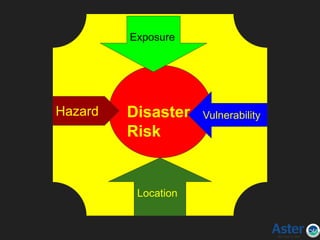
The document outlines the principles and preparedness strategies for disaster management, emphasizing the need for effective planning to minimize losses and ensure efficient response during disasters. It discusses types of disasters, including natural and man-made, and highlights the importance of training, resource allocation, and triage to manage mass casualty incidents. The document advocates for developing systematic disaster management plans and communication strategies to enhance hospital readiness and community resilience.