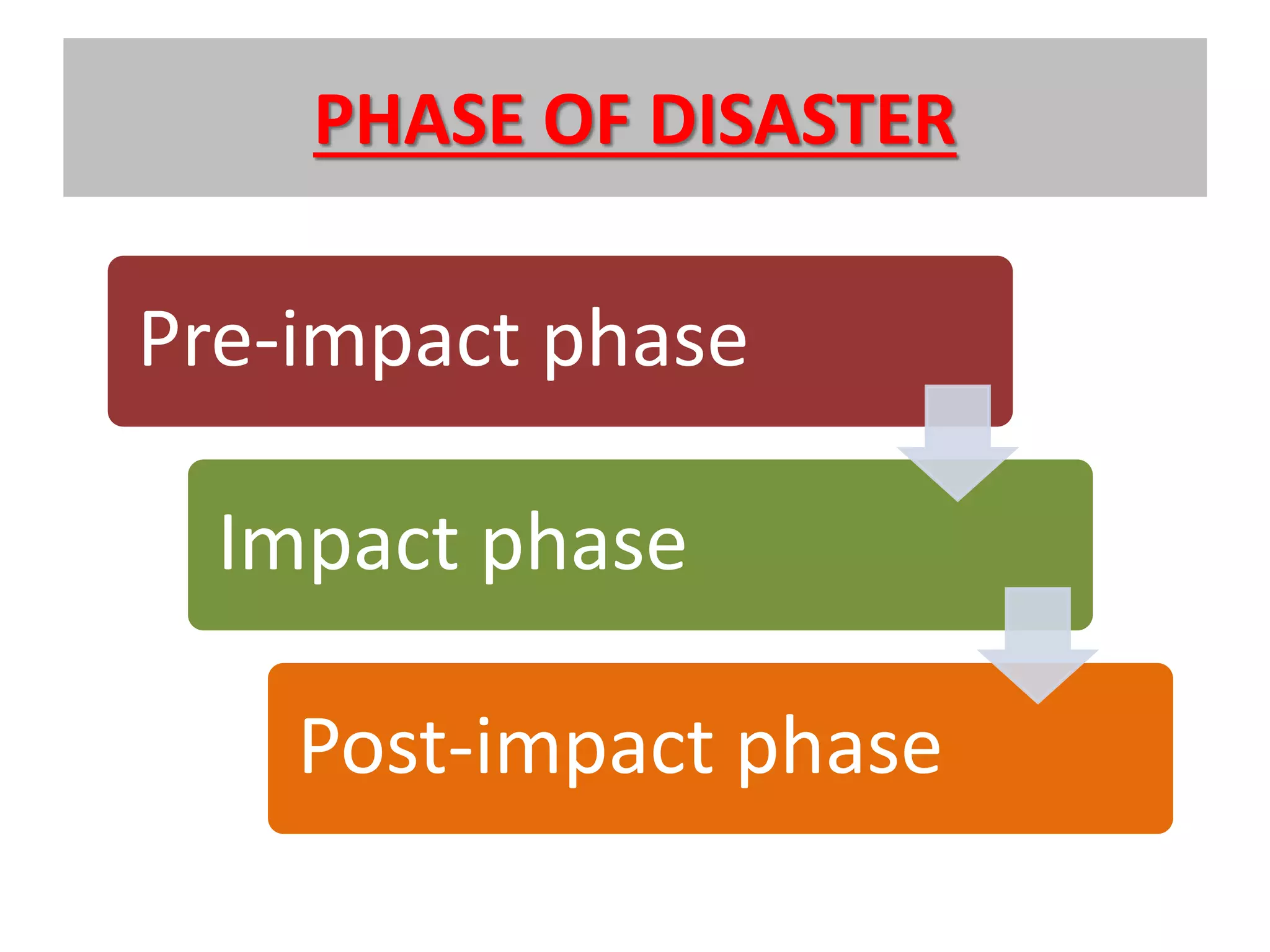
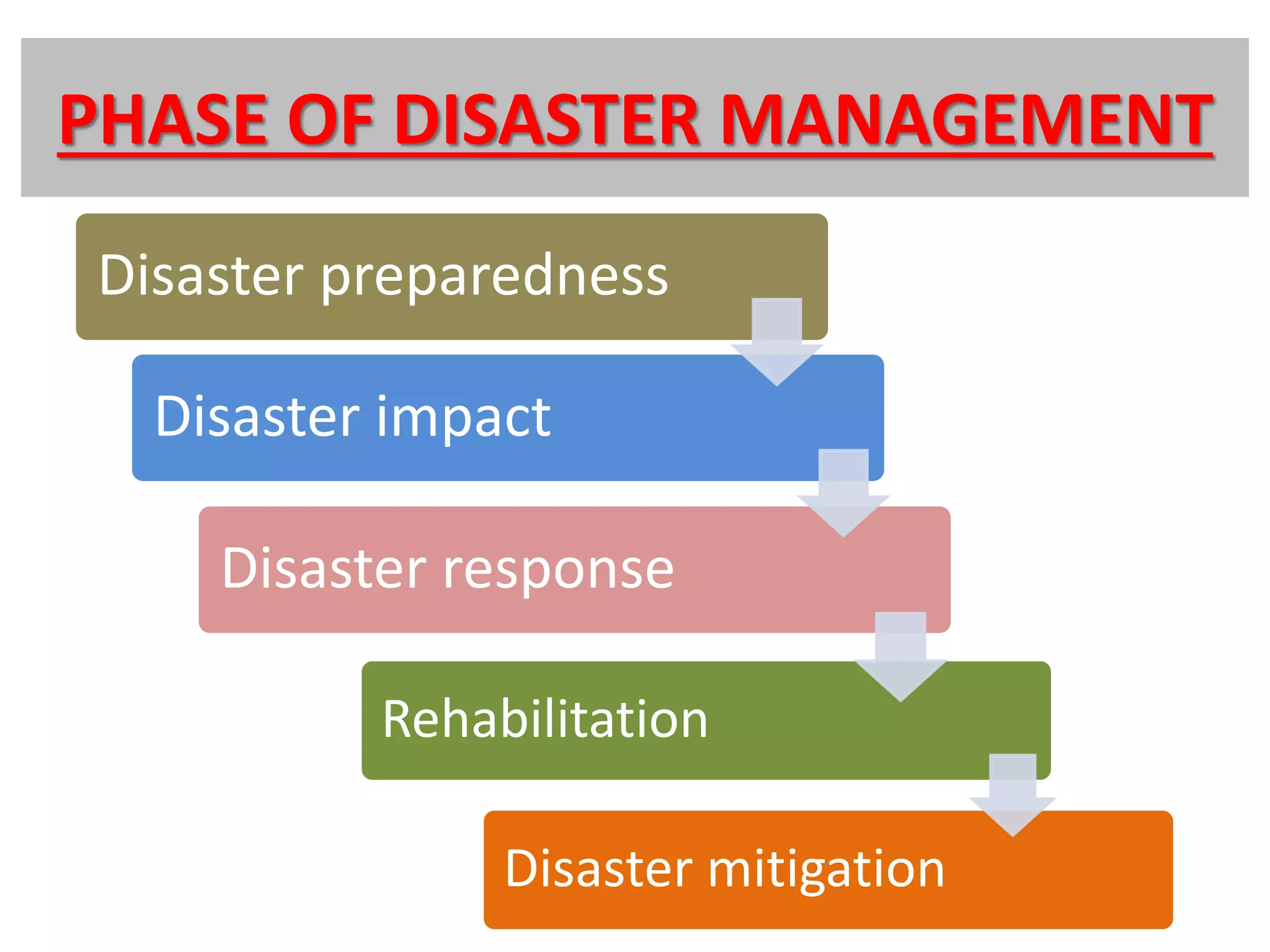
This document discusses disaster management and is presented by Akshay Kumar, a student with roll number 13EEBCE002. It defines a disaster and outlines different types of natural and man-made disasters. It also describes factors that affect disasters, characteristics of disasters, phases of disasters, principles of disaster management, and phases of disaster management including preparedness, impact, response, rehabilitation, and mitigation. The document provides details on preparedness, impact, response, rehabilitation, mitigation, effects, and recovery related to disaster management.