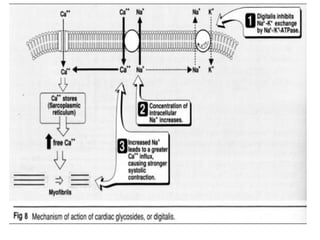
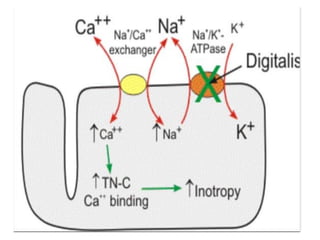
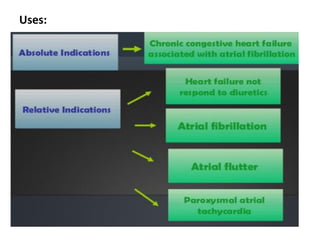
Digitalis is a drug prepared from dried foxglove leaves that contains cardiac glycosides like digoxin. It stimulates the heart muscle and has been used to treat heart conditions since 1775. Digitalis works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium ATPase pump, increasing intracellular sodium and calcium levels, which promotes cardiac muscle contraction. It has indications for congestive heart failure, atrial flutter, arterial tachycardia, and atrial fibrillation.