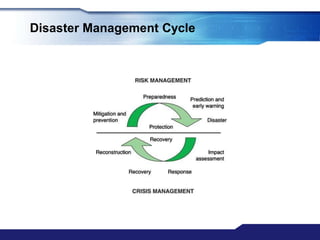
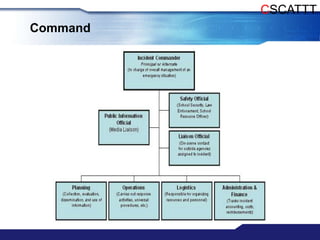
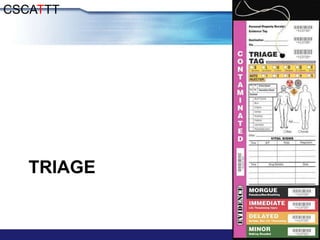
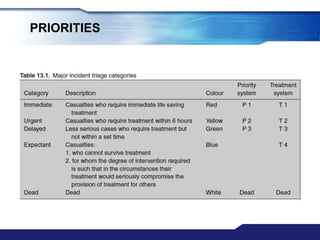
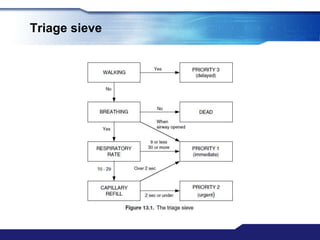
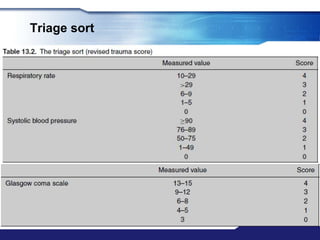
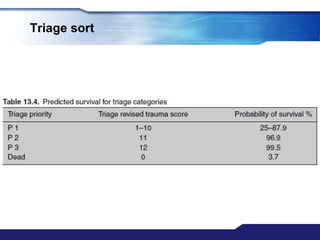
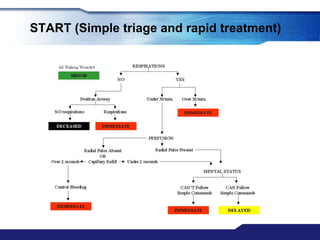
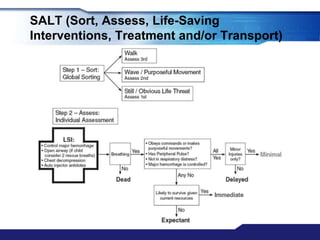
The document discusses Major Incident Medical Management and Support (MIMMS), which is a training course that teaches a systematic approach for managing medical care during mass casualty incidents. It describes the DISASTER paradigm and MIMMS principles for command, safety, communication, assessment, triage, treatment, transport, and recovery. Key aspects covered include incident command structure, safety procedures, communication protocols, triage categories and methods, and priorities for treatment and transport to various hospitals based on patient needs.