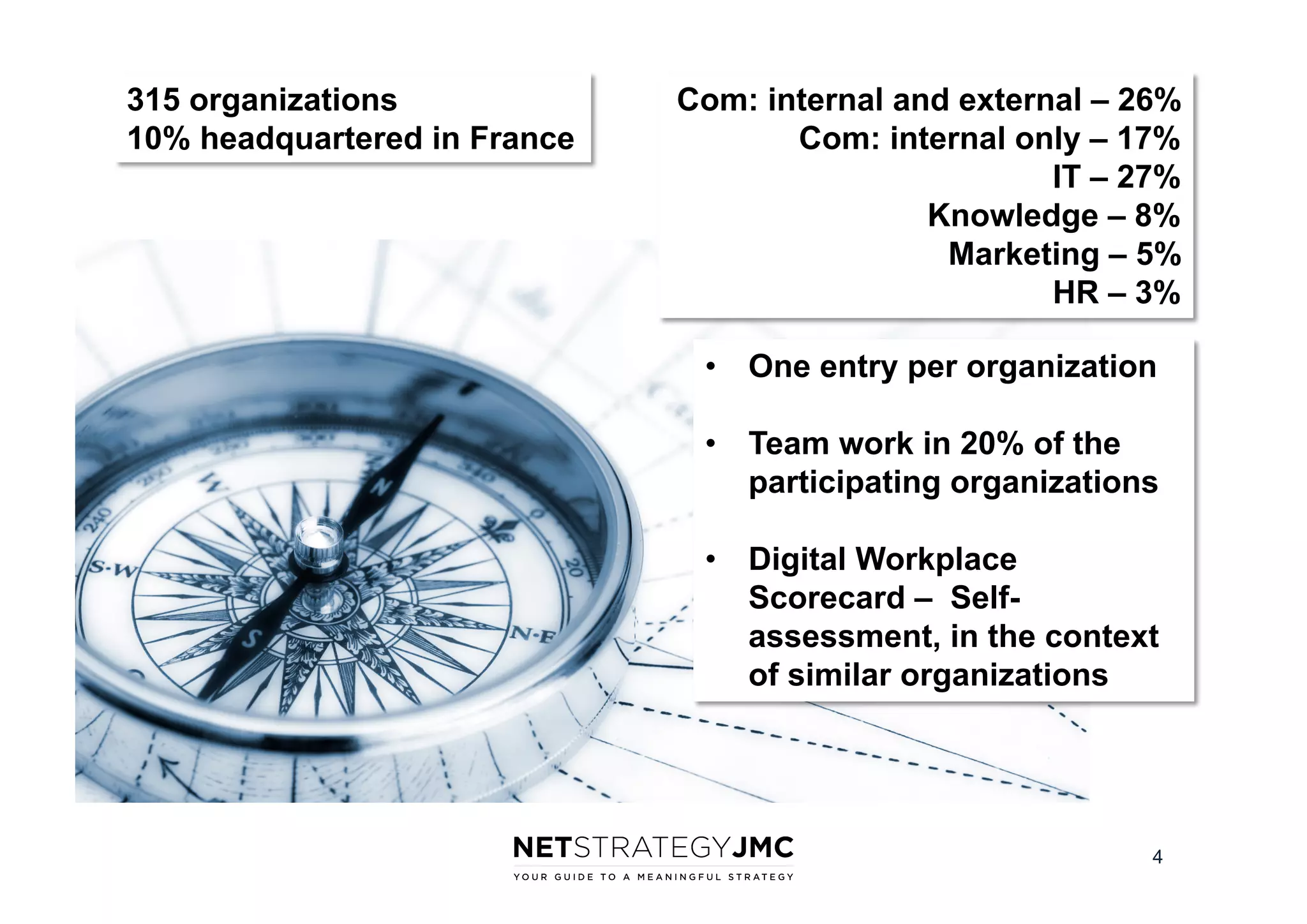
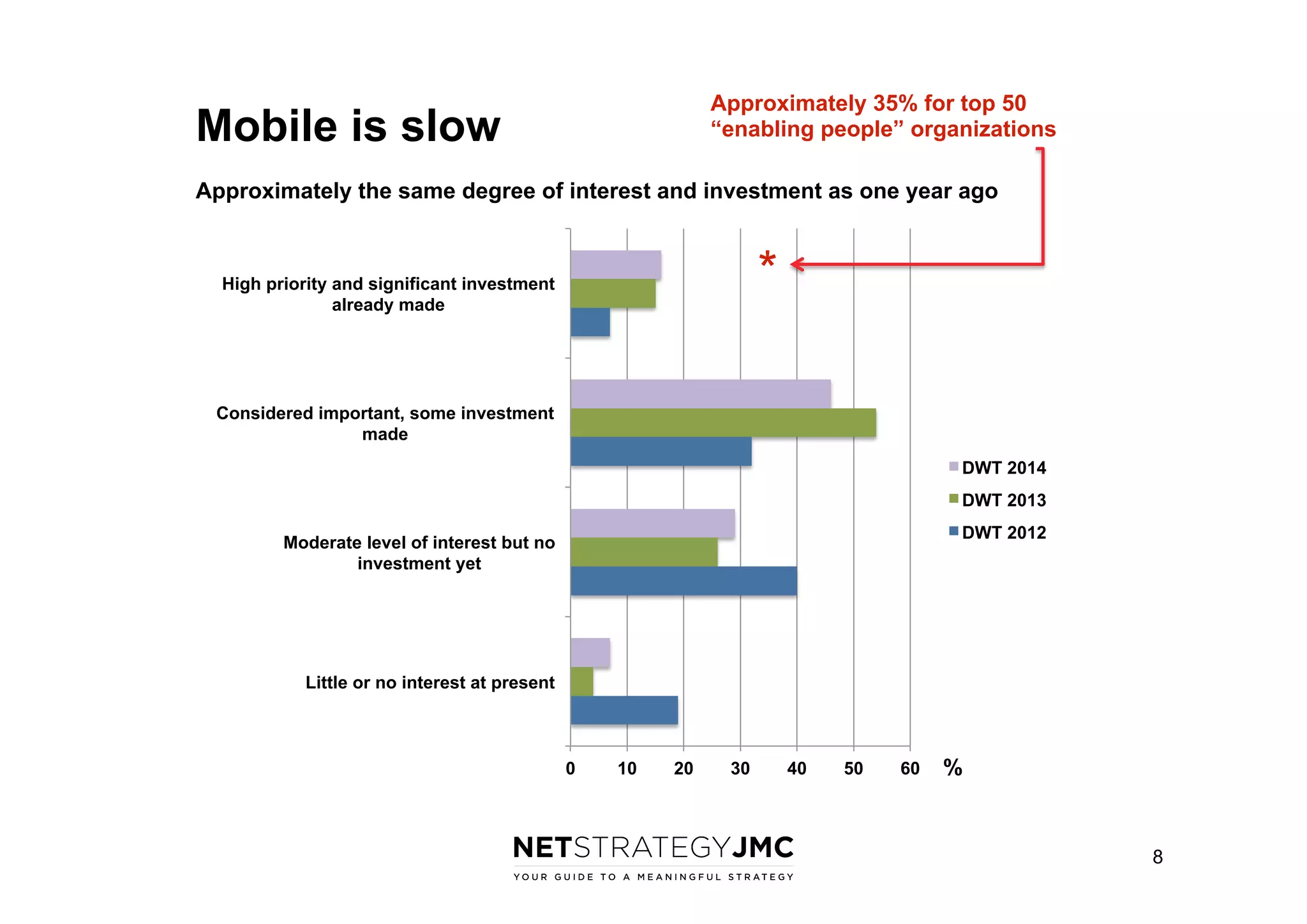
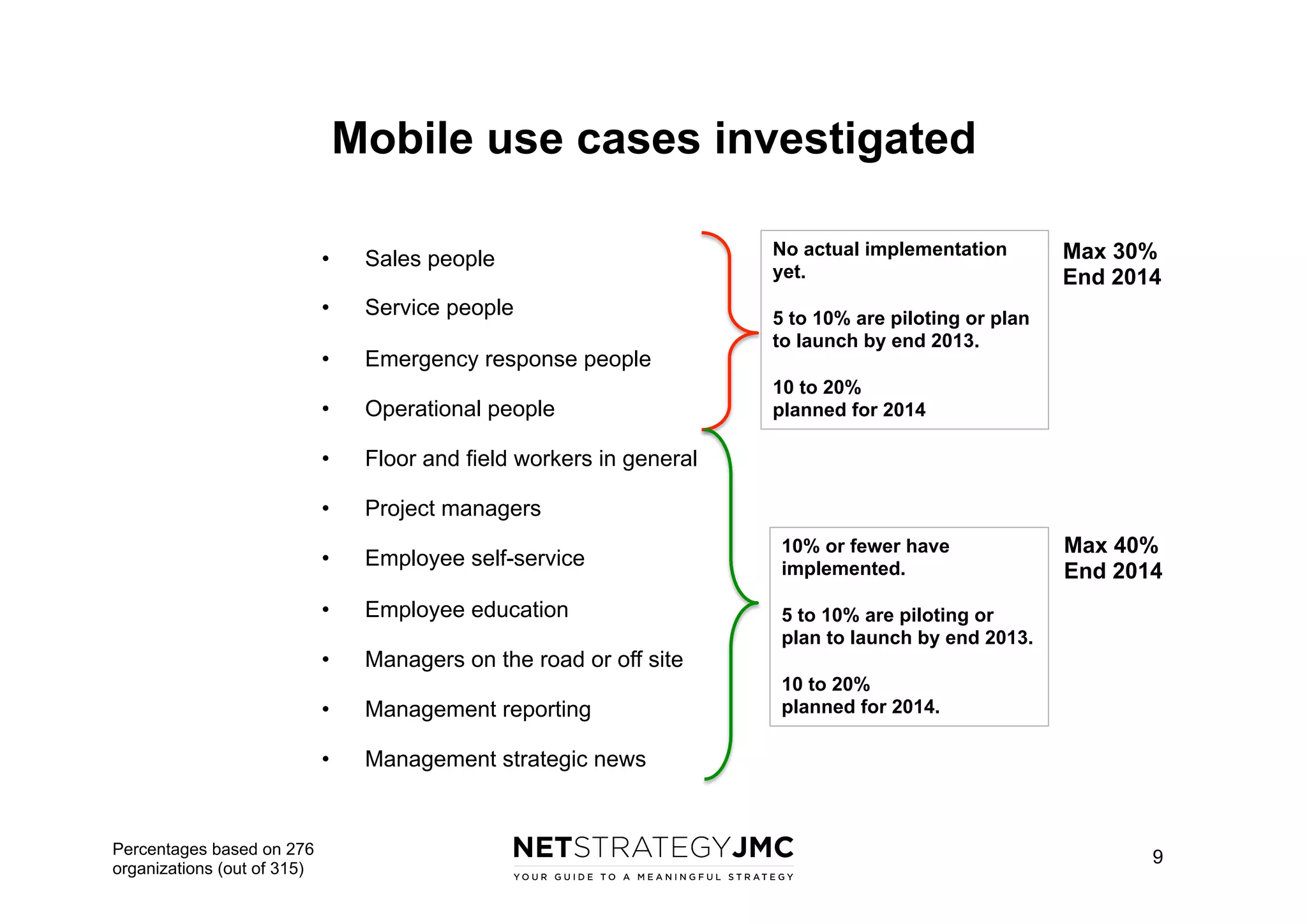
