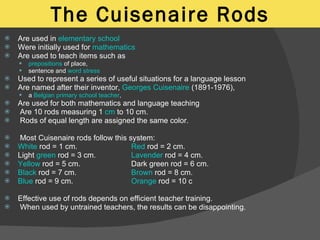
The Silent Way approach focuses on developing learner independence and autonomy through problem-solving activities. It uses visual aids like colored rods, charts, and fidels to teach vocabulary, grammar structures, and pronunciation in a discovery learning manner. The teacher acts as a facilitator and refrains from repetition or direct correction, allowing students to self-correct and learn through inner feedback.