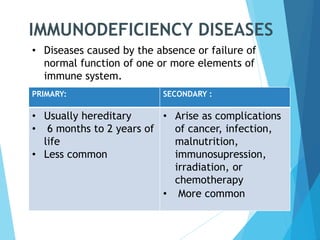
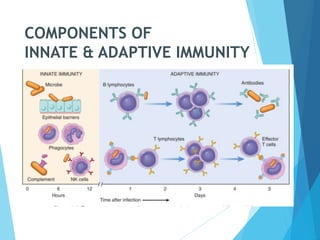
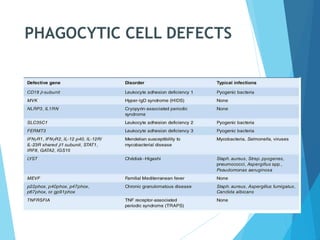
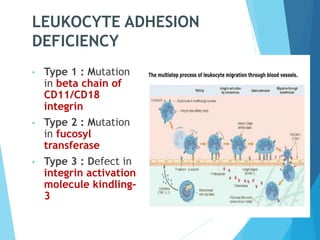
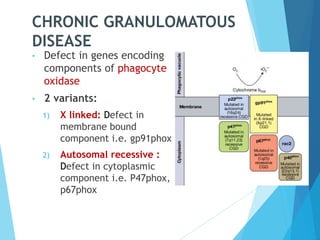
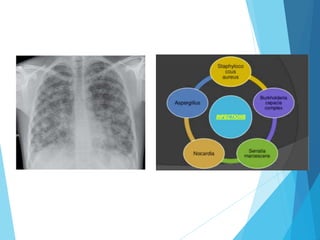
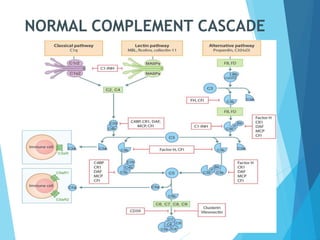
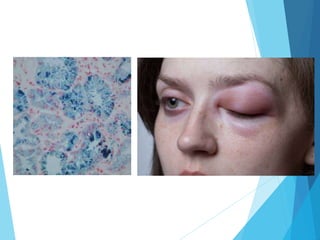
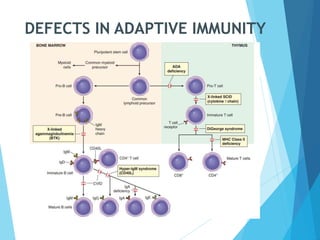
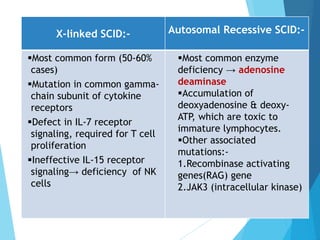
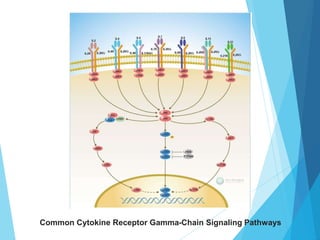
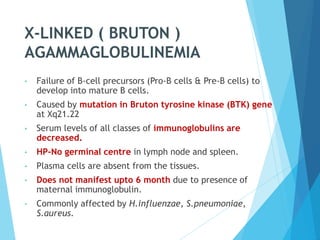
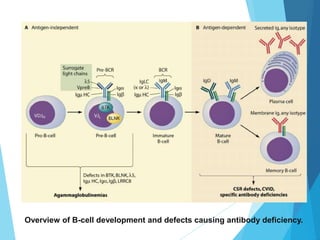
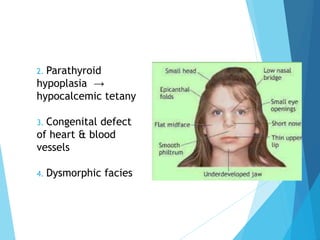
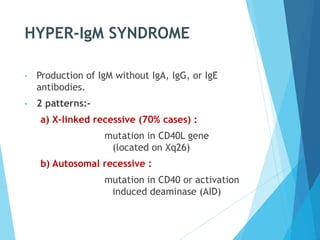
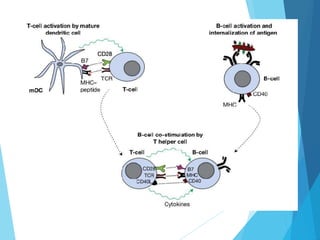
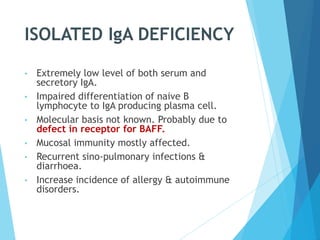
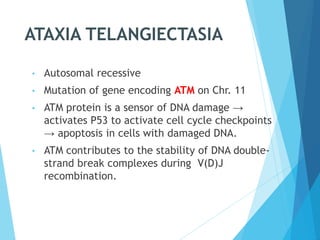
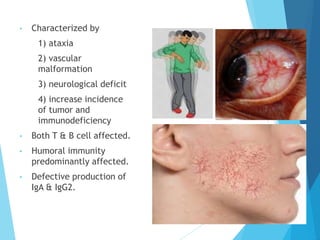
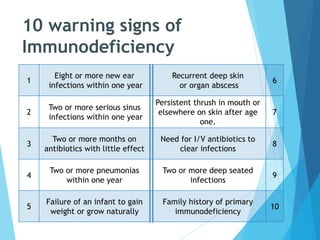
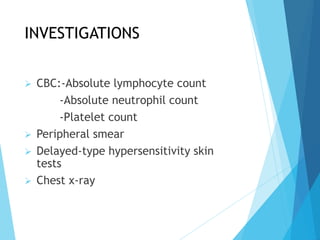
This document discusses primary and secondary immunodeficiency diseases. Primary immunodeficiencies are caused by inherited genetic defects affecting the innate or adaptive immune system. They can involve defects in phagocytic cells, complement pathways, or pattern recognition receptors. Defects in adaptive immunity include severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCID), X-linked agammaglobulinemia, DiGeorge syndrome, and others. Secondary immunodeficiencies are acquired and can result from infections, malnutrition, cancer, or immunosuppressive treatments. The document provides details on the genetic causes and clinical manifestations of various primary immunodeficiencies.