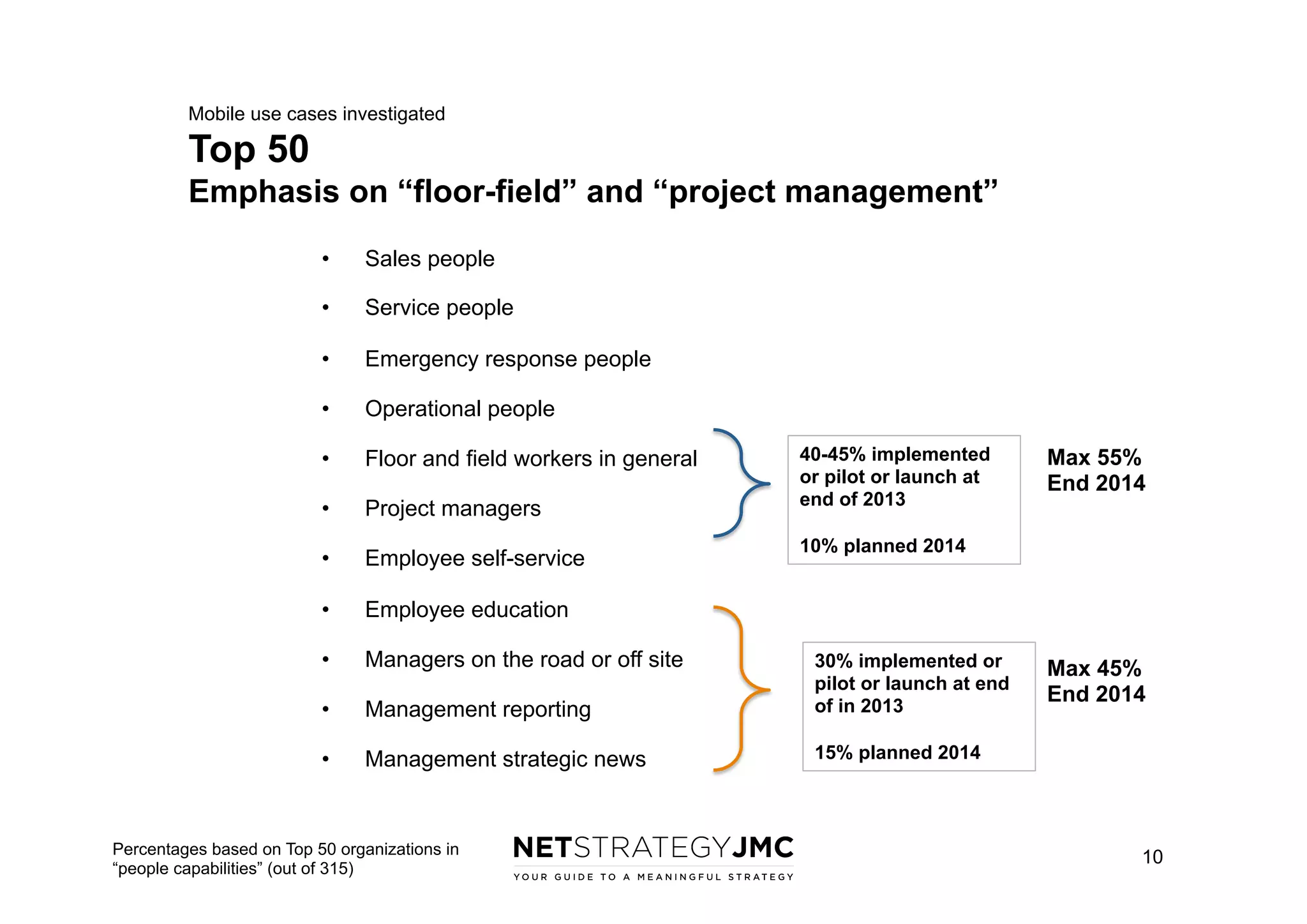
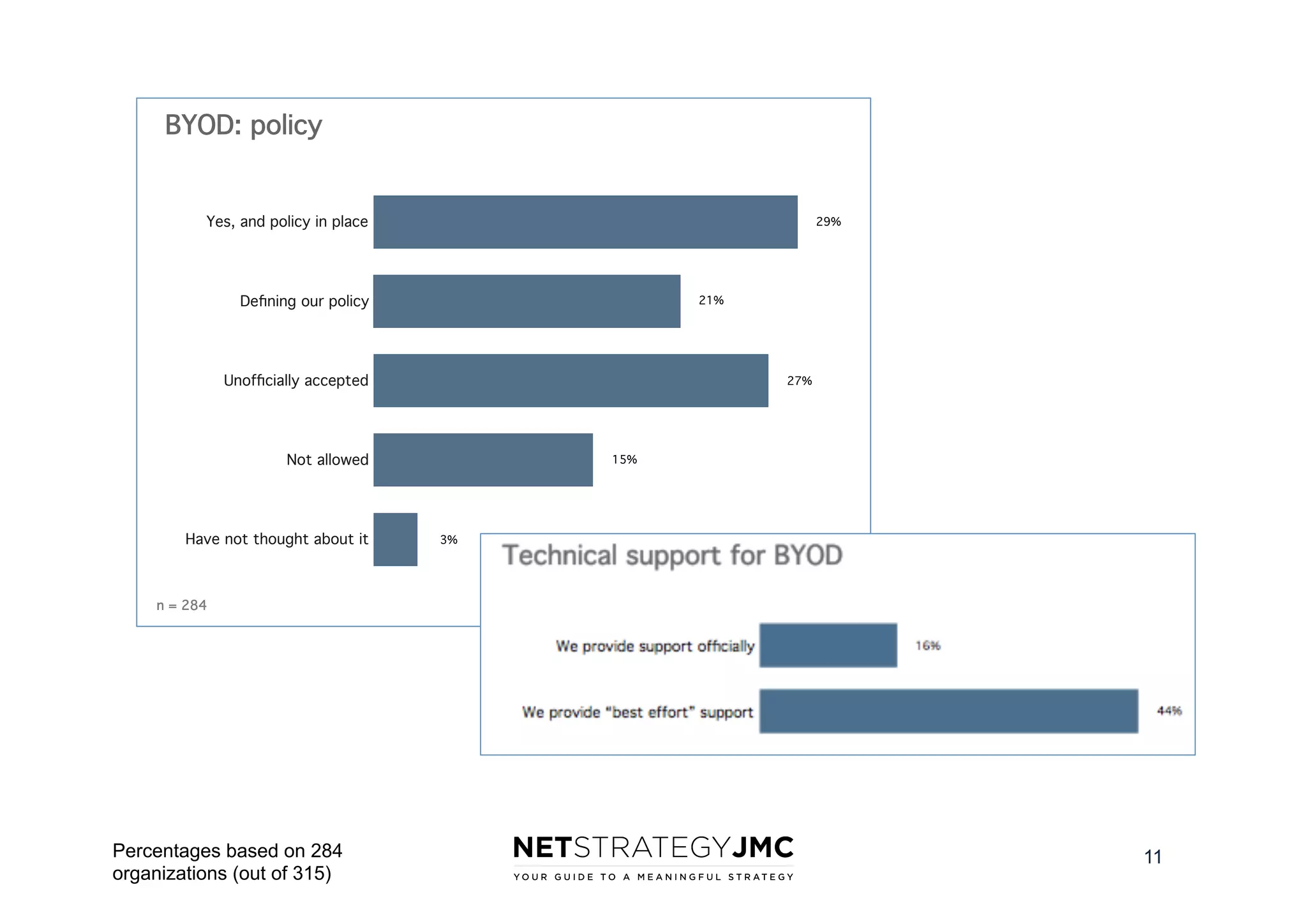
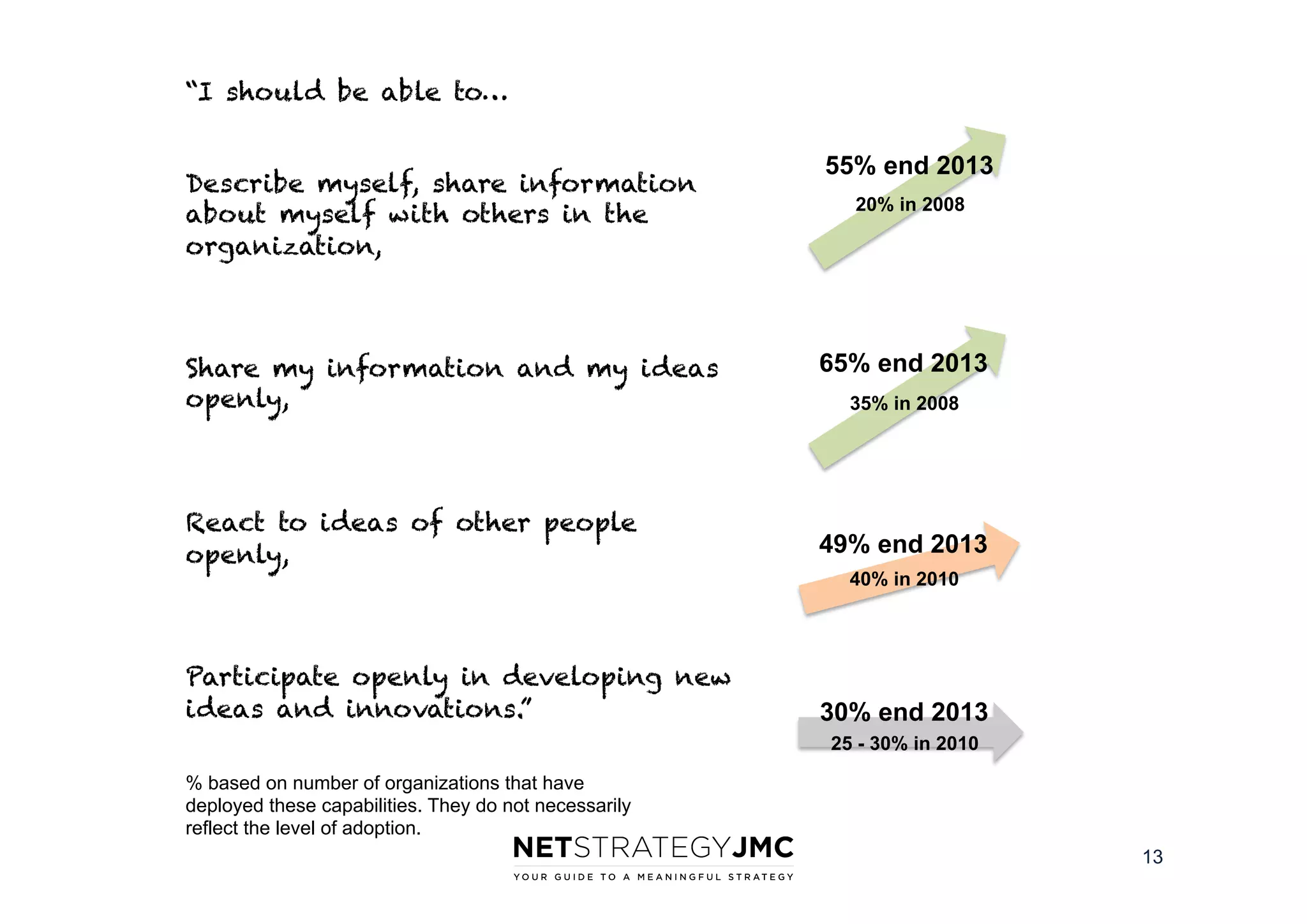
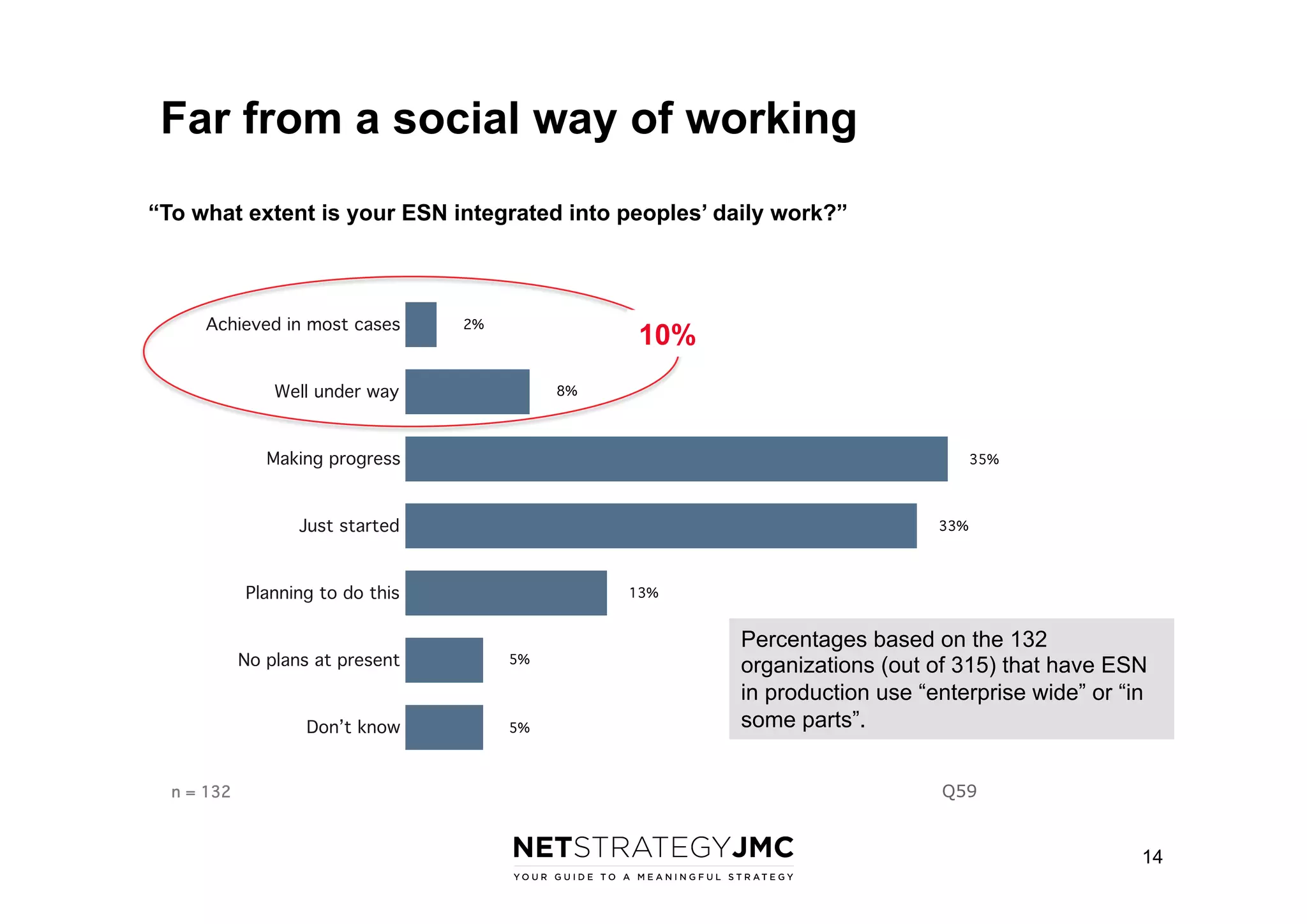
