1. A disaster is defined as an event that exceeds the ability of a community to cope using its own resources. It results when needs are greater than available resources.
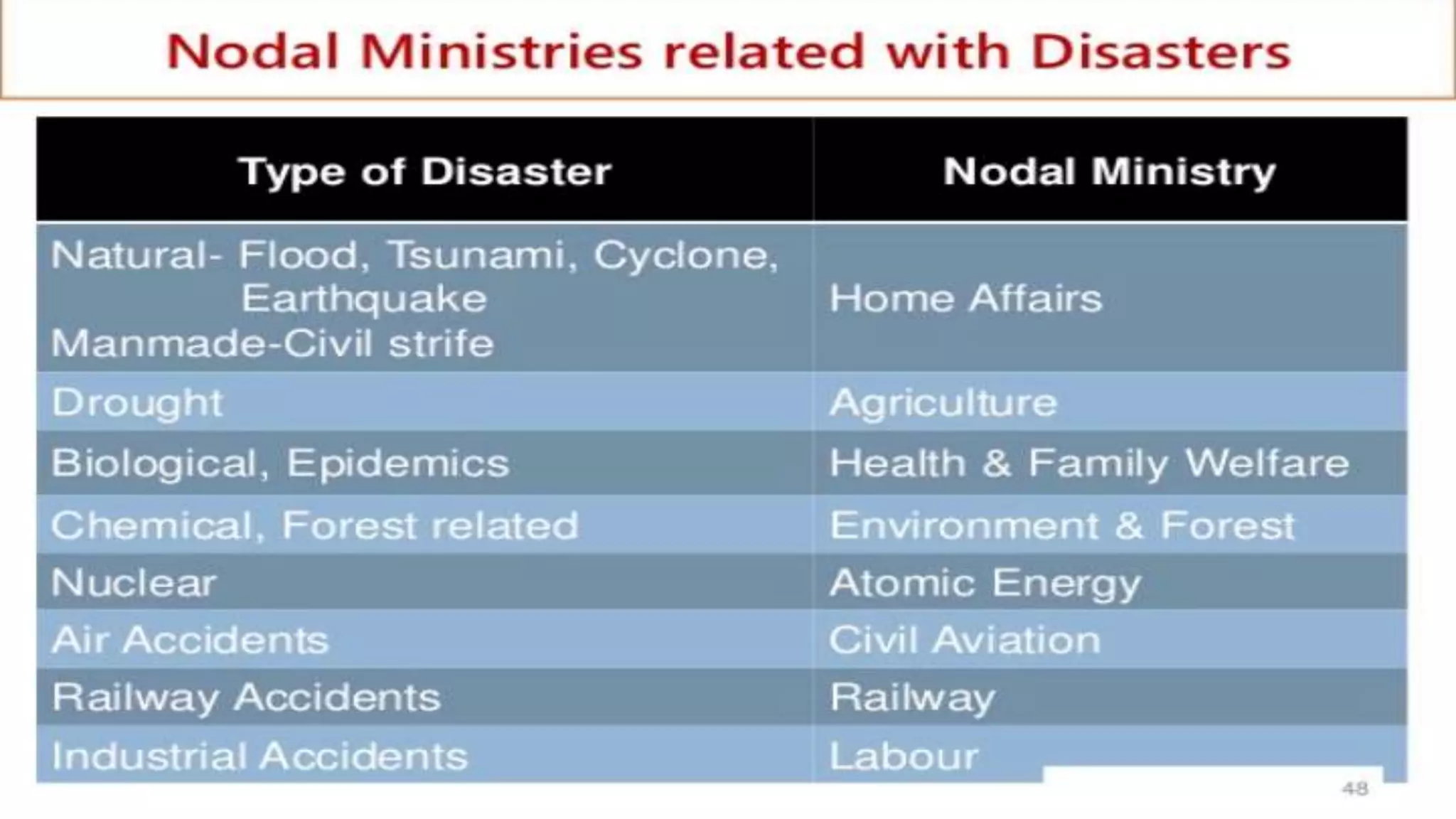
2. Disasters can be classified based on causes into natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, droughts or man-made disasters caused by human intent, negligence or technological failures.
