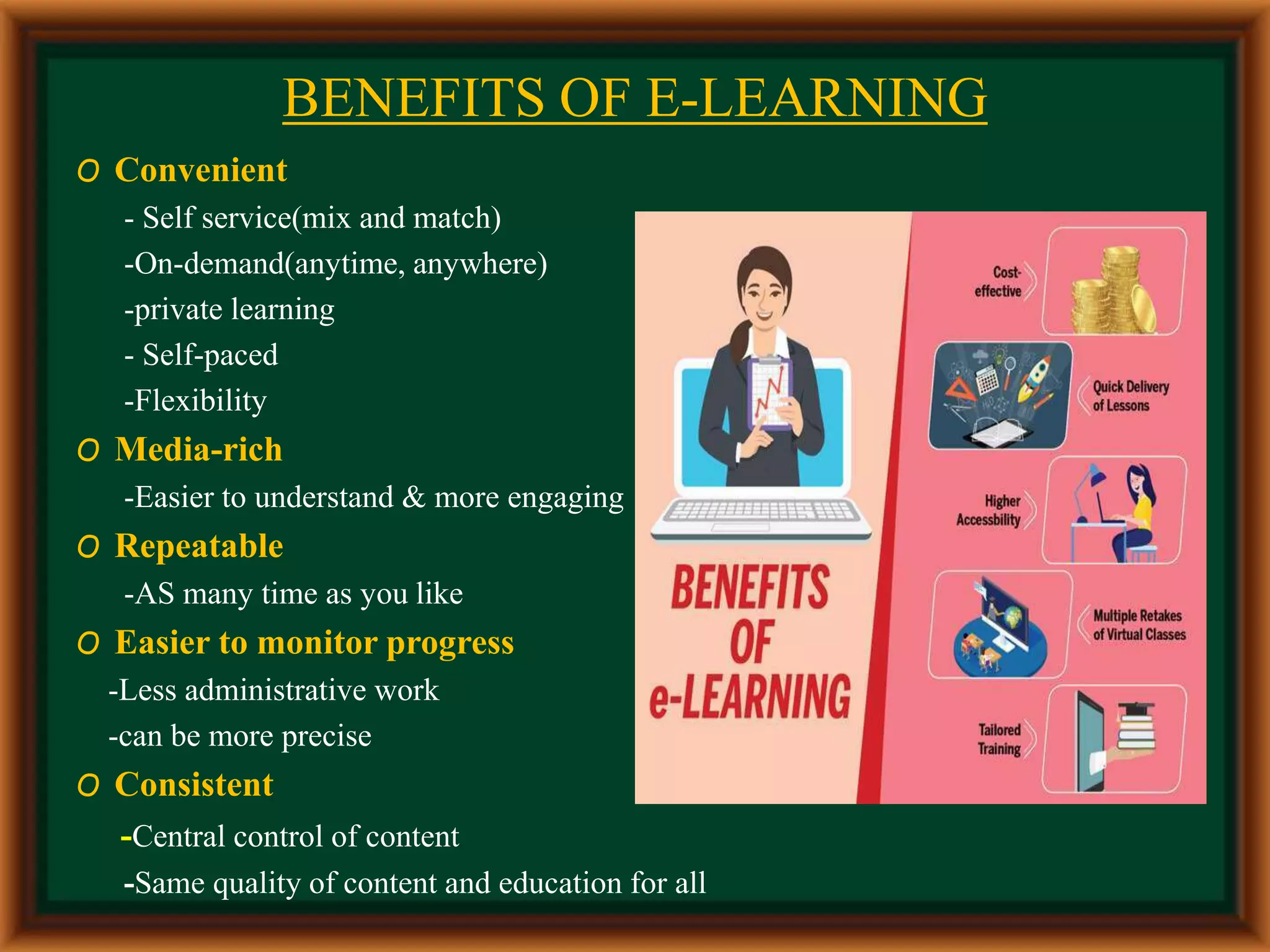
The presentation discusses e-learning for divine food recipes and its benefits, features, and impact on teaching and learning processes. It defines e-learning as a technology that supports education using web-based resources and highlights its advantages such as flexibility, accessibility, and the promotion of varied learning styles. Additionally, it addresses challenges such as the necessity for motivation and the potential for isolation among learners.