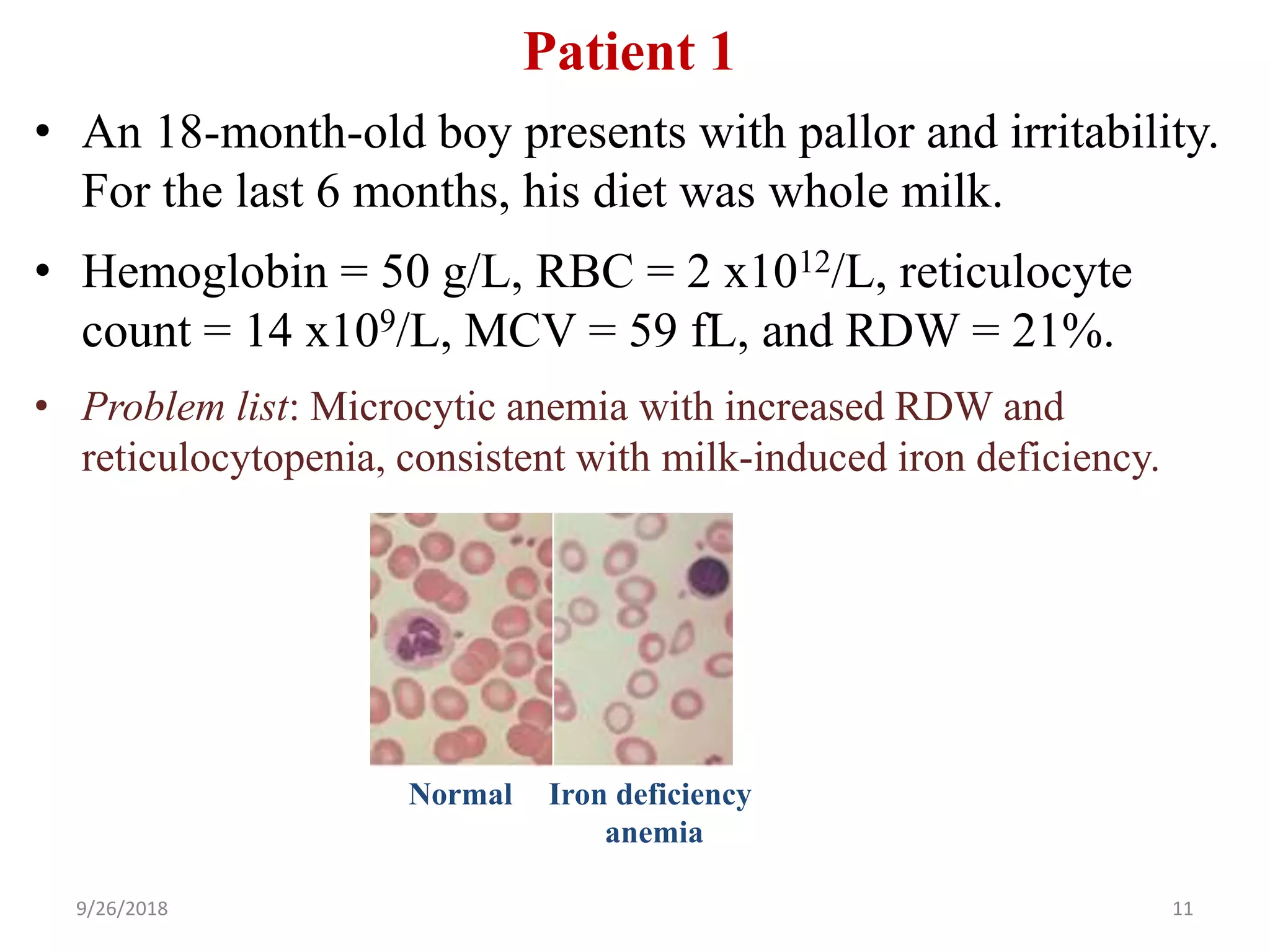
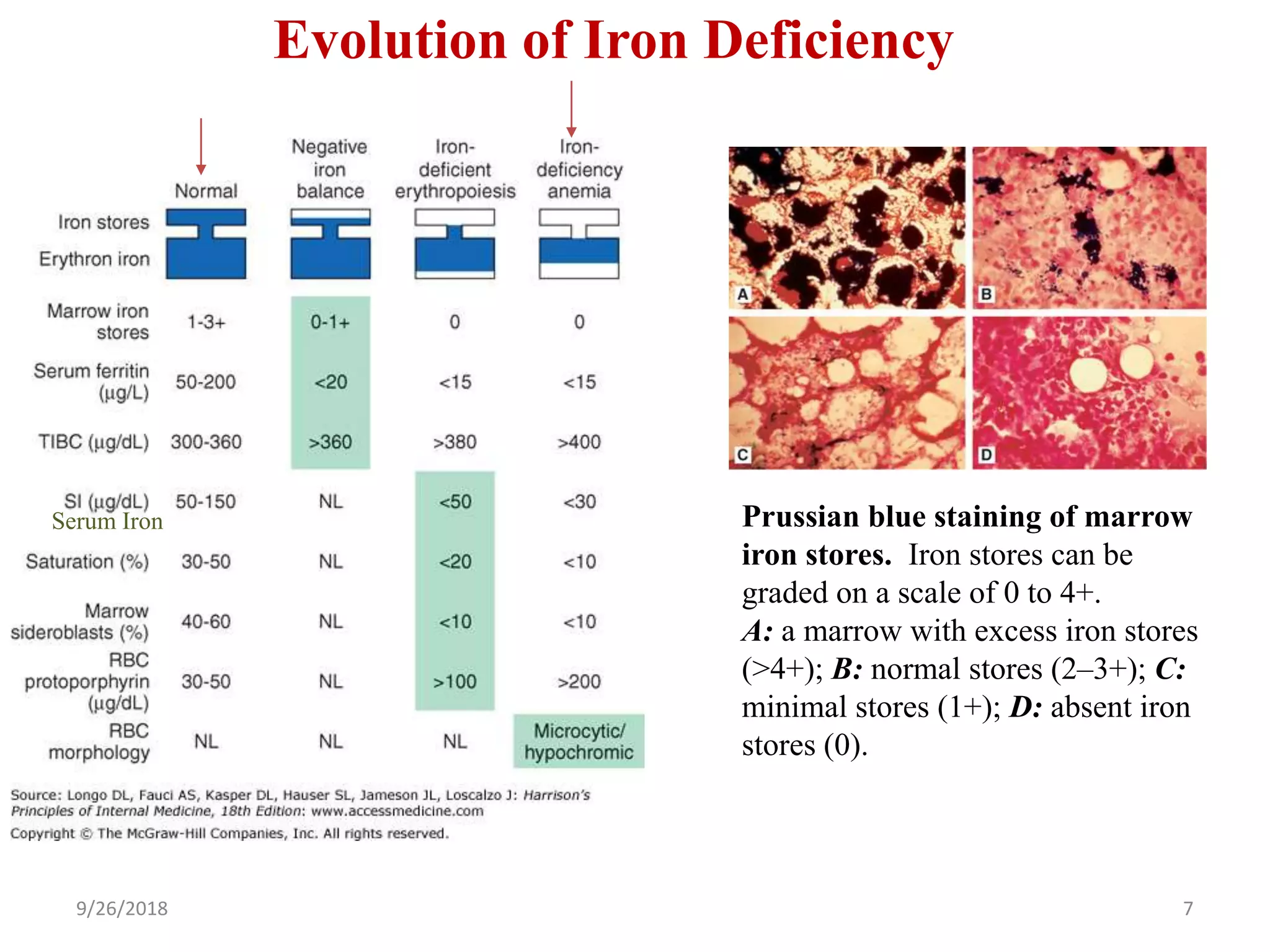
The document discusses microcytic anemia and its causes, primarily focusing on iron deficiency anemia, which results from impaired hemoglobin synthesis and can occur due to various factors like nutritional deficiencies, inflammation, or blood loss. Key mechanisms related to iron absorption and regulation, such as the roles of hepcidin and ferroportin, are explained, along with diagnostic markers and treatment principles. The document also highlights the prevalence of iron deficiency anemia in different populations and emphasizes the importance of dietary sources and supplementation in management.