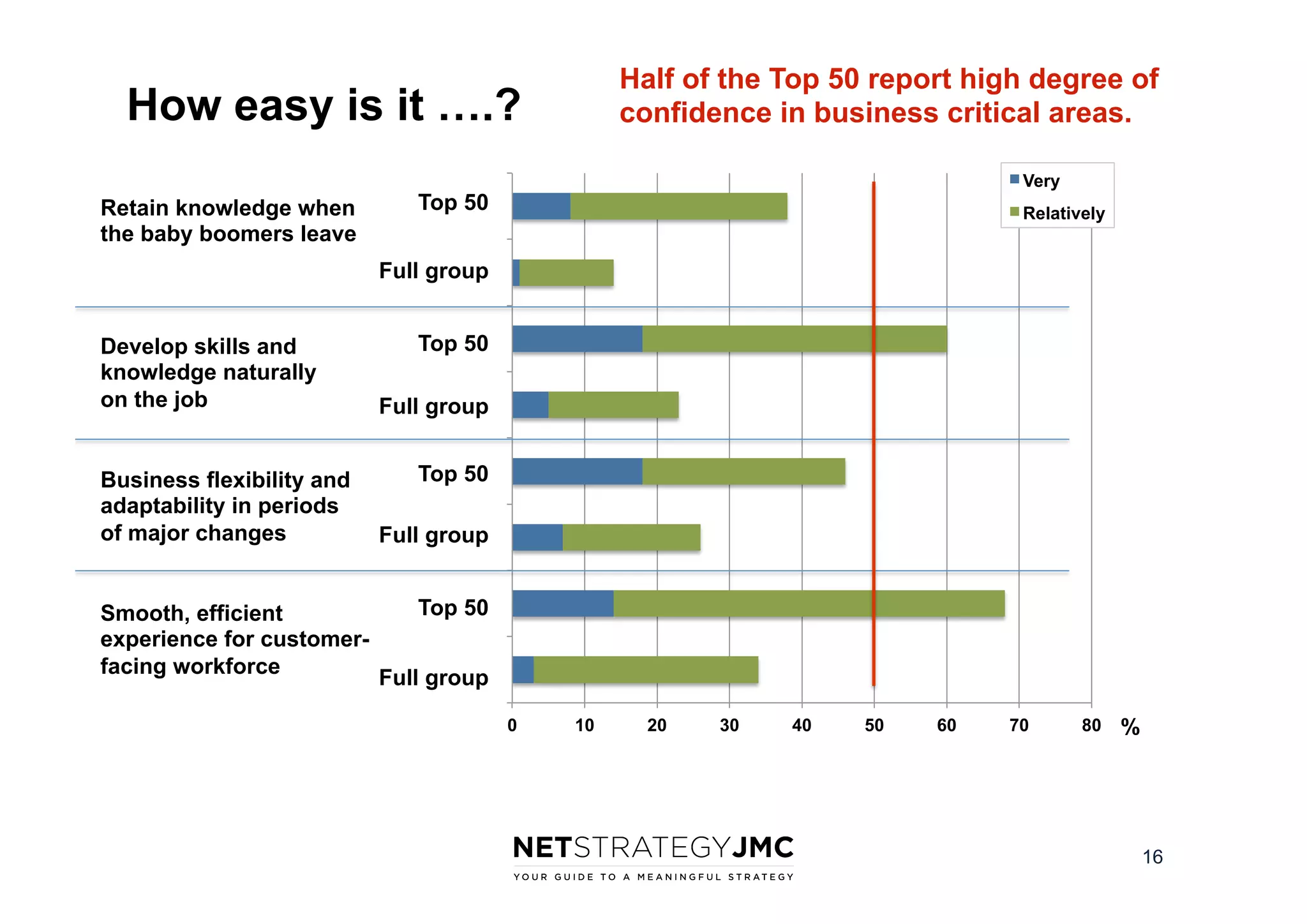
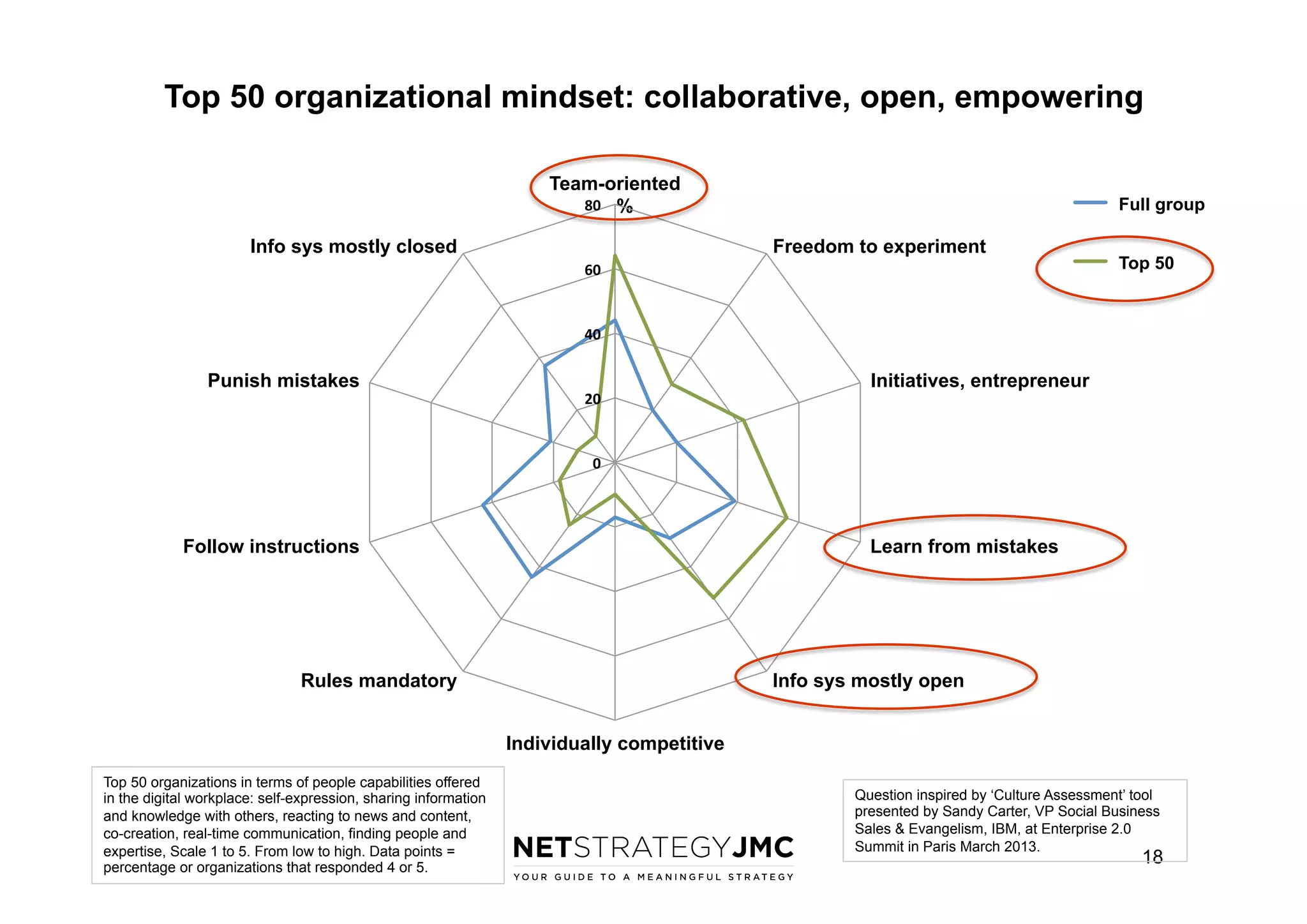
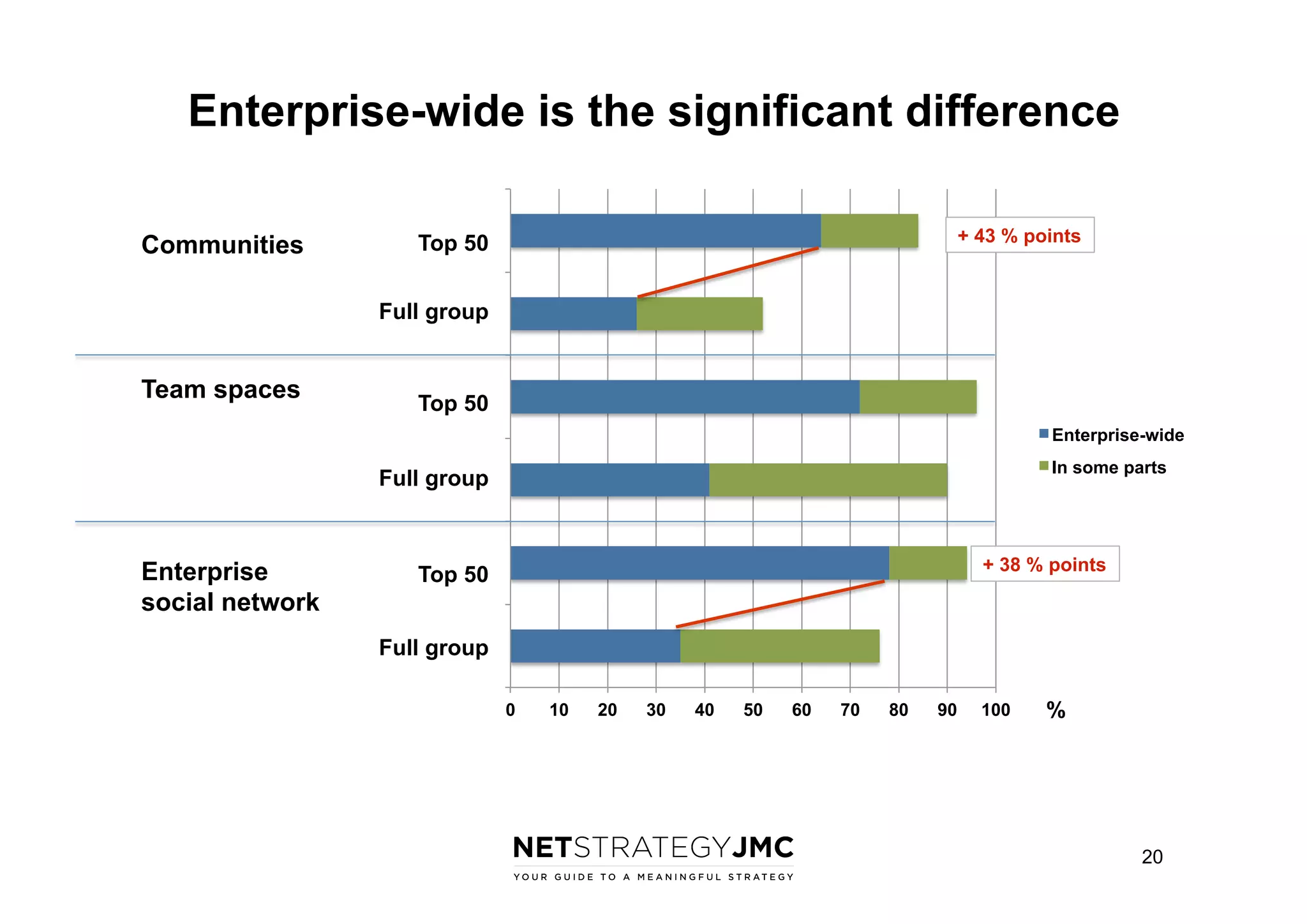
