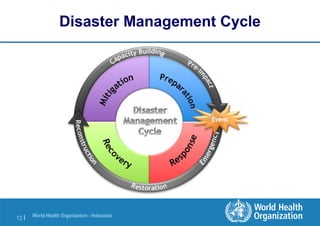
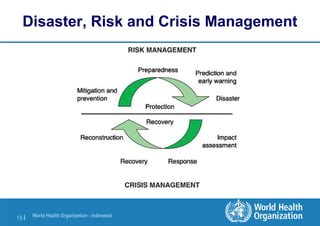
The document presents an overview of disaster and crisis management, focusing on definitions, management strategies, and comparisons between significant earthquakes in Haiti and Chile. It details the importance of preparedness and response strategies, along with the crisis life cycle and risk management approaches. Additionally, the discussion includes disaster management activities such as mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery.