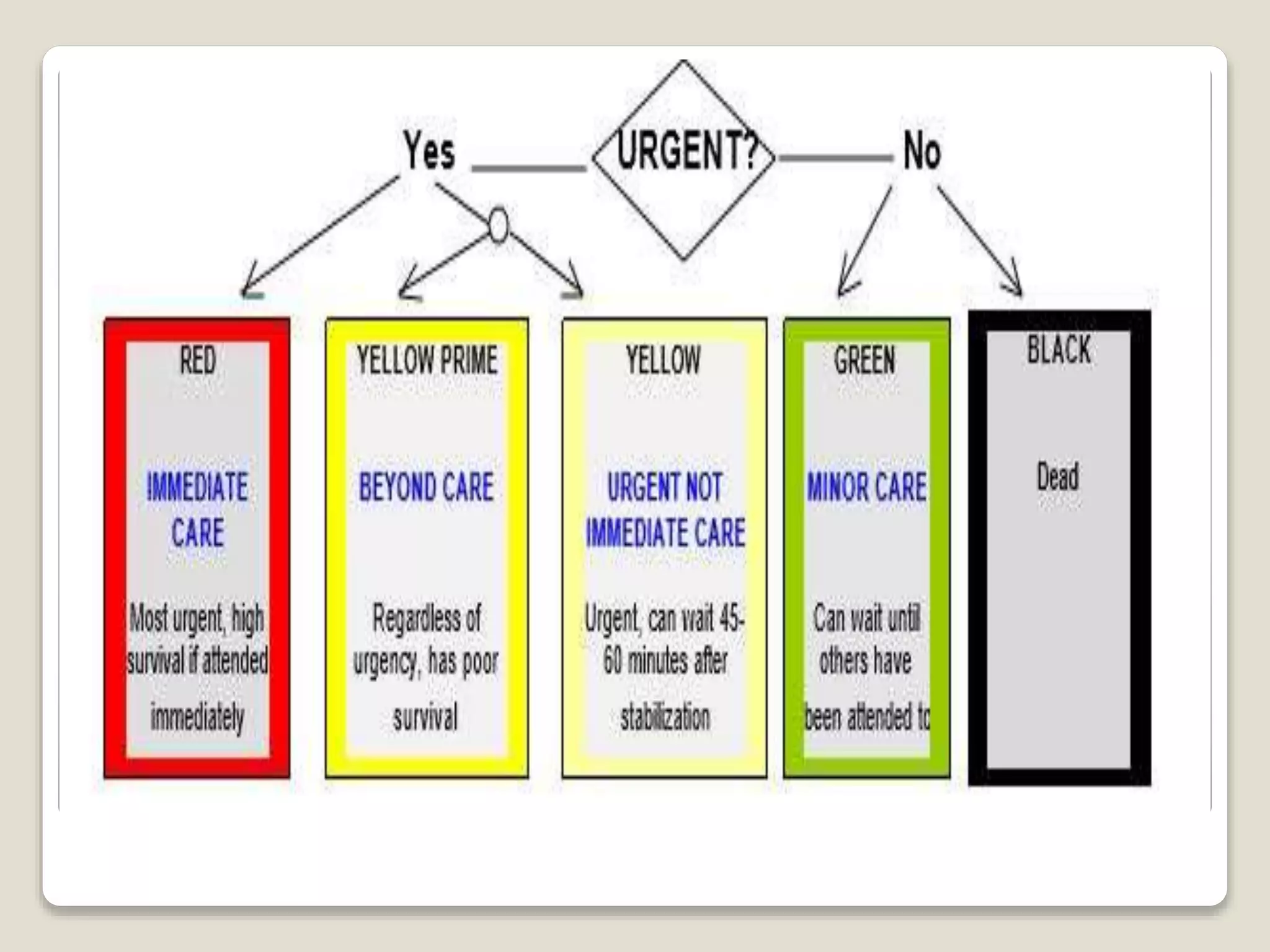
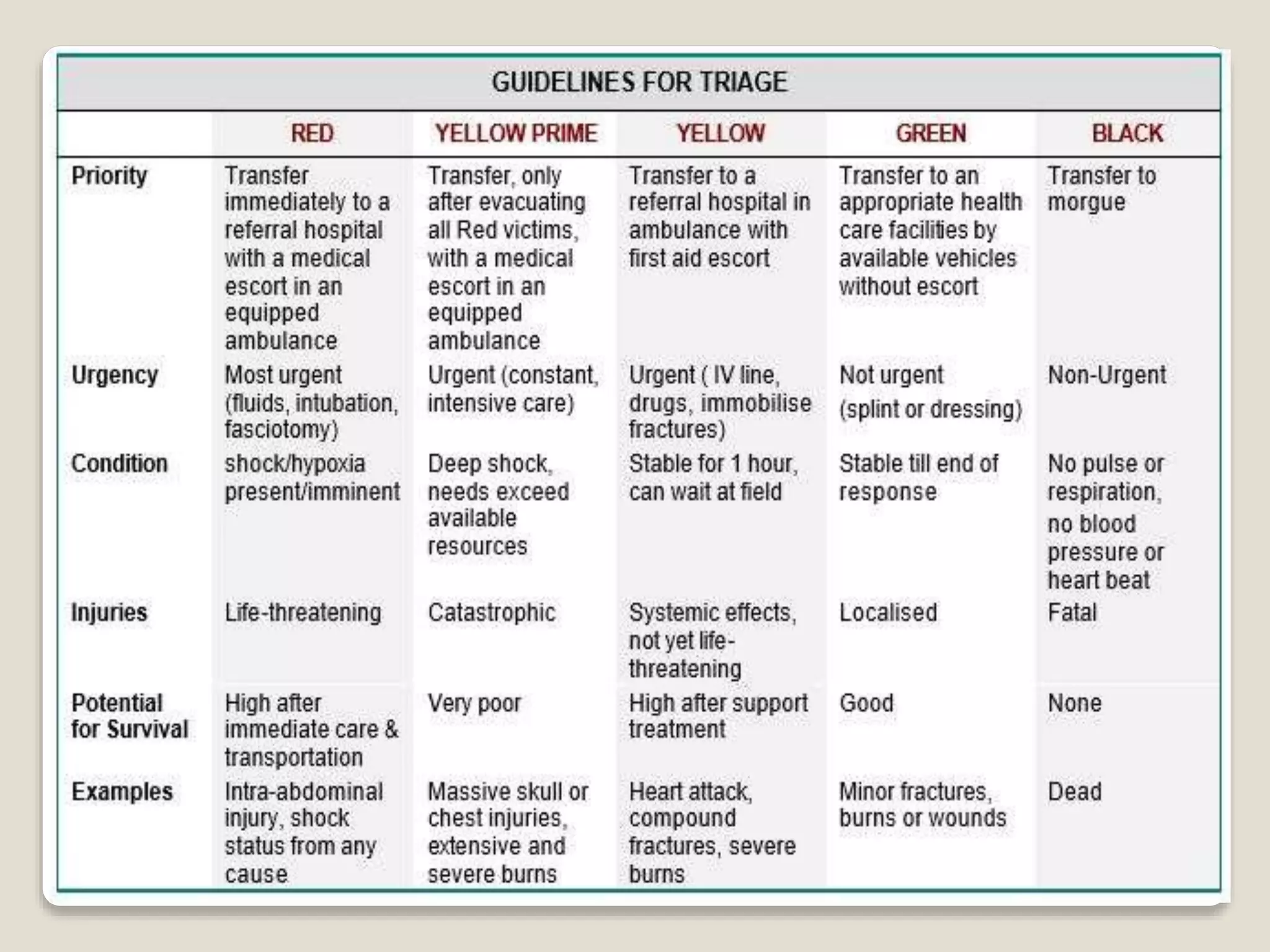
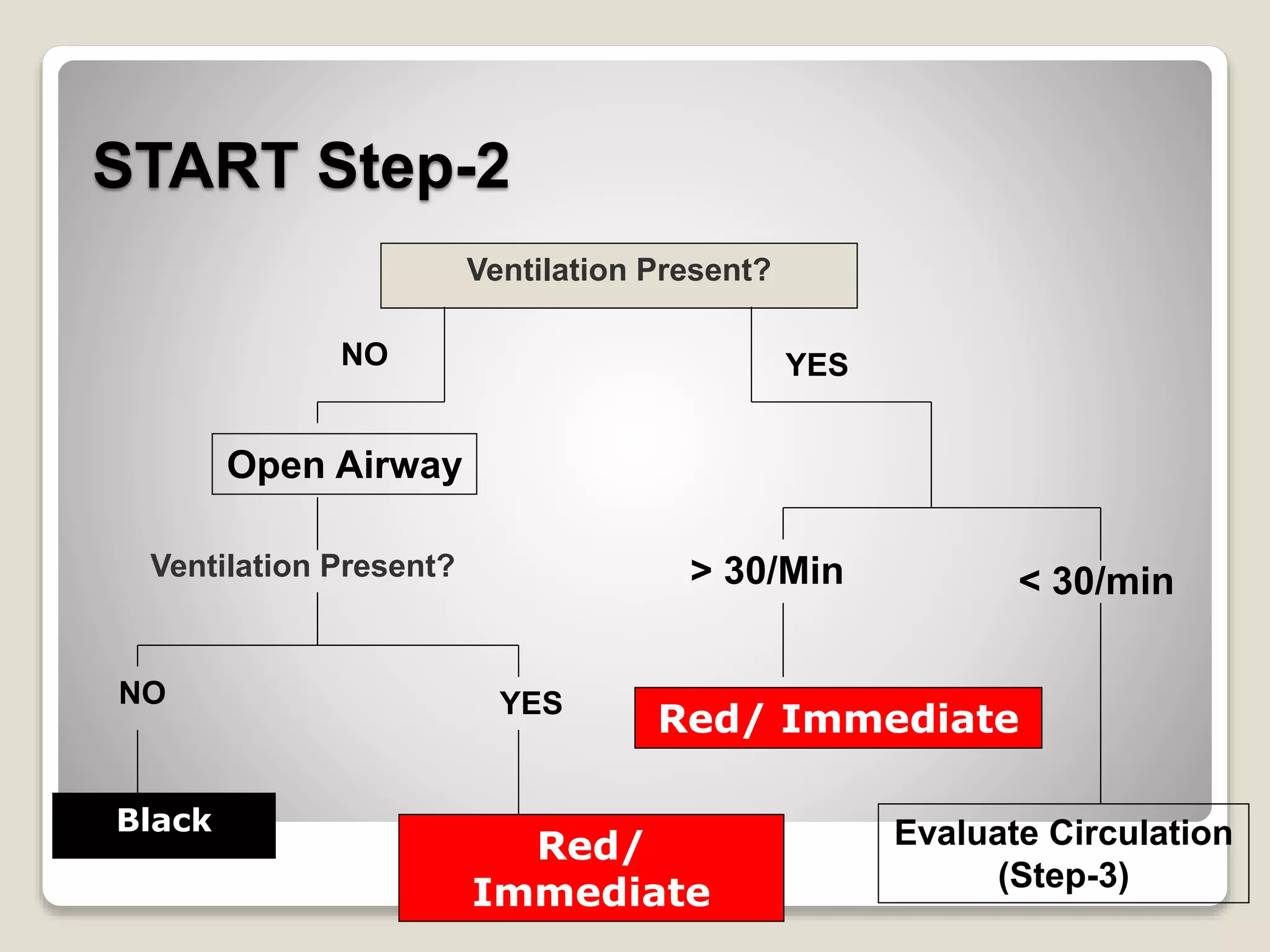
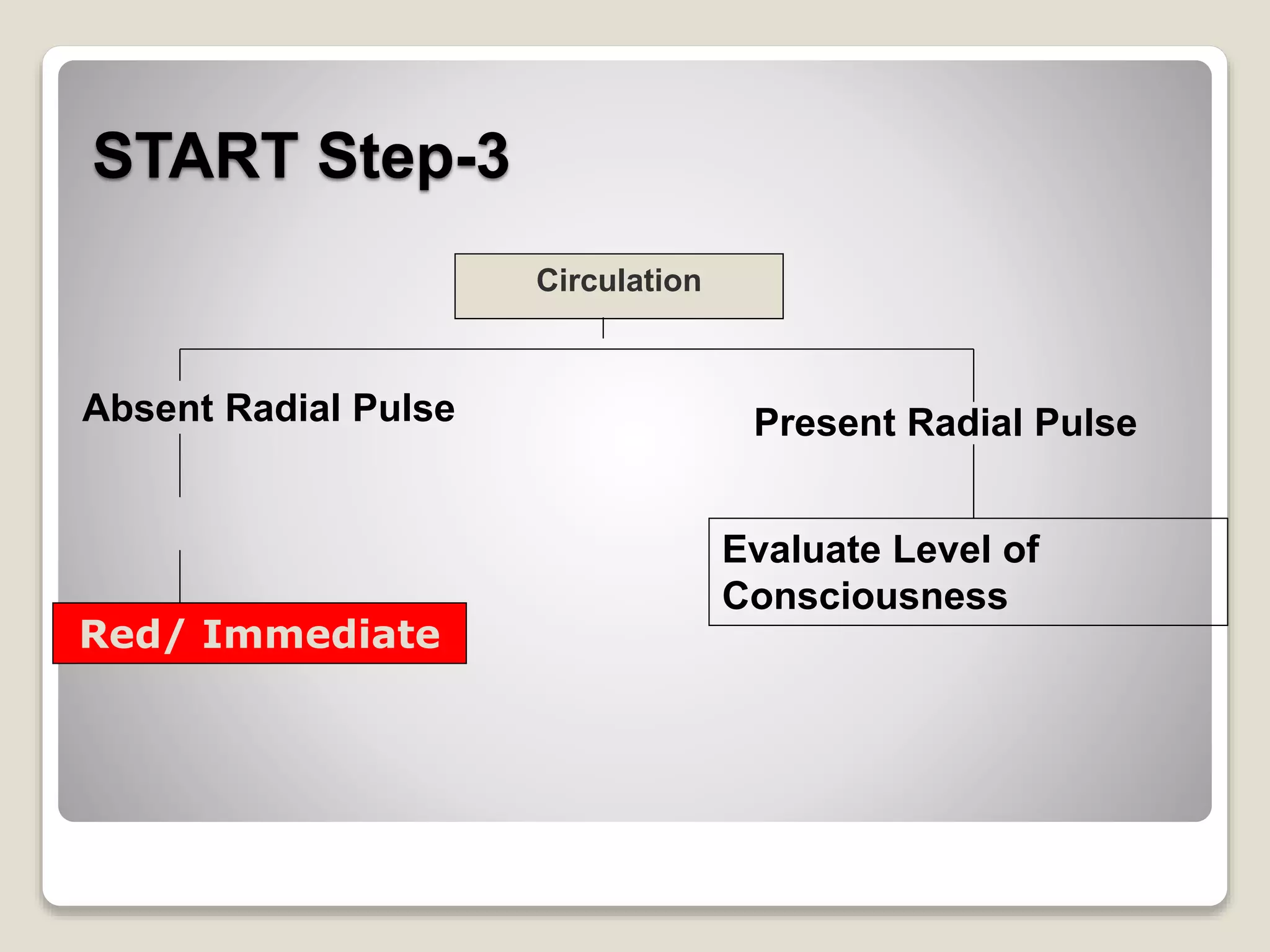
Triage is a method for prioritizing treatment of victims in mass emergencies, derived from the French word ‘triar,’ meaning 'to separate out.' It quickly identifies those with life-threatening injuries who have the best chance for survival, categorizing patients based on their respiratory status, perfusion, and mental state. The START system, created in the 1980s, enables rapid assessment of victims in under 15 seconds and includes classifications for minor injuries and contaminants.