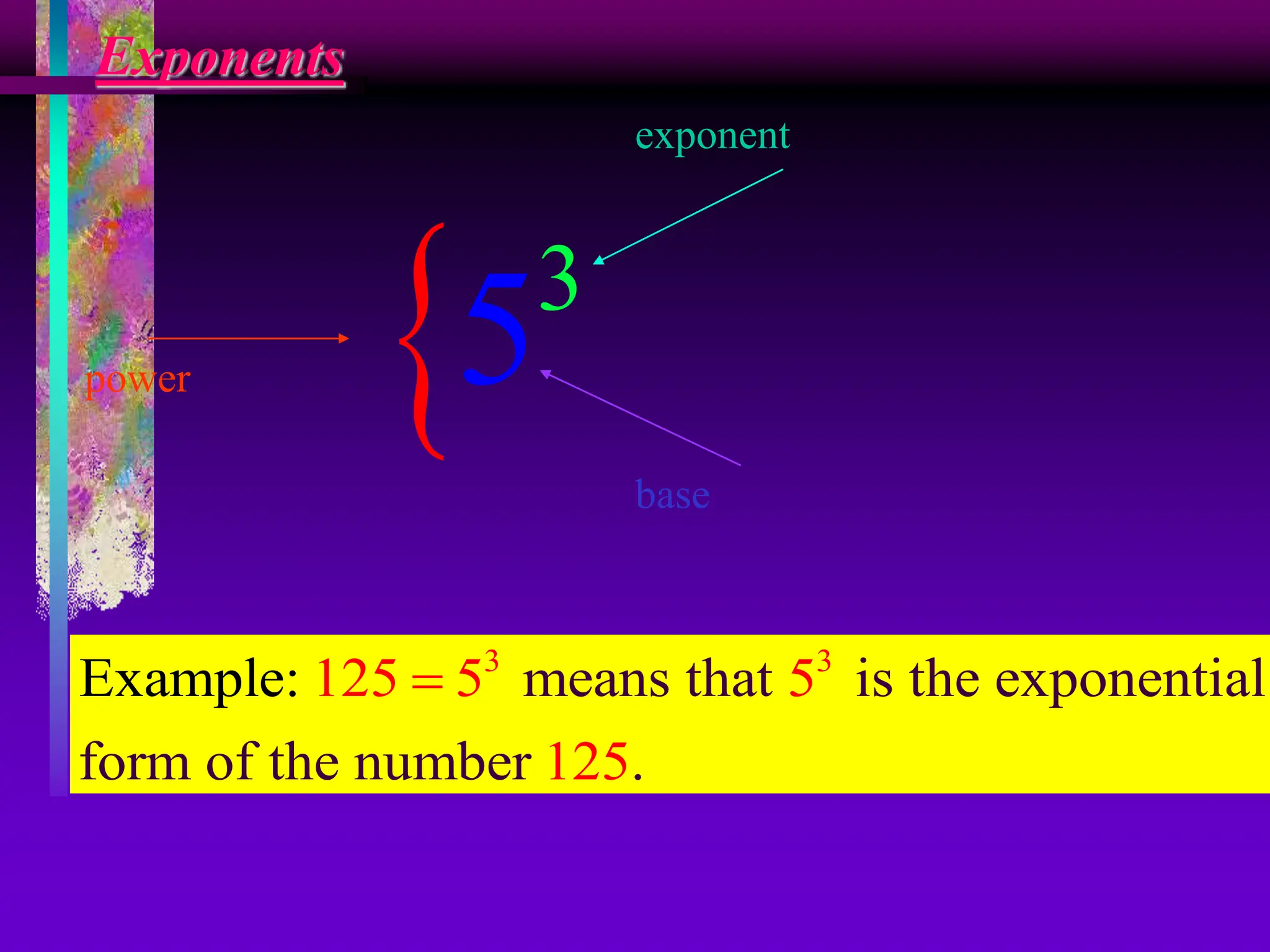
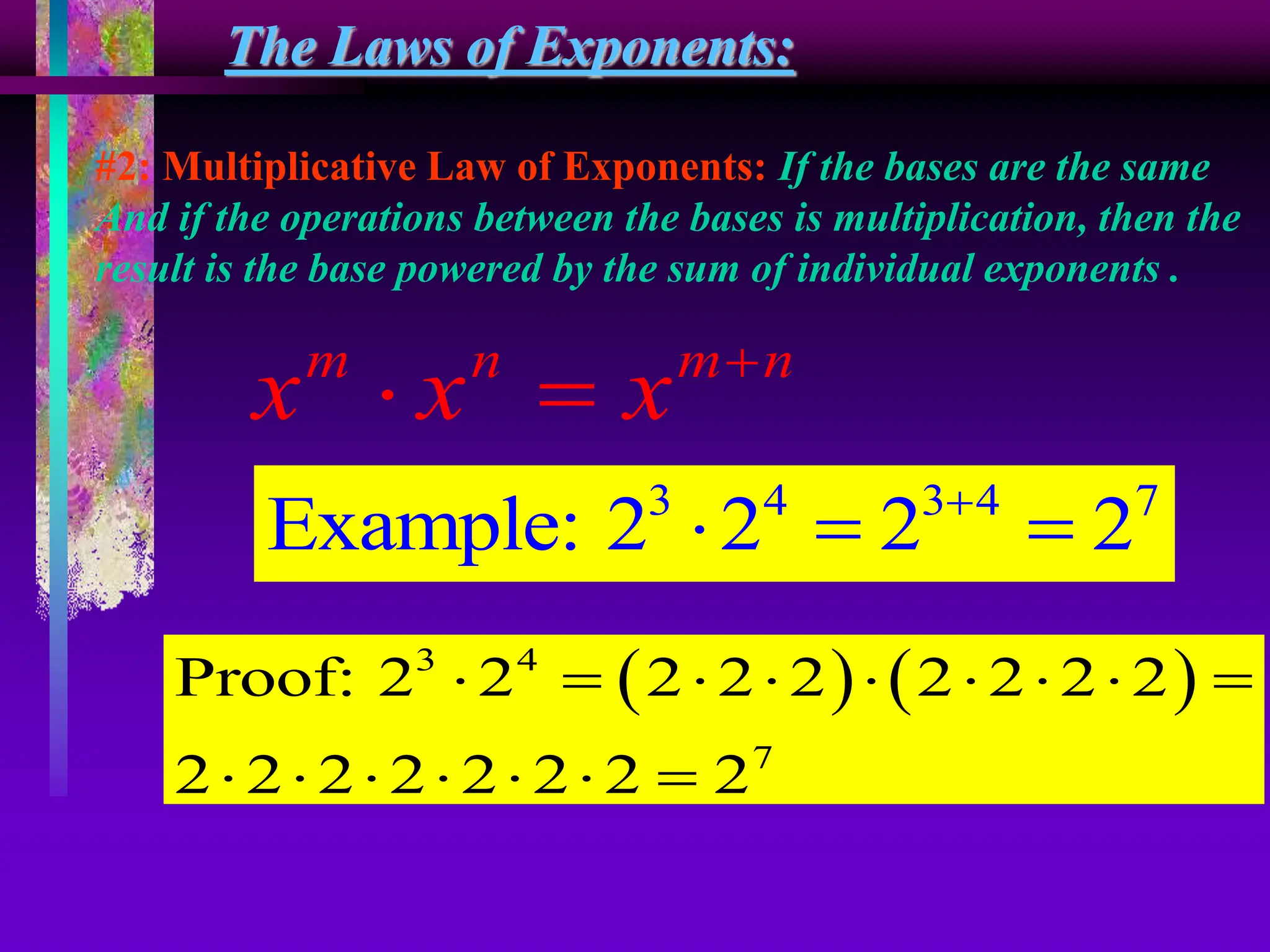
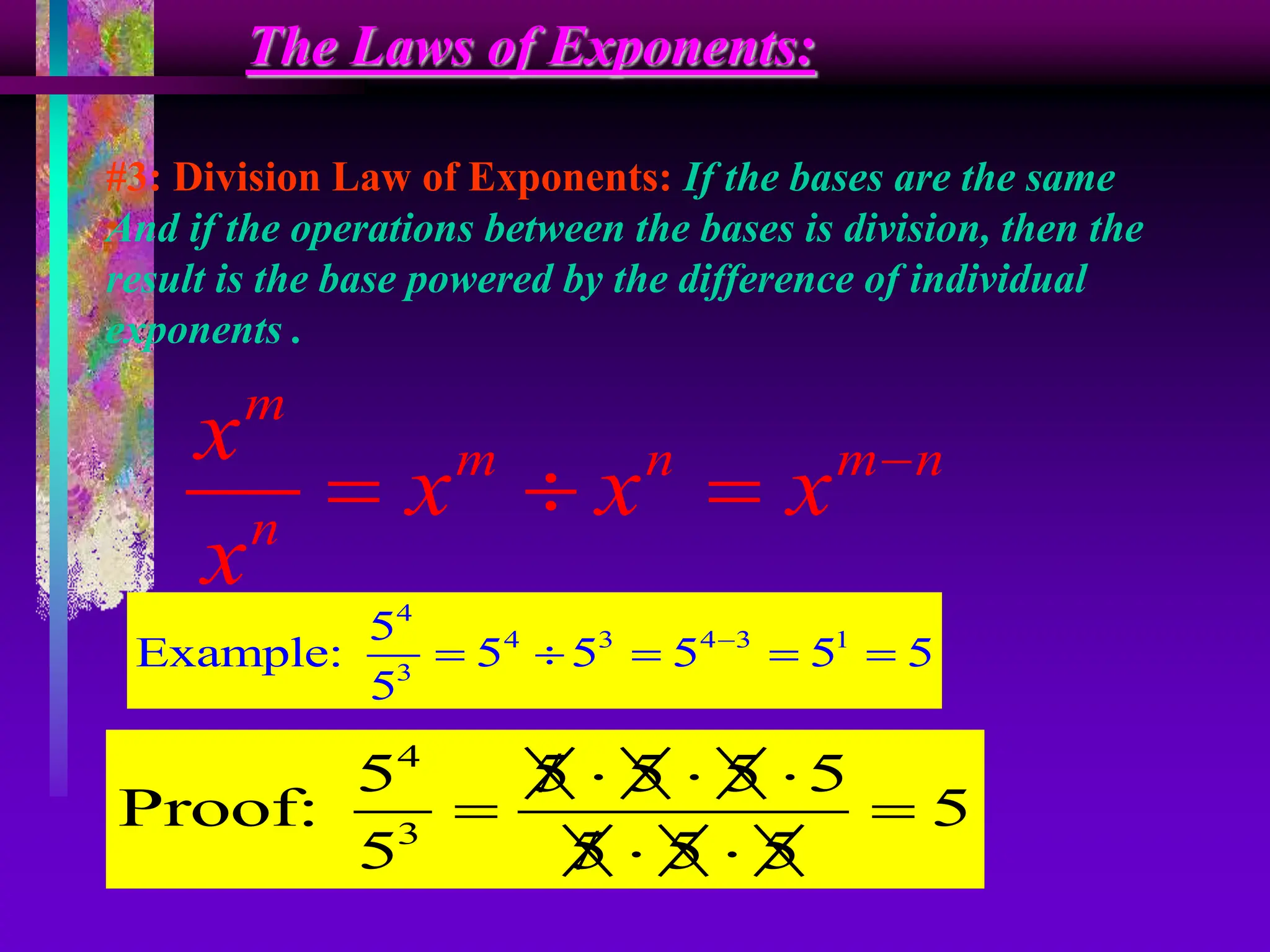
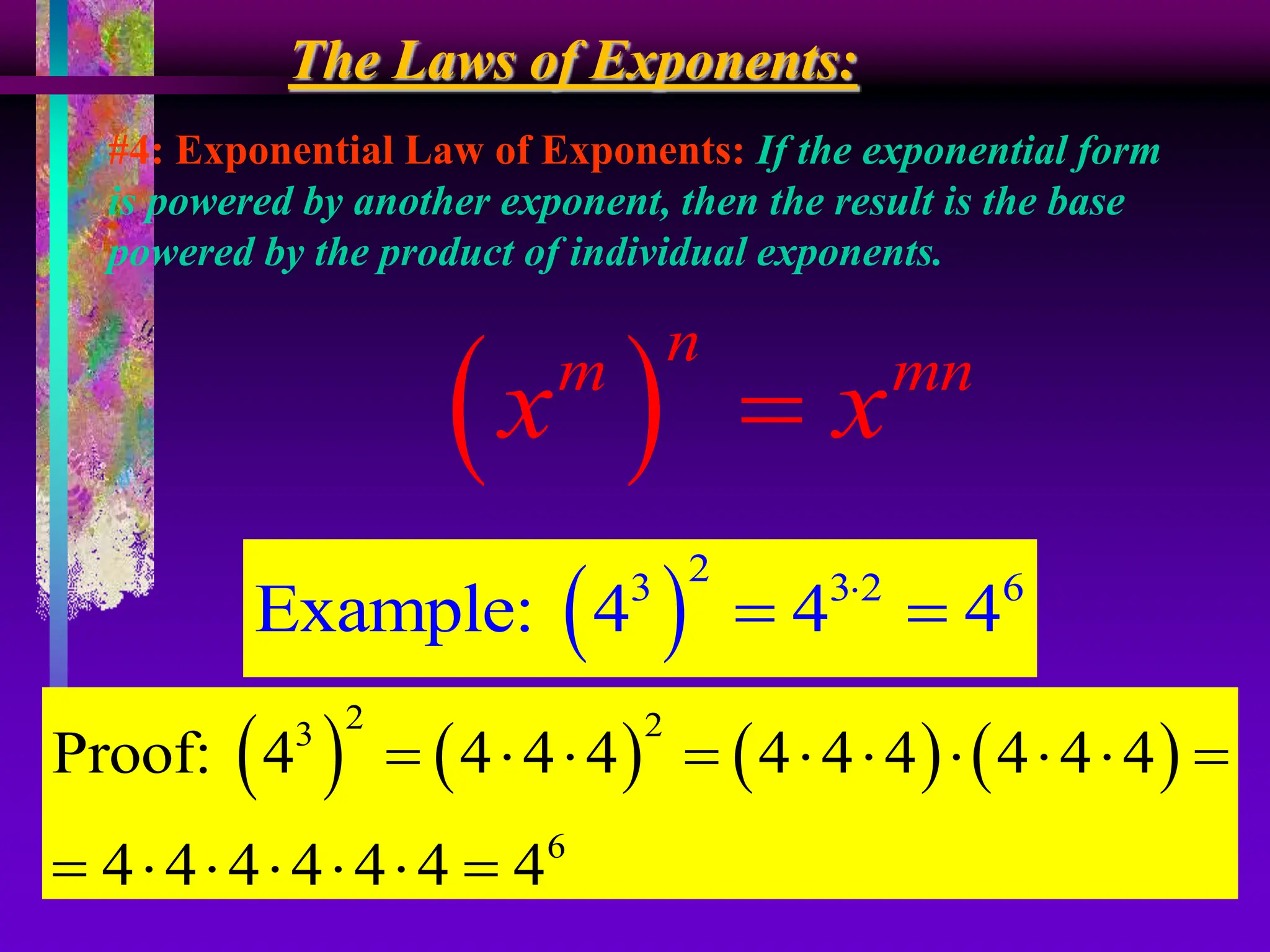
The document covers the concepts of exponents and powers, defining key terms such as base, exponent, and different forms of representing numbers. It elaborates on the laws of exponents, including multiplication, division, and zero exponent rules, along with examples illustrating these concepts. Additionally, it provides exercises for application and comparison of large and small numbers expressed in scientific notation.















![Find the value of n :
𝑎5
𝑎3 X [ a8 ] = (a n-6 )
Solution :
= a5-3 x a 8 = a n-6 [ am ÷ an = a m-n ]
= a2 x a8 = an-6
= a 10 = a n-6
= a 10 + 6
Ans. n = 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptexp-240630132202-306cbfda/75/ppt-exp-pptx-NCERT-based-Class-8-2024-28-2048.jpg)

