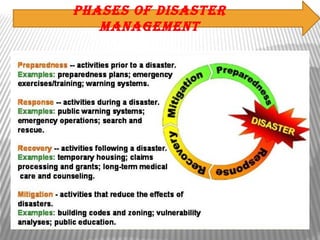
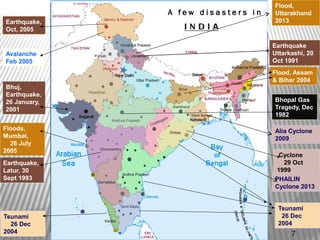
The document discusses disaster management and defines disasters. It notes that disasters can be natural or man-made, and lists some common types of each. The key phases of disaster management are prevention, preparedness, response, and rehabilitation/reconstruction. Major disasters that have impacted India between 1980-2005 are also outlined, including floods, cyclones, earthquakes, and tsunamis. The principles of disaster management focus on minimizing casualties, preventing further harm, rescuing victims, providing first aid and evacuation, medical care, and reconstruction.