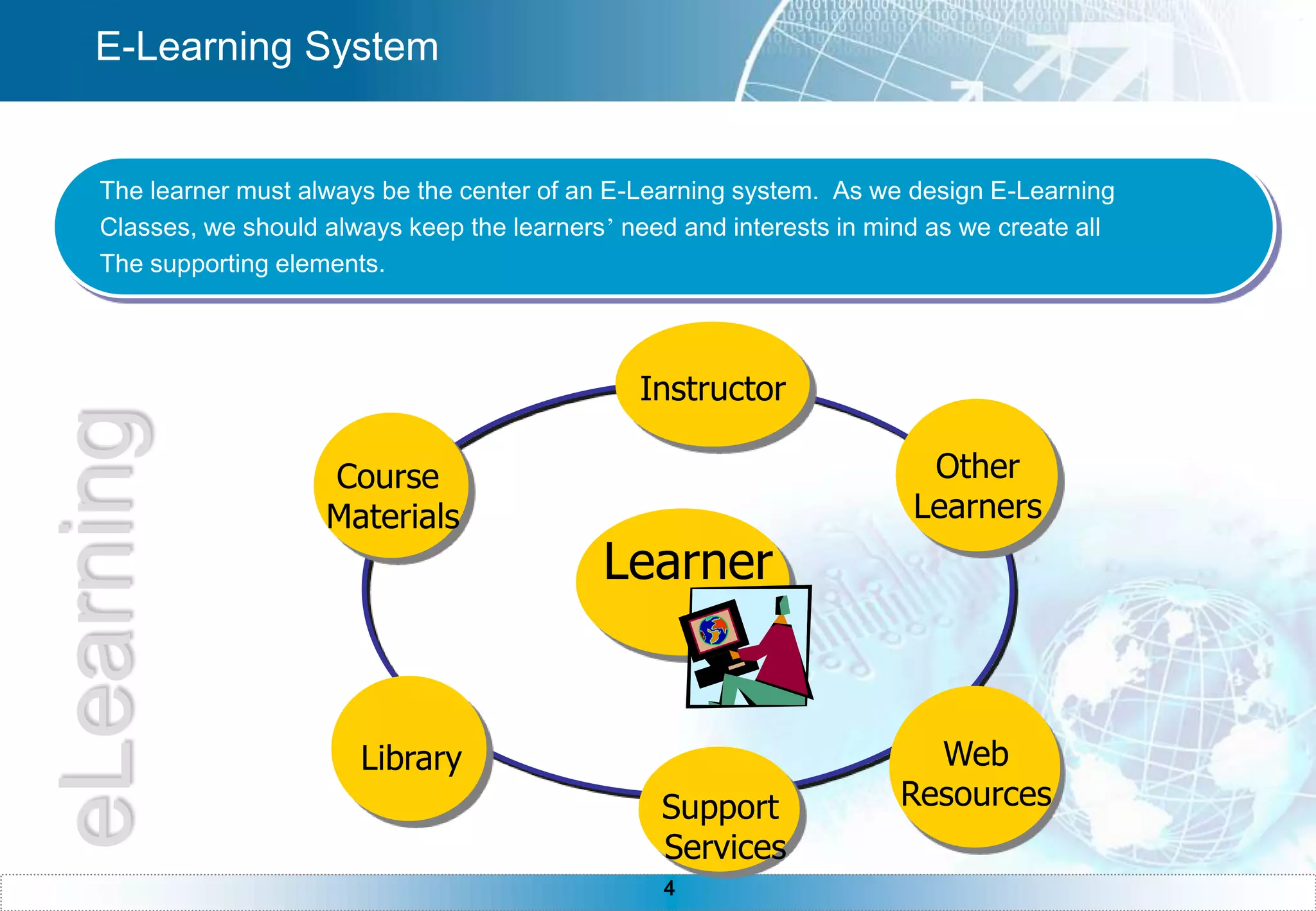
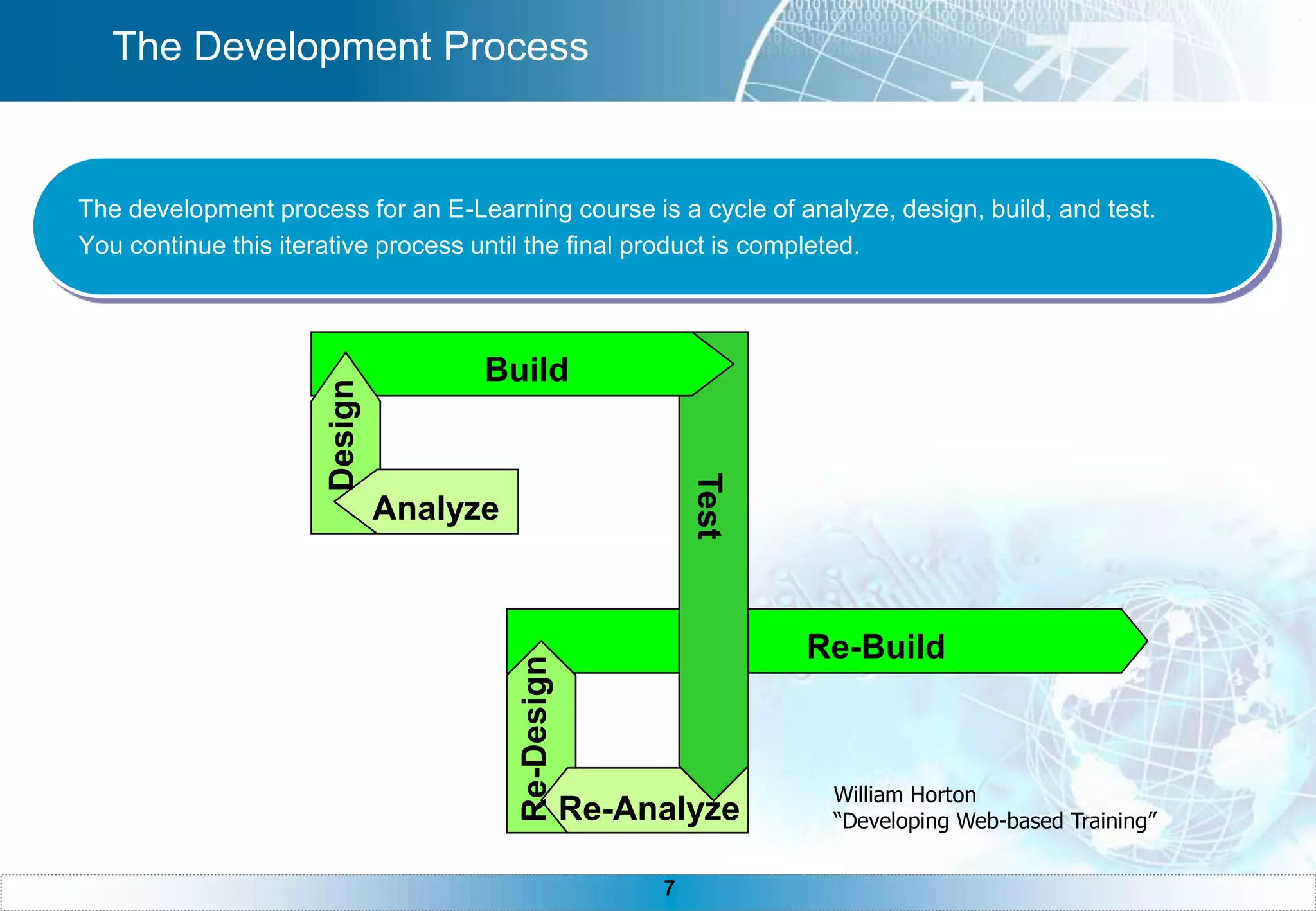
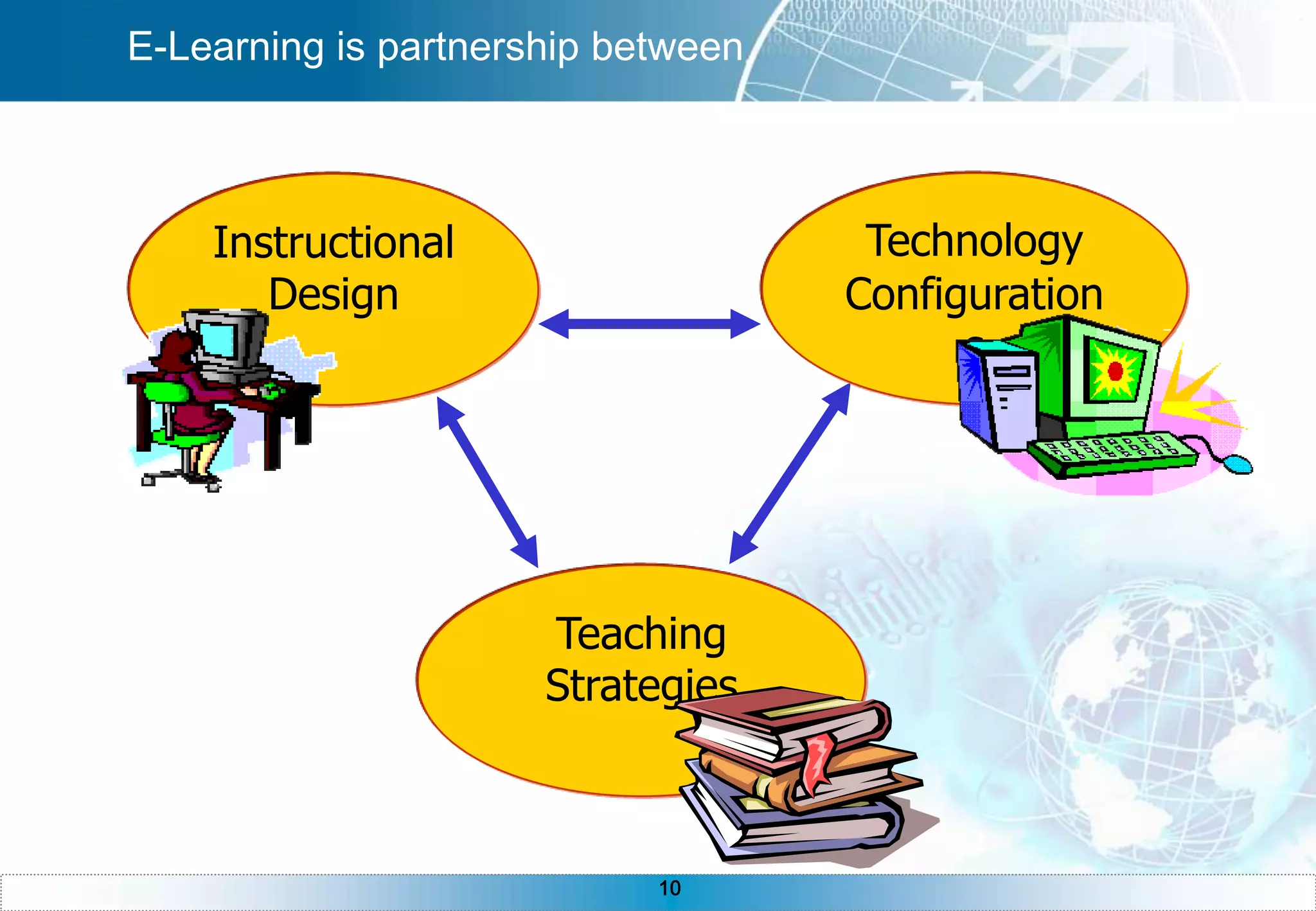
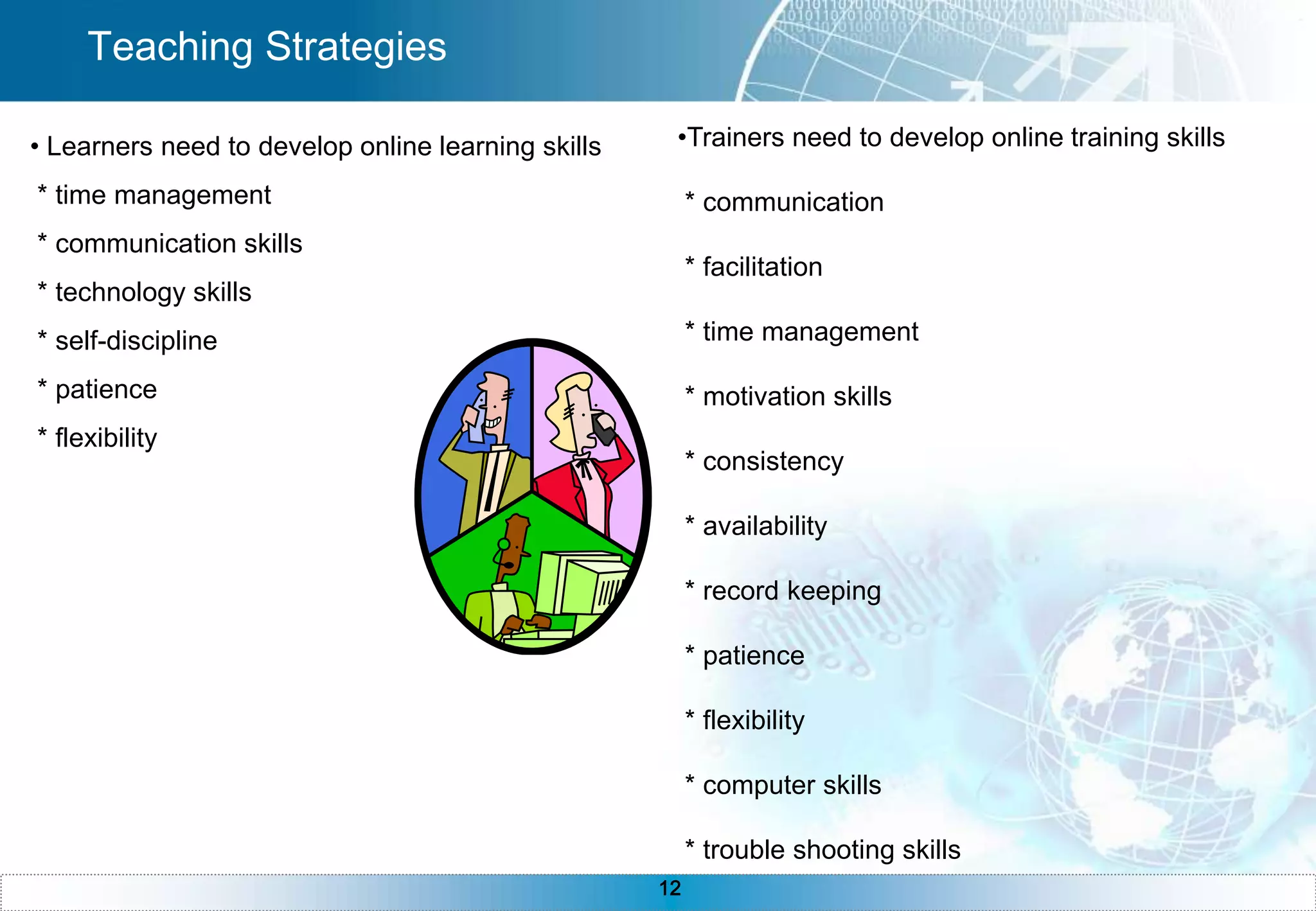
The document provides an overview of e-learning, including definitions of e-learning, the components of an e-learning system with the learner at the center, benefits of e-learning like just-in-time training and 24/7 accessibility. It also discusses e-learning requirements like technology and self-discipline. The development process is described as iterative, and asynchronous e-learning is outlined as separated by distance and time while synchronous is separated by distance but meeting at the same time. The document concludes with sections on instructional design, teaching strategies, technologies, and common questions about e-learning.