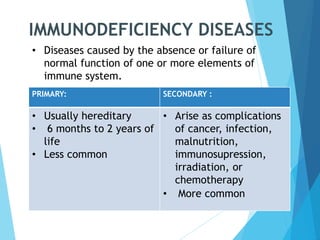
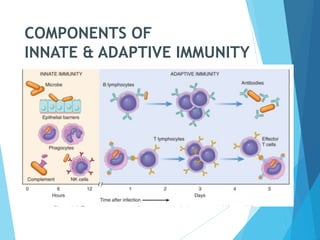
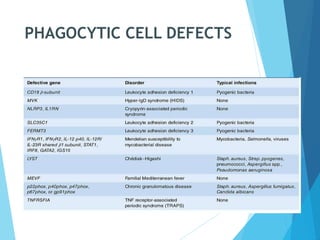
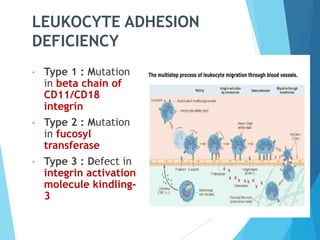
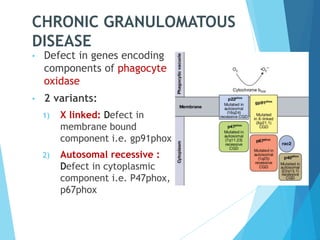
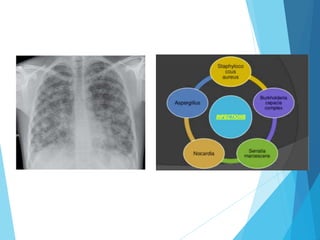
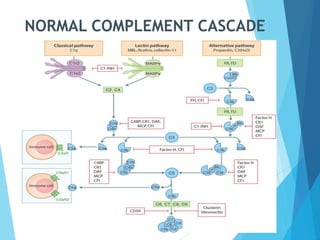
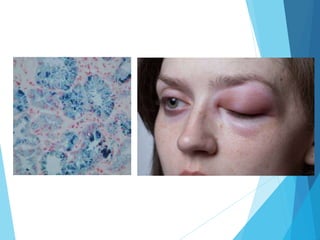
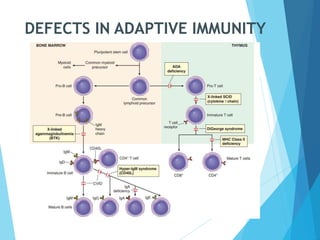
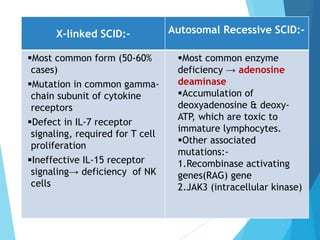
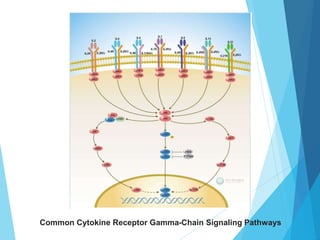
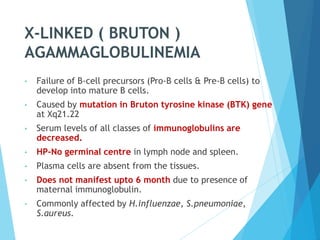
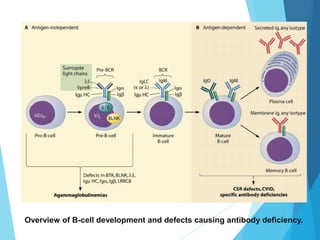
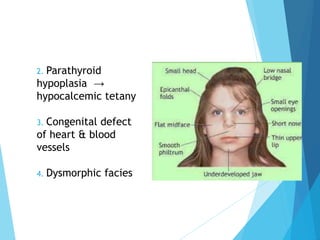
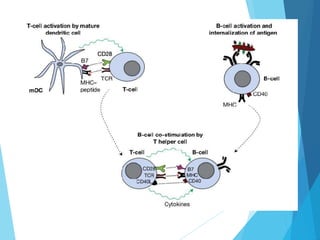
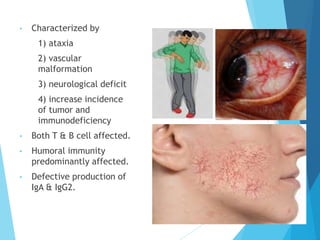
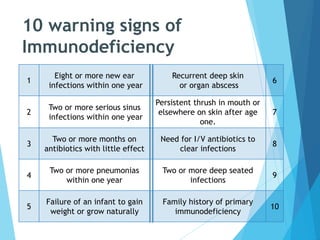
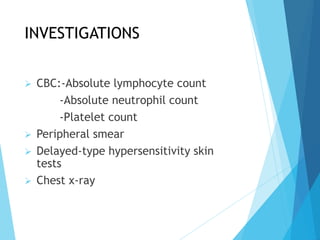
This document discusses primary and secondary immunodeficiency diseases. Primary immunodeficiencies are caused by inherited genetic defects affecting the innate or adaptive immune system. They can involve defects in phagocytic cells, complement pathways, pattern recognition receptors, or lymphocyte development/activation. Examples discussed include leukocyte adhesion deficiency, chronic granulomatous disease, Chediak-Higashi syndrome, complement deficiencies, and defects causing SCID, XLA, DiGeorge syndrome, and others. Secondary immunodeficiencies are acquired and include those caused by infections, malnutrition, drugs, or radiation/chemotherapy. The document provides details on approaches to diagnosis and management of immunodeficiency patients.