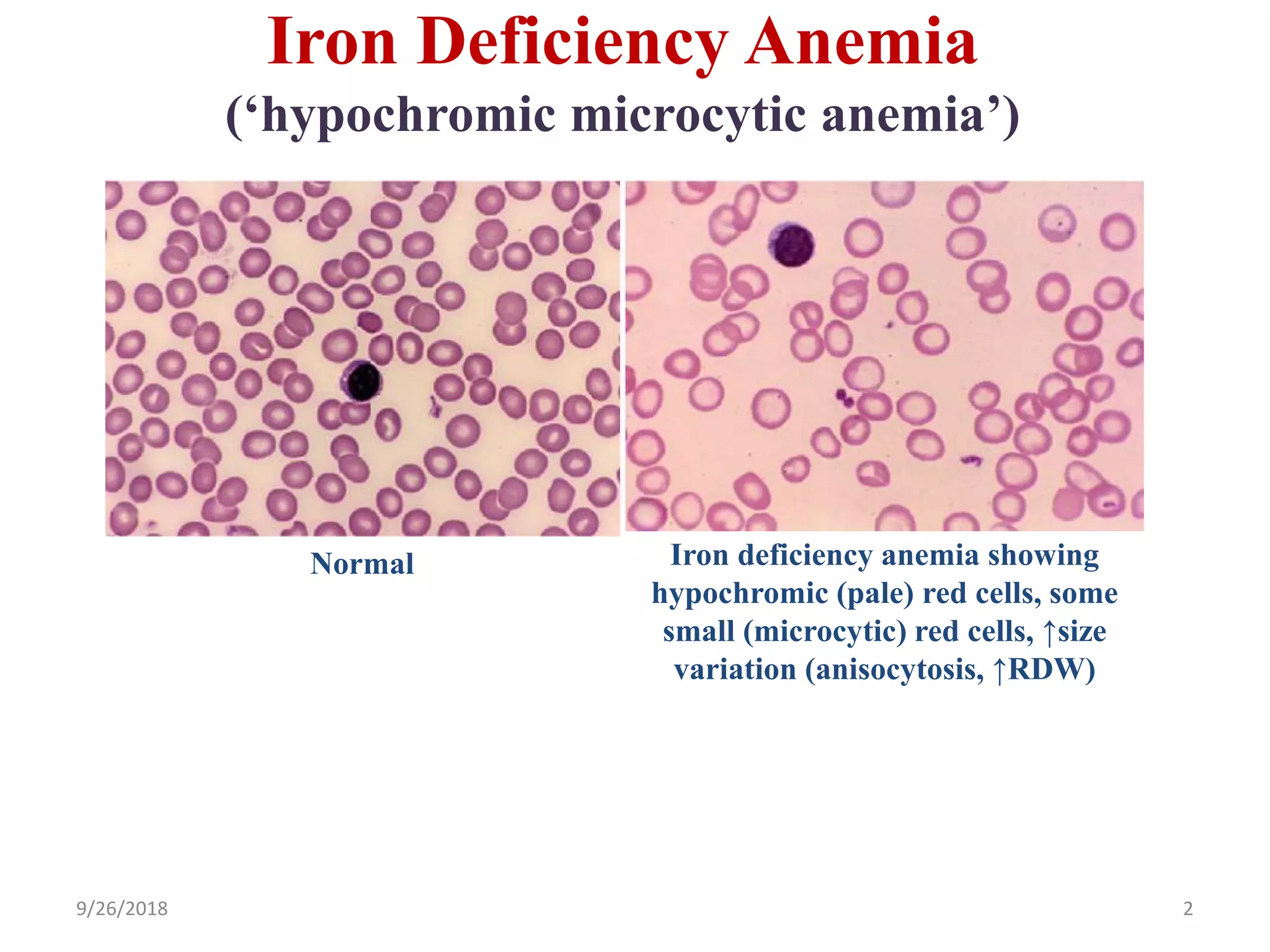
![Microcytosis (MCV <80 fL)
Microcytosis =↓hemoglobin synthesis (↓iron, ↓globin, or ↓protoporphyrin):
• Iron deficiency (iron-limiting erythropoiesis; nutritional vs. blood loss)
• Thalassemia trait (↓a or b globin synthesis)
• Inflammation (↓Fe bioavailability due to ↑hepcidin [blocks Fe absorption])
• ↓Protoporphyrin (hereditary sidroblastic anemia)
9/26/2018 3
Must know](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2microcyticanemia-i-irondeficiency-180926043107/75/2-microcytic-anemia-i-iron-deficiency-ppt-3-2048.jpg)
