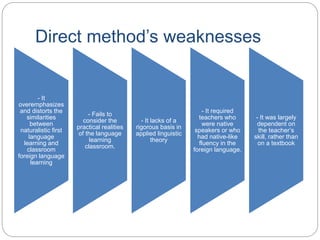
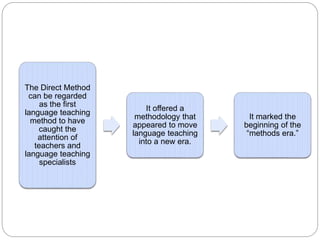
The Direct Method originated in the 19th century and was based on principles of the Natural Method. It aimed to teach language without translation or use of the learner's native language. Meaning was conveyed through actions, demonstrations, and active use of the target language in the classroom. Grammar rules were induced from classroom activities. Speaking was emphasized, with new vocabulary introduced through association with known words, miming, and pictures. The Direct Method was officially endorsed in France and Germany and was known commercially as the Berlitz Method. It utilized principles like conducting class only in the target language and building oral skills through question-and-answer exchanges. However, it overemphasized similarities between naturalistic first language learning and classroom learning,