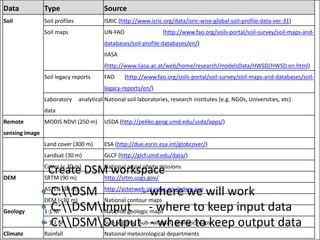
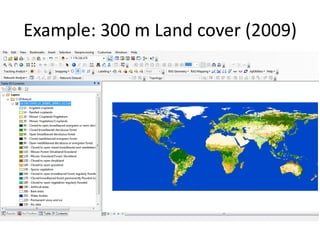
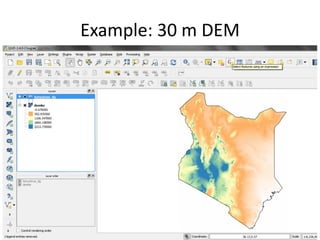
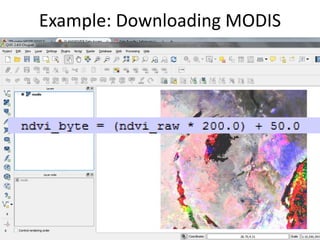
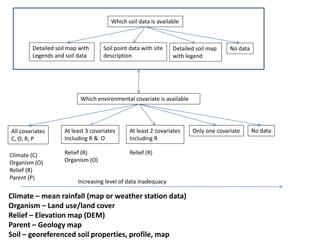
The document focuses on developing a database for Digital Soil Mapping (DSM), emphasizing user-friendly features and necessary software tools. It outlines steps for obtaining and documenting soil data from various sources, creating a workspace for DSM processes, and providing examples of data acquisition methods. Additionally, it includes guidance for building a geo-database, detailing the characteristics of the data that should be documented and reported.