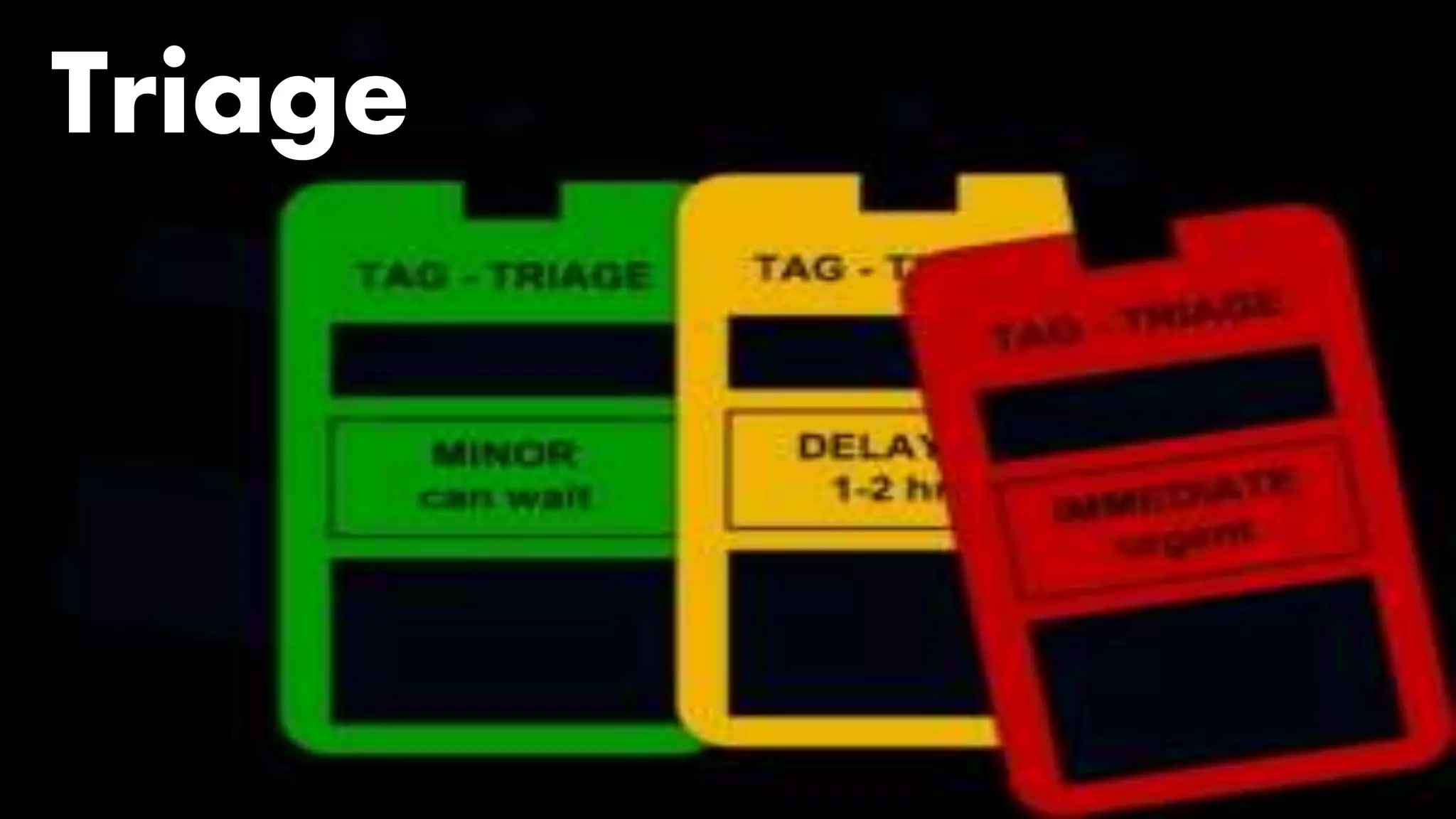
3. Key aspects of disaster management include preparedness through risk evaluation, resource mobilization and training; response during impact through evacuation, search and rescue, and triage; and recovery through rehabilitation and mitigation measures to reduce future risk.