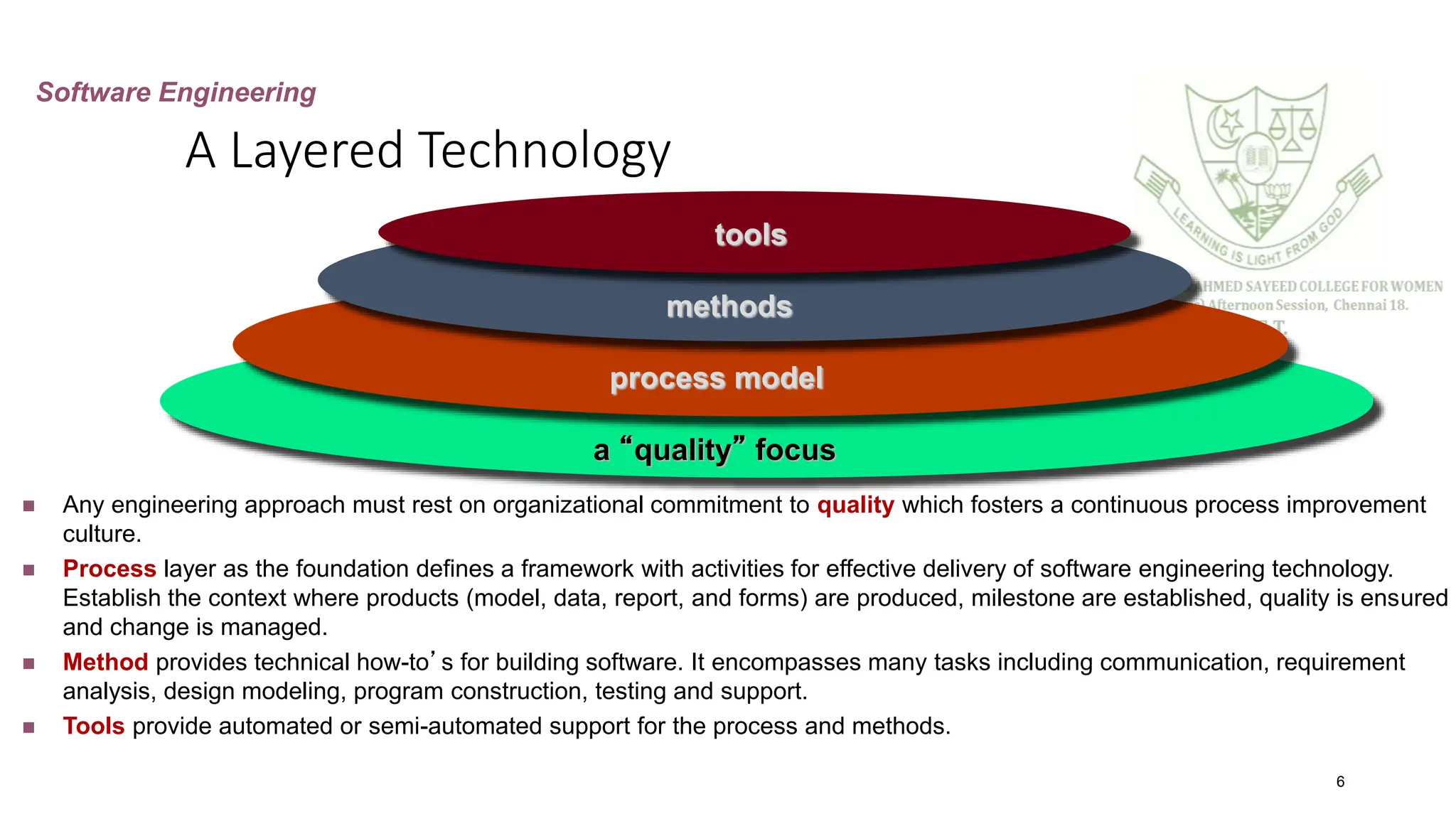
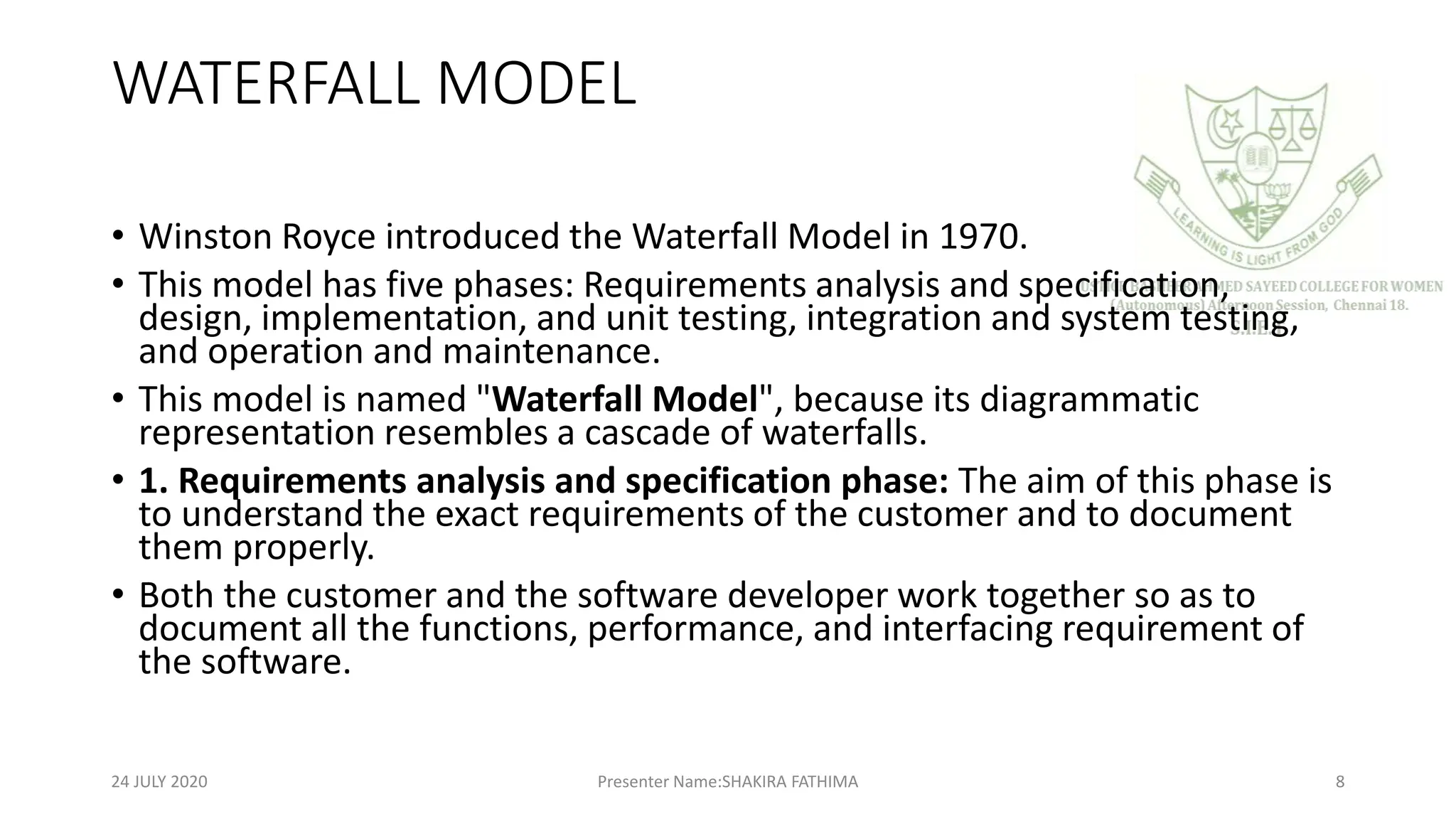
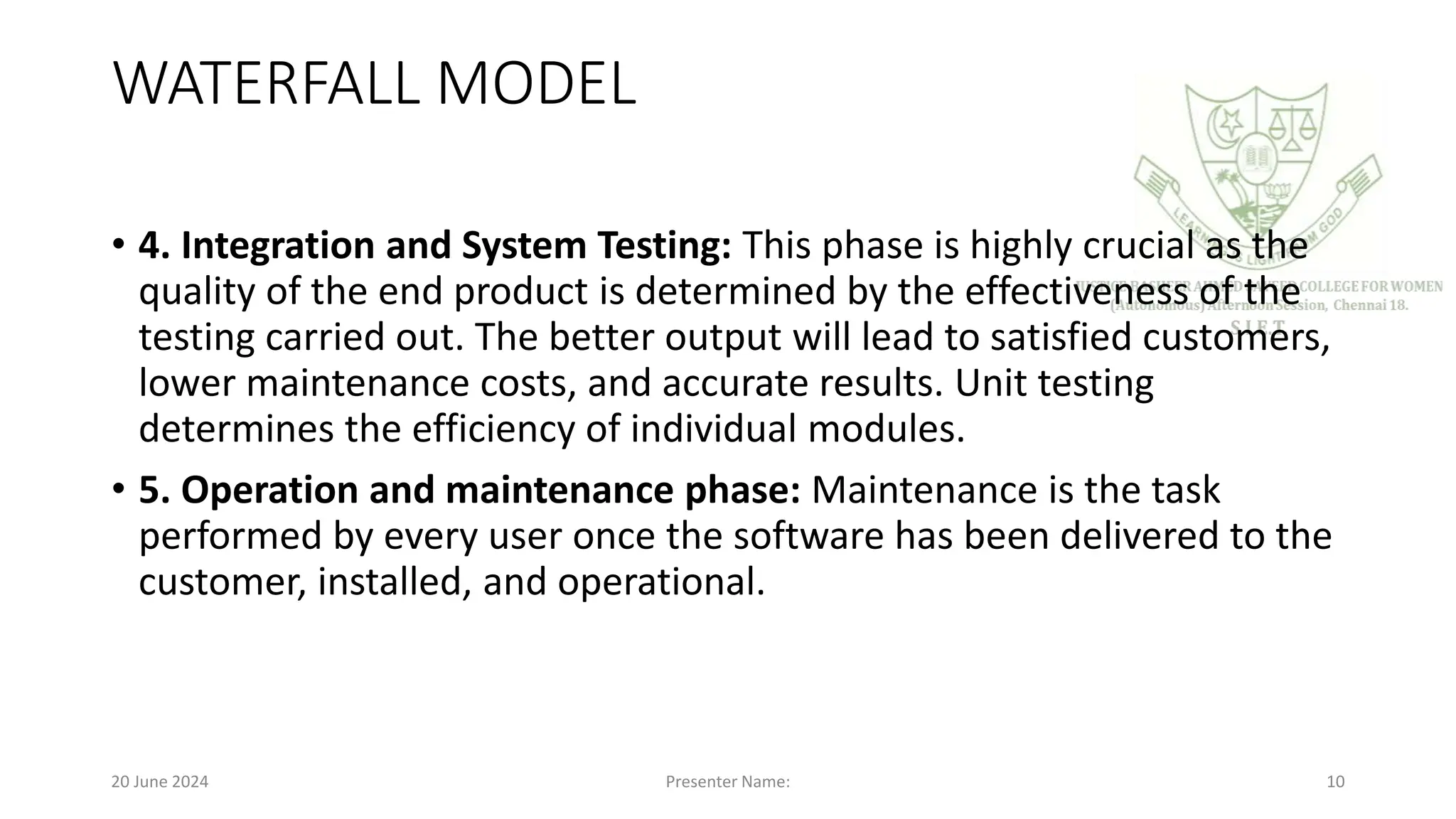
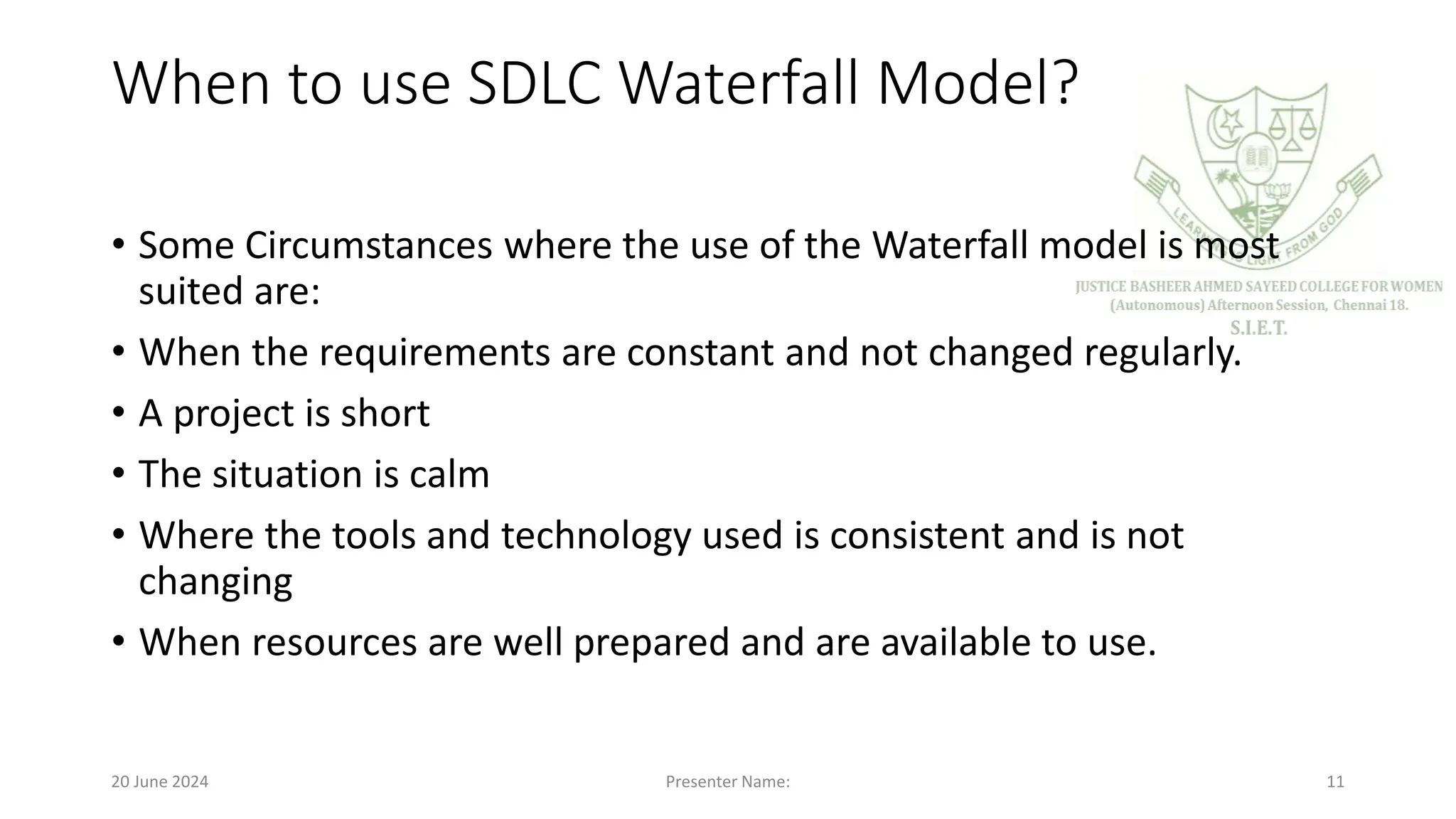
The document provides an overview of software engineering, defining software as a collection of programs, procedures, and documentation. It outlines various software development models, including the Waterfall model, Rapid Application Development (RAD), Incremental, Spiral, and Concurrent models, detailing their phases, advantages, and disadvantages. Key points include the importance of a structured software process, risk management, and the adaptability of development methods to meet project requirements.


![The IEEE definition:
Software Engineering: (1) The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the
development, operation, and maintenance of software; that is, the application of engineering to
software. (2) The study of approaches as in (1).
[Software engineering is] the establishment and use of sound engineering principles in
order to obtain economically software that is reliable and works efficiently on real
machines.
According to Fritz Bauer:
[Software engineering is] he establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order
to obtain economically software that is reliable and works efficiently on real machines.
Software Engineering Definition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seunit1-240620085345-d6422c92/75/SOFTWARE-ENGINEERING-FOR-BEGINNERS-UNIT-1-pptx-3-2048.jpg)