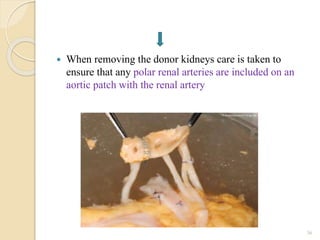
This document provides an overview of renal transplantation. It discusses the history of renal transplantation in Bangladesh, indications and contraindications for transplantation, types of donors, organ donation and recovery processes, criteria for donor and recipient selection, pre-transplant evaluation steps, organ preservation techniques, transplantation surgery, and potential post-transplant complications. The key points covered include types of living and deceased donors, brain death criteria, immunological risks like hyperacute rejection, and surgical risks such as vascular thrombosis or ureteral complications.