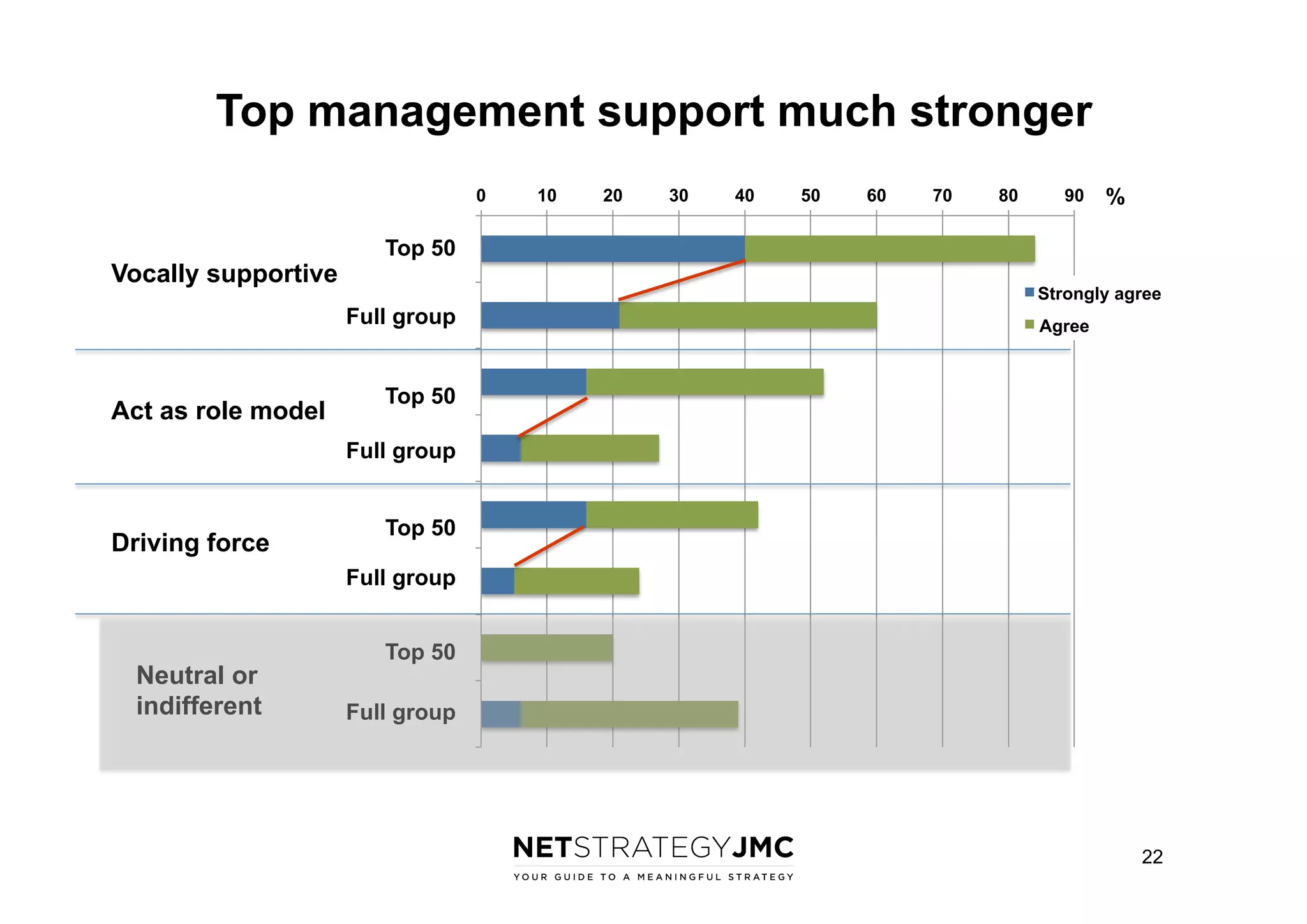
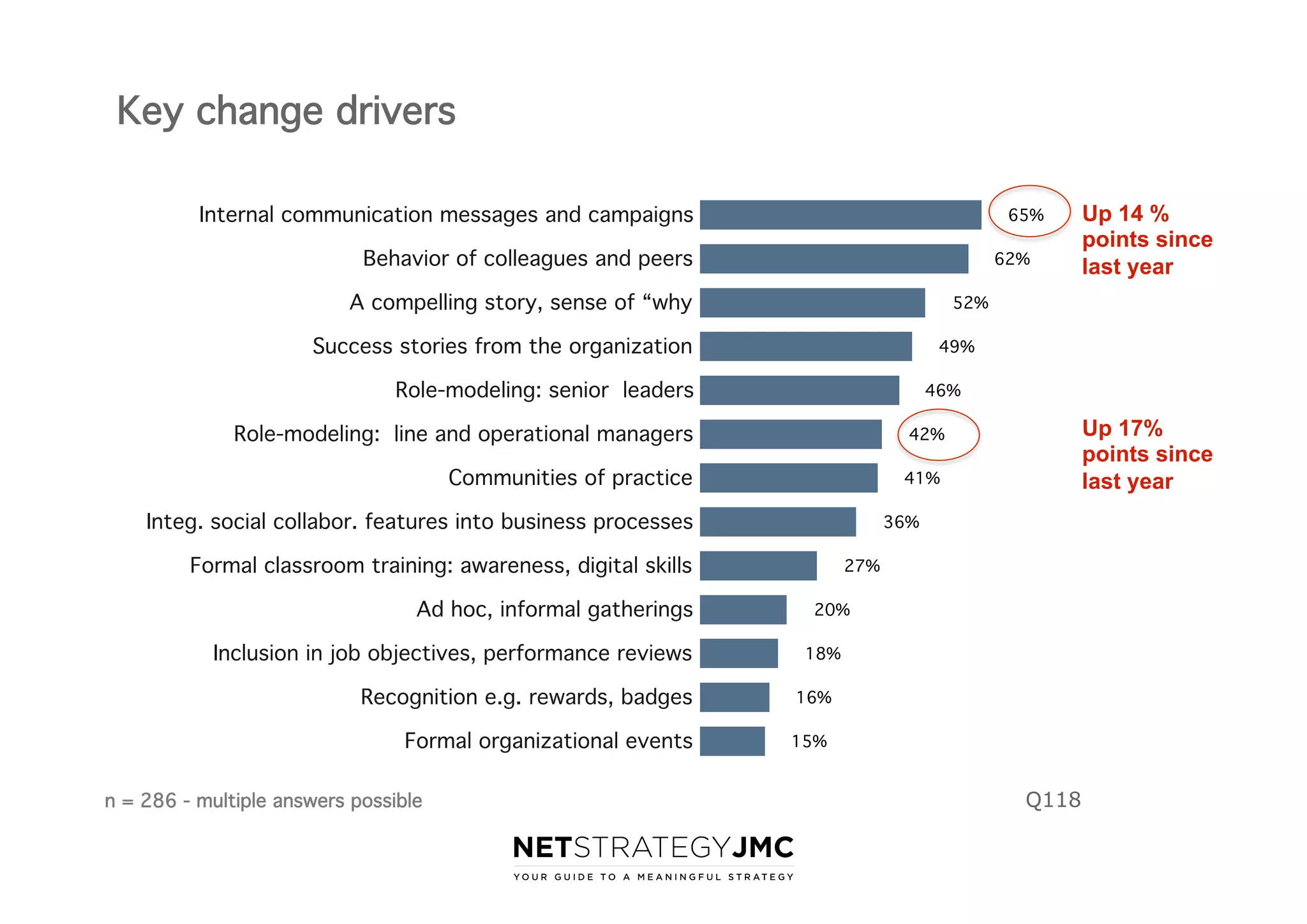
The document reports findings from the 2014 Digital Workplace Trends survey, which involved over 300 organizations and aimed to provide insights into current practices and the evolution of digital workplaces. It highlights key areas such as collaboration, mobile use cases, and the impact of social networks on business, noting that leadership and community engagement are vital for effective transformation. The study emphasizes that a digitally connected workforce can enhance efficiency and responsiveness to customer needs, positioning the digital workplace as a critical asset for modern organizations.