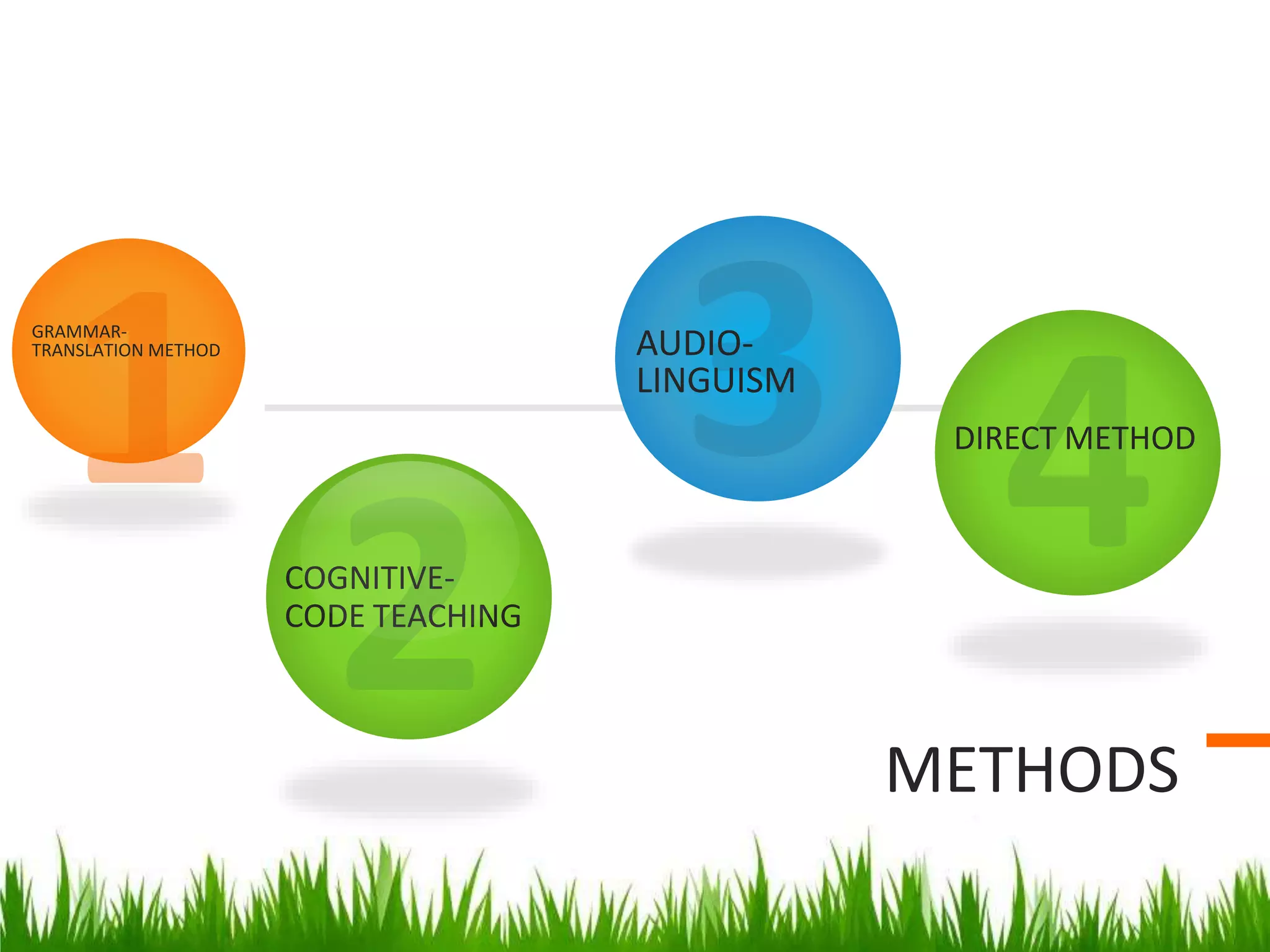
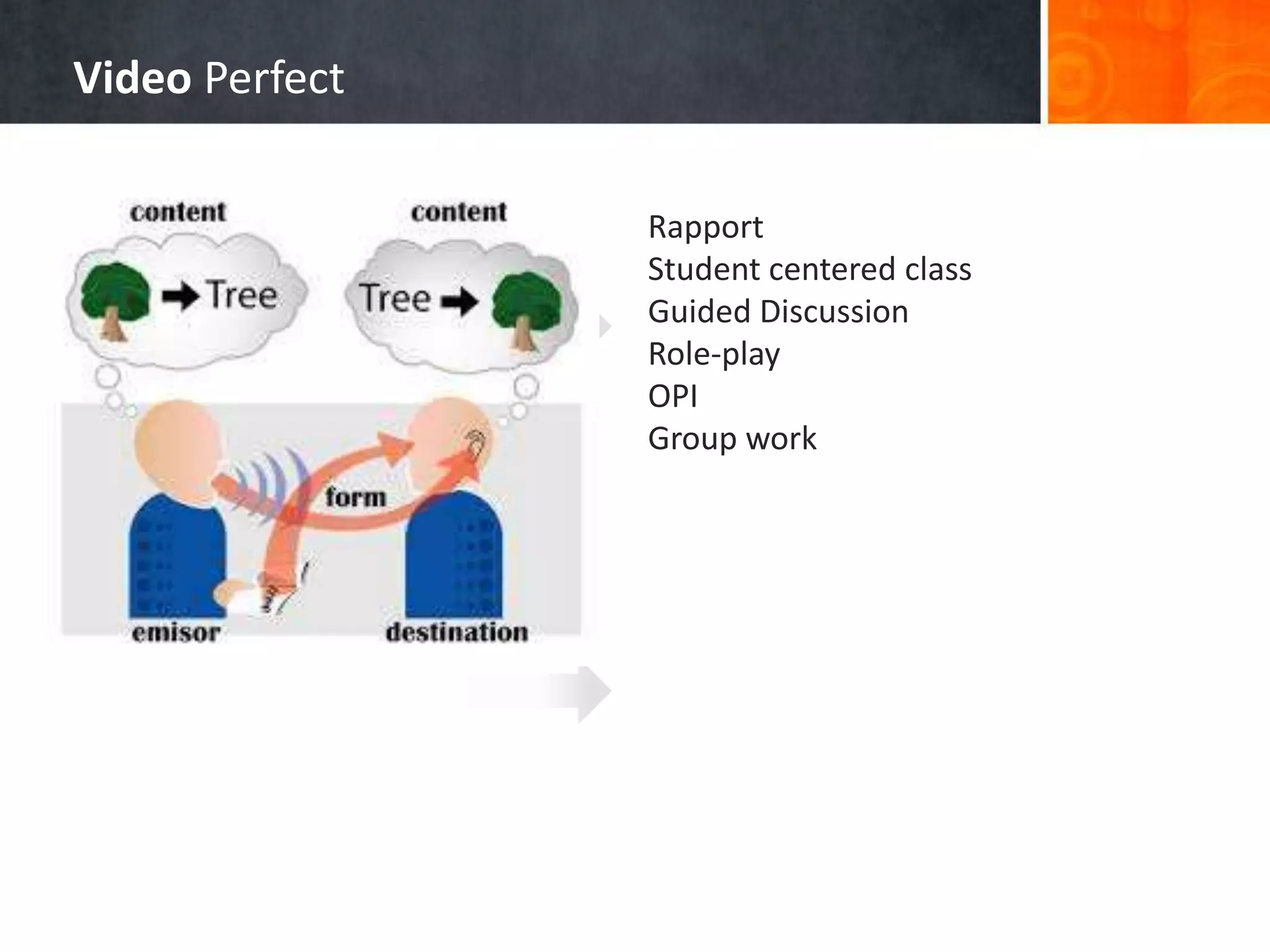
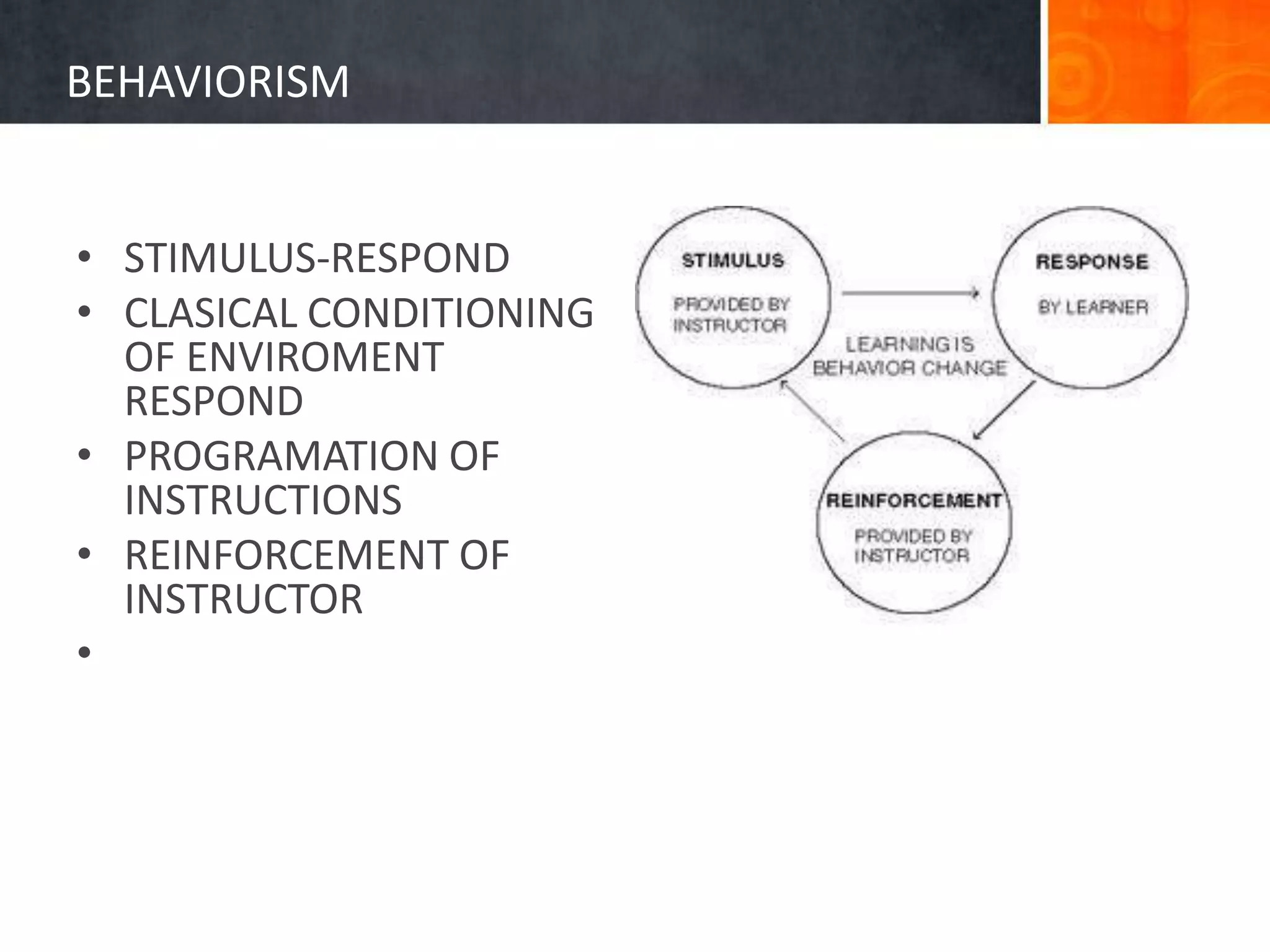
