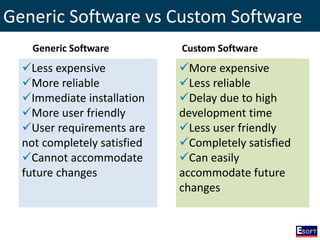
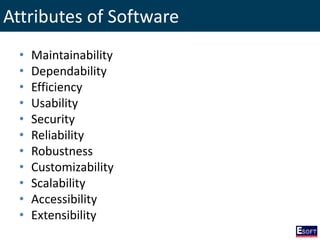
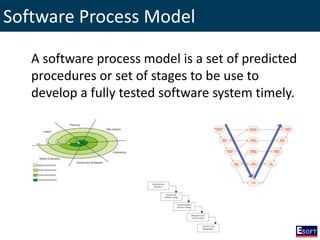
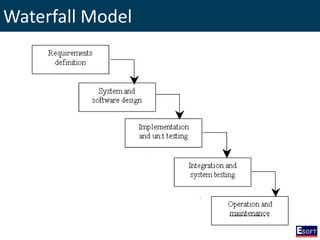
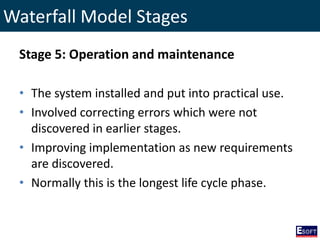
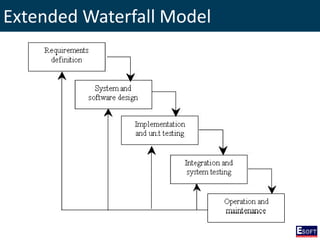
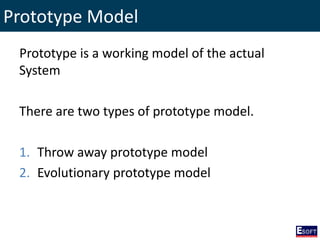
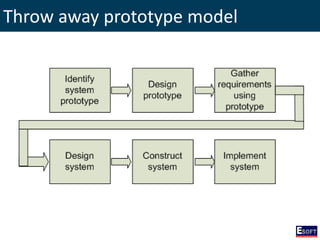
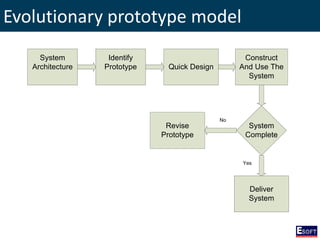
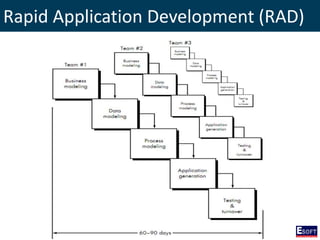
This document provides an overview of software engineering concepts including different types of software, software classification, software attributes, and common software development process models. It describes system software and application software, and distinguishes between generic/off-the-shelf software and custom software. Popular process models covered include waterfall, prototyping, and rapid application development (RAD). The waterfall model and its stages are explained in detail.