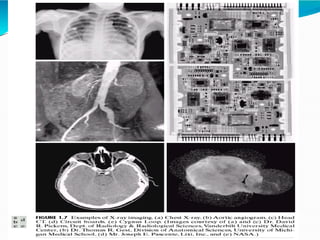
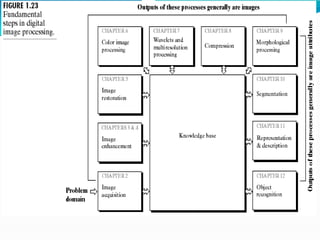
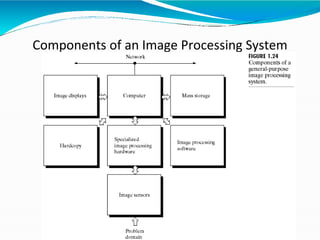
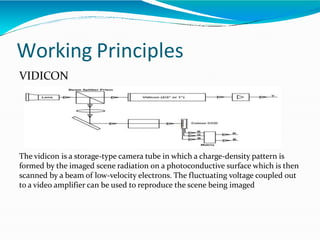
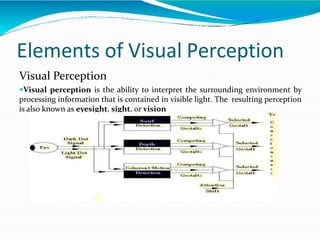
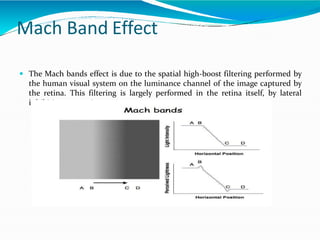
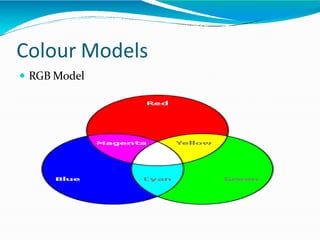
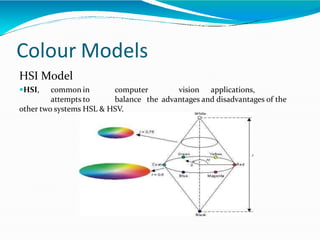