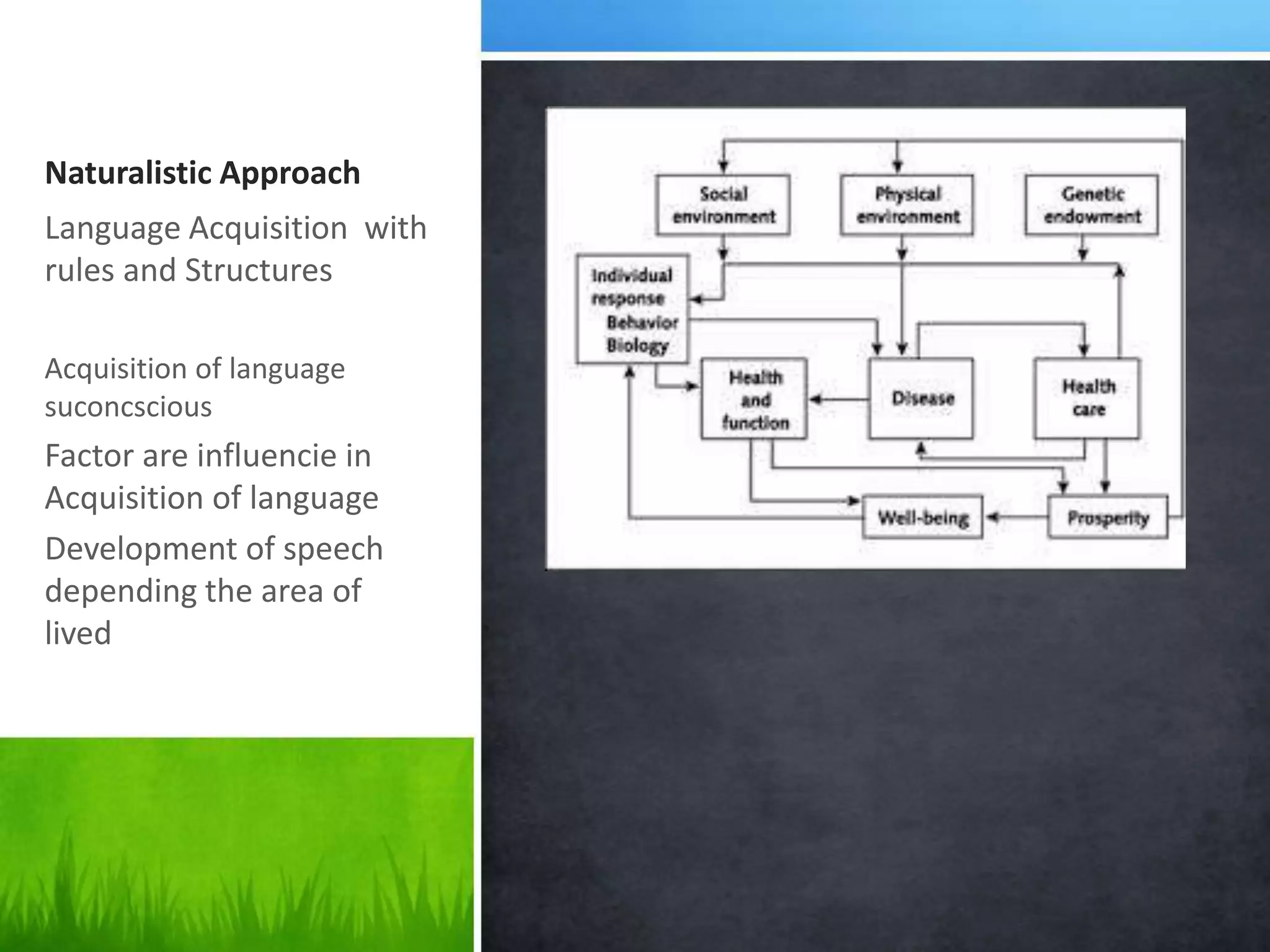
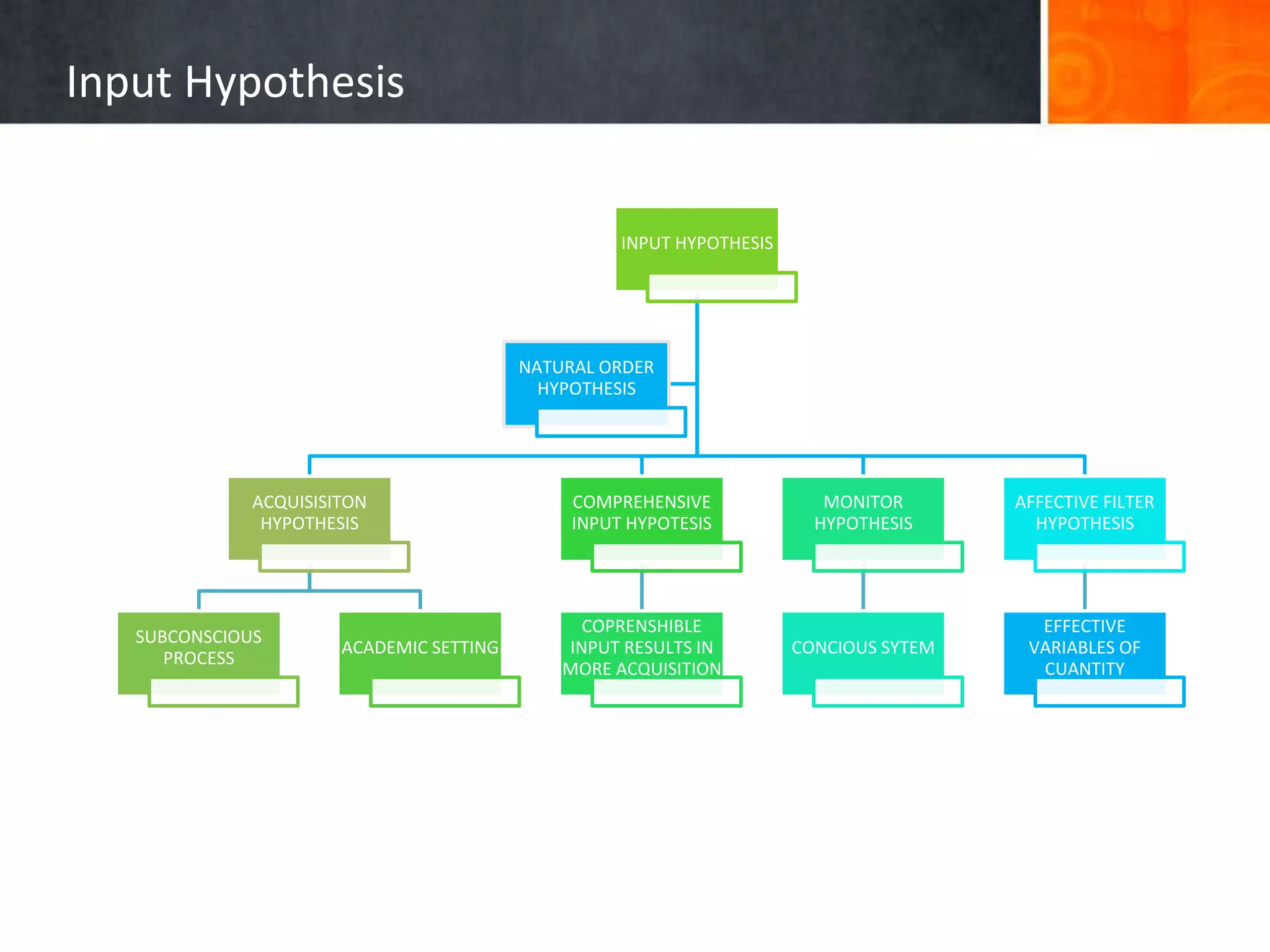
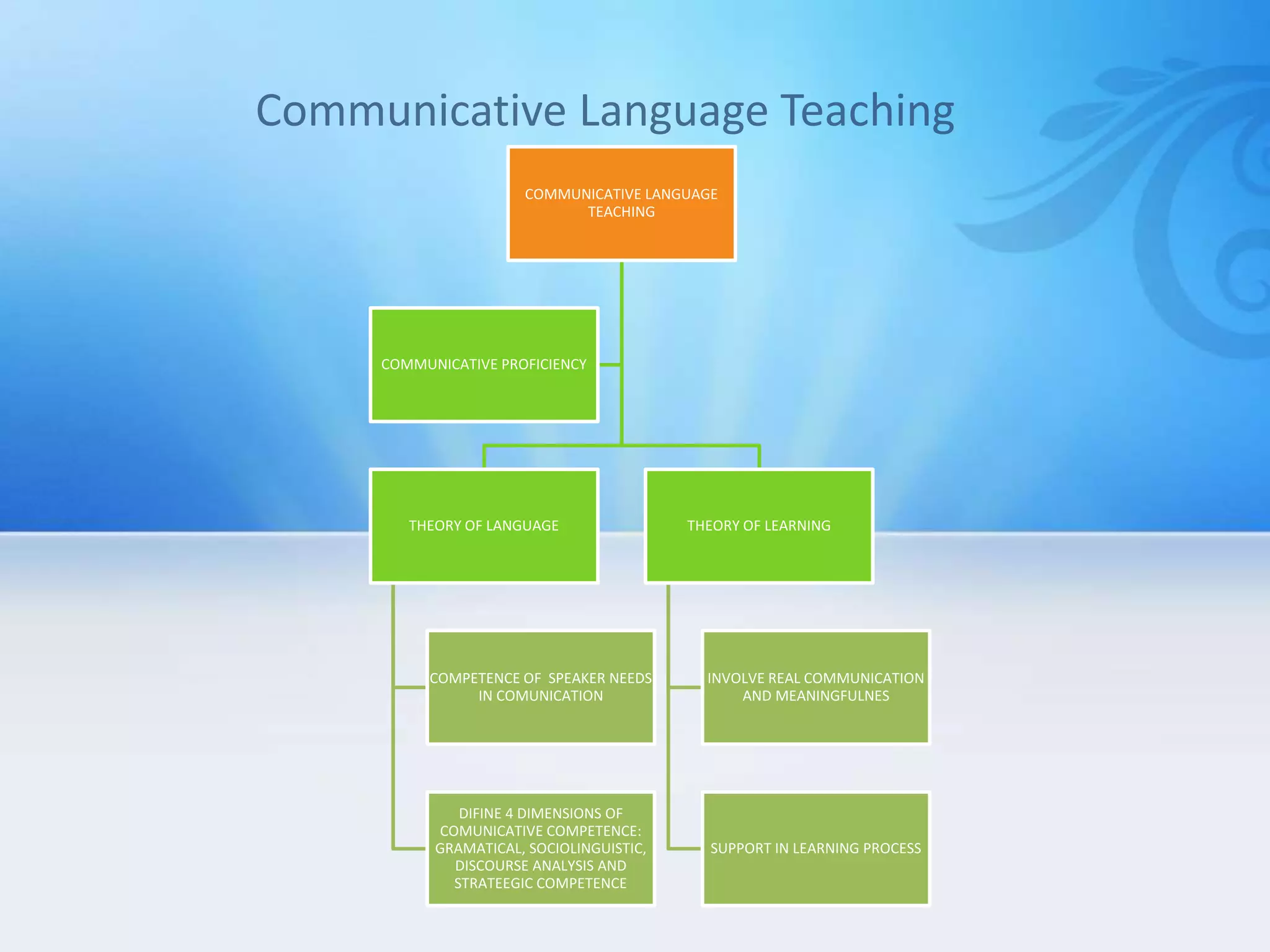
This document summarizes several approaches to language teaching including the grammar-translation method, audio-lingualism, cognitive-code teaching, direct method, and interactive communicative approach. It also discusses theories of second language acquisition including behaviorism, cognitive approaches, naturalistic approaches, input hypothesis, monitor hypothesis, affective filter hypothesis, natural order hypothesis, and communicative language teaching. Finally, it mentions models of language including the attention-processing model and implicit/explicit models.