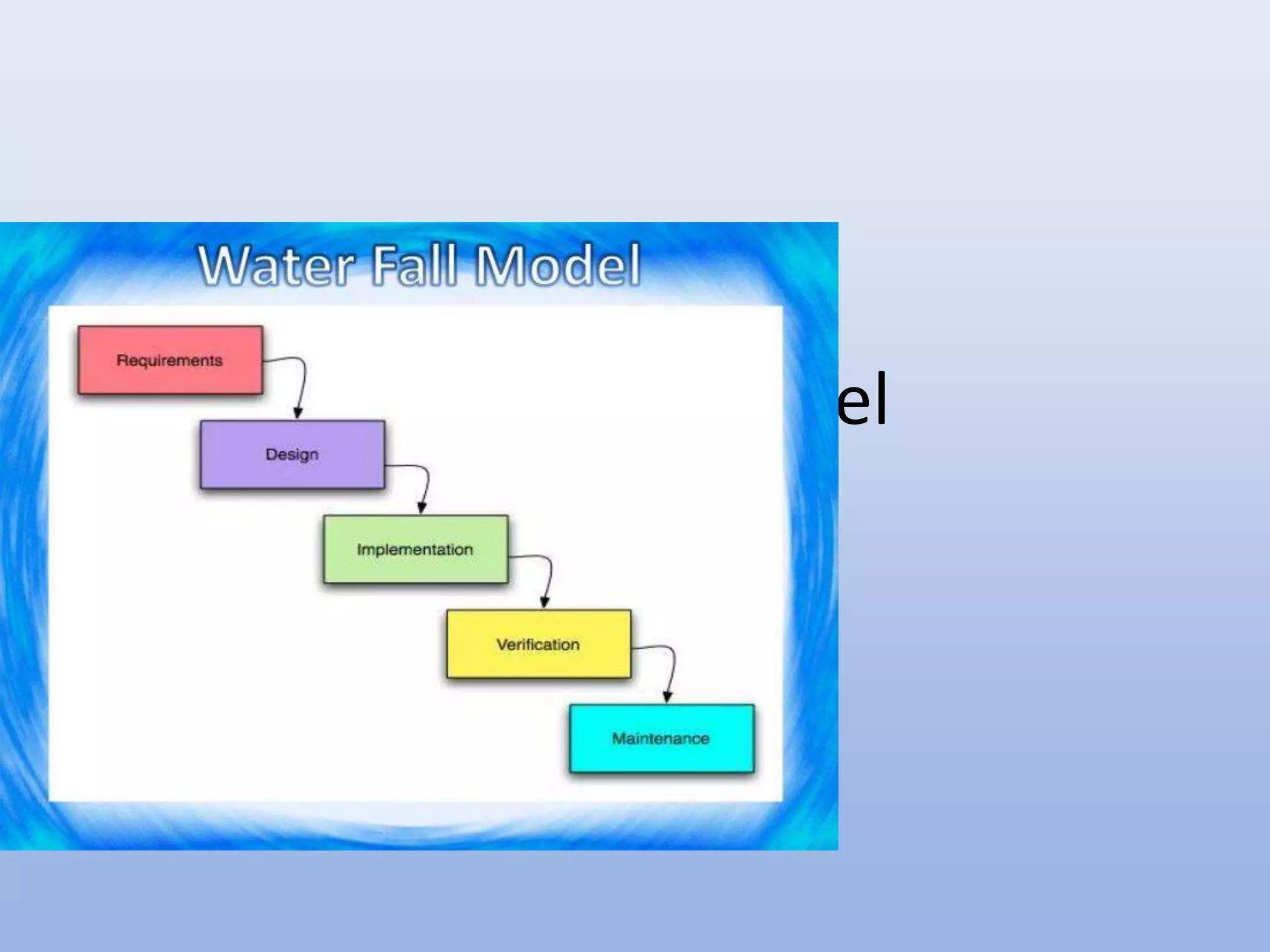
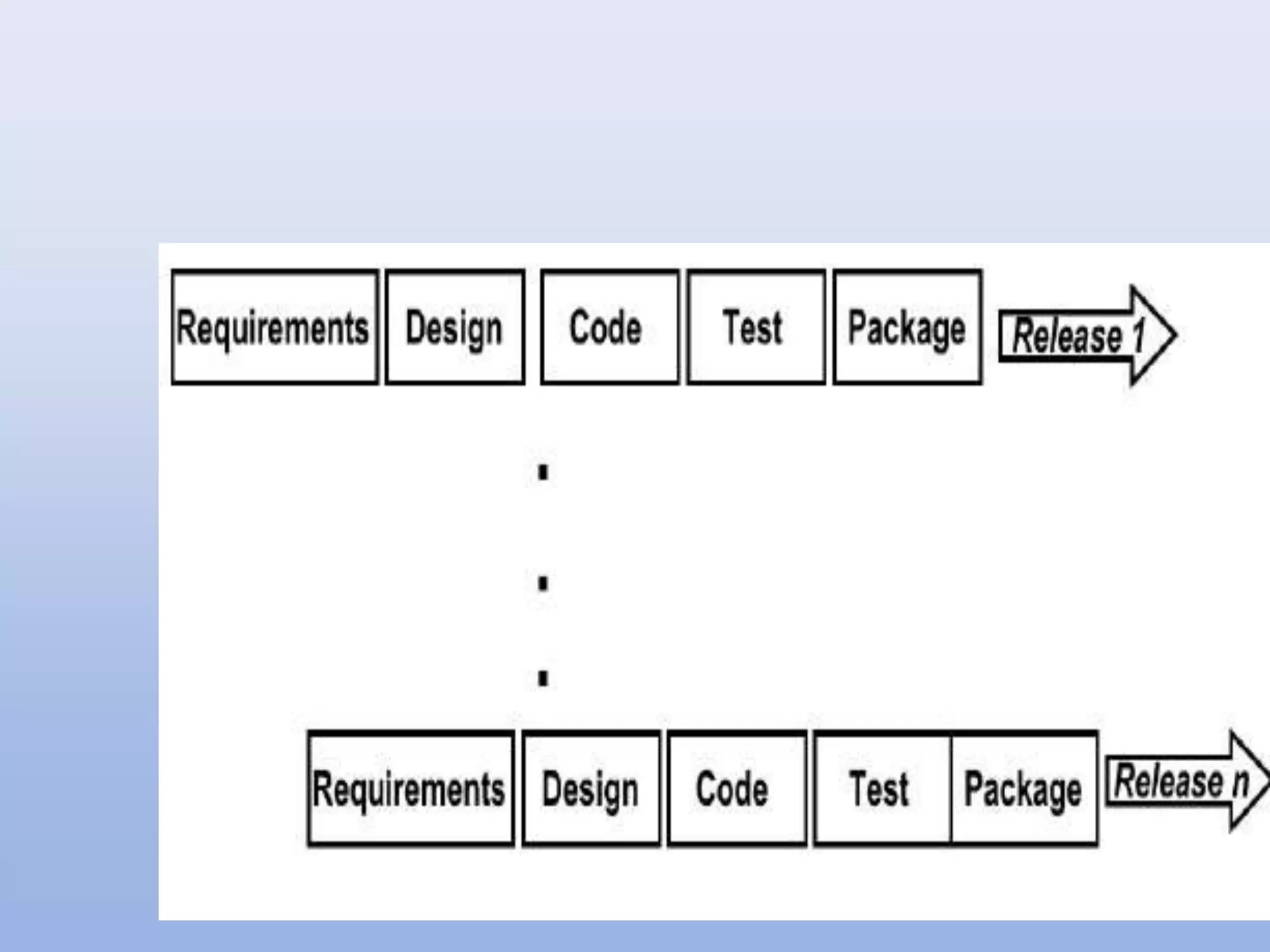
The document discusses different software development models. It describes the waterfall model as the oldest and most linear sequential model, where each phase must be completed before moving to the next. The phases are requirements, design, coding/implementation, testing, and maintenance. While simple, it is not suitable for complex or long-term projects where requirements may change. The incremental model allows for more flexibility and ability to change requirements by developing the product incrementally in iterations until complete.