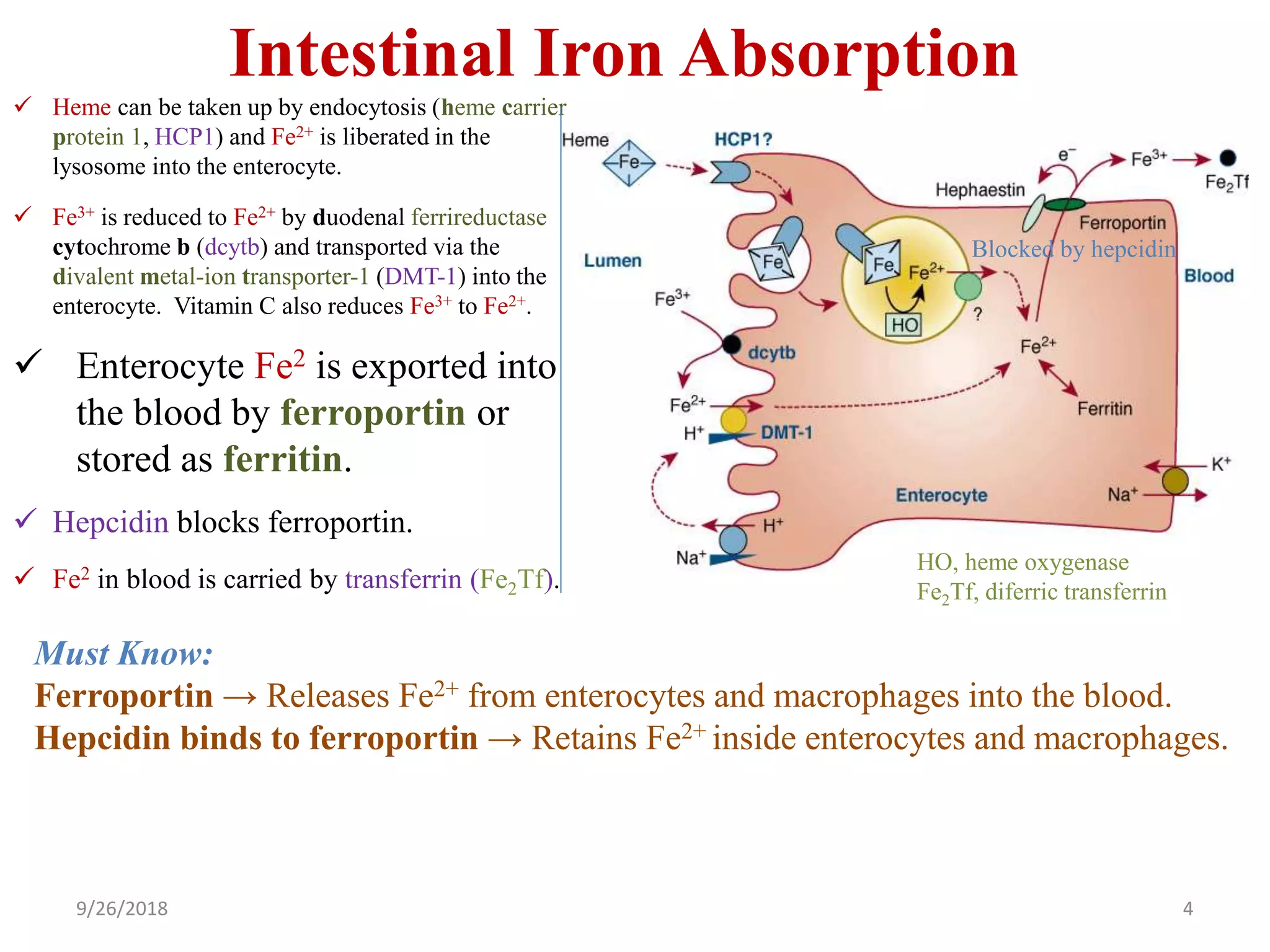
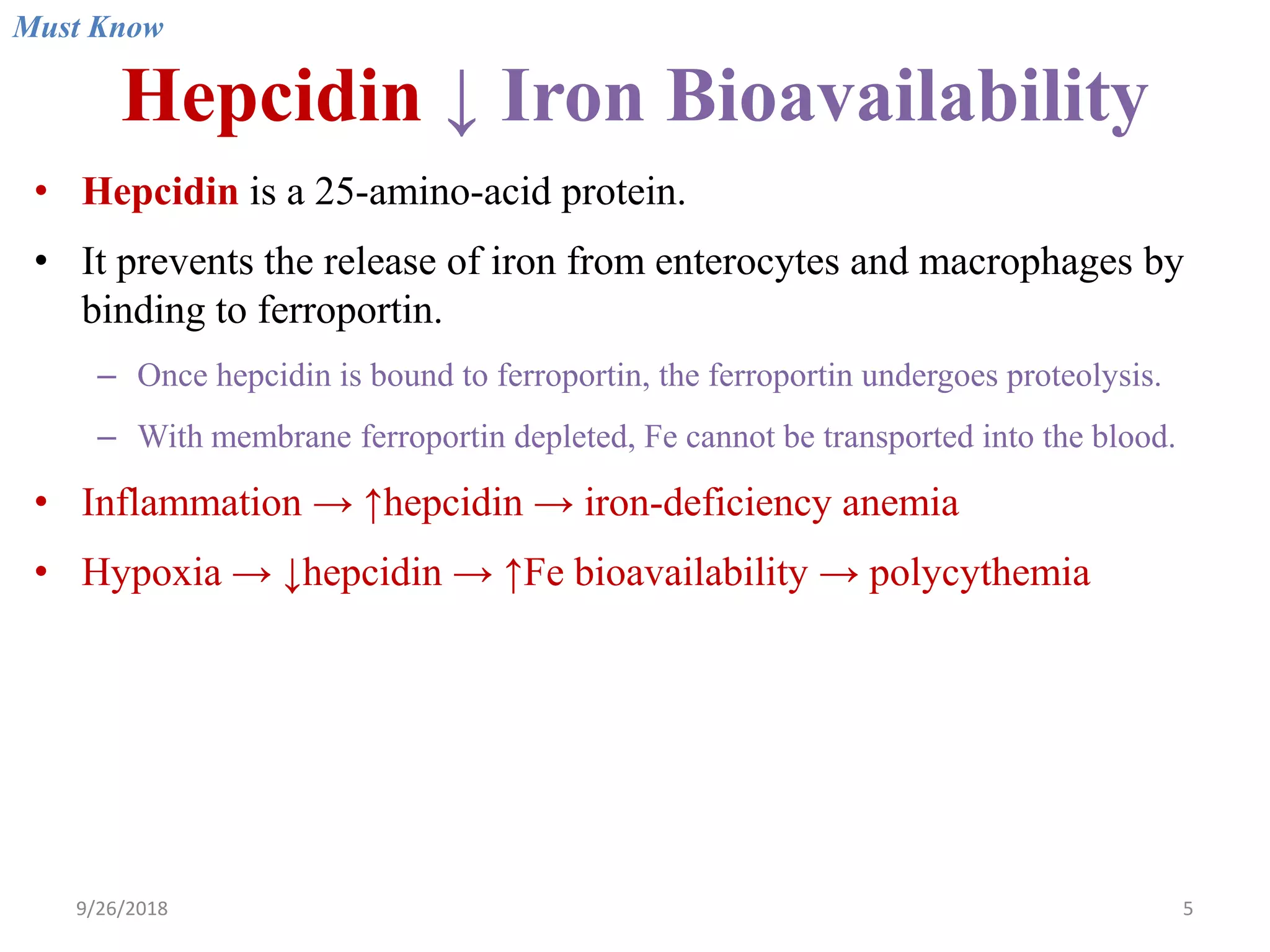


![Iron Deficiency Anemia
Prevalence
• Adult males <1%
• Adult females 20%
Mechanisms of iron deficiency
• ↑ Need for iron: Infants during their rapid growth, premature infants, growth
spurt during puberty, pregnancy, lactation, etc.
• ↓ Iron intake (nutritional iron deficiency due to poor diet): Prolonged
breastfeeding, iron-poor diet (vegetables and milk have low iron bioavailability).
• ↑ Loss: Menorrhagia, GI bleeding (bleeding ulcer, colorectal cancer [fecal
occult blood], infants on whole milk (milk-induced colitis), non-steroidal anti-
inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced gastritis, hereditary hemorrhagic
telangiectasia (HHT).
• ↓ Absorption (relatively rare): Gastric or duodenal resection, coeliac disease, etc.
Notes: Iron absorption from meat is better than that from plants. Phytates (cereals,
nuts, legumes) inhibit iron absorption. Vitamin C promotes Fe absorption.
Must Know](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2microcyticanemia-i-irondeficiency-180926043107/75/2-microcytic-anemia-i-iron-deficiency-ppt-9-2048.jpg)