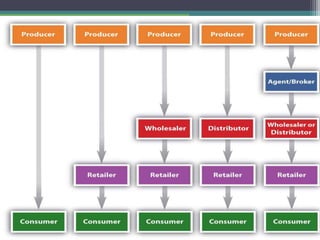
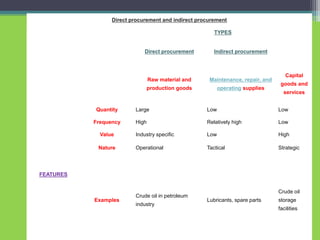
This document discusses marketing channels for agricultural products. It defines marketing channels as the routes through which agricultural goods move from producers to consumers. The document outlines different types of marketing channels, including direct sales from producers to customers, and sales through wholesalers or retailers. It also describes some innovative marketing channels used in India, such as farmer's markets, and discusses specific models like Apni Mandi in Punjab and Hadaspar vegetable market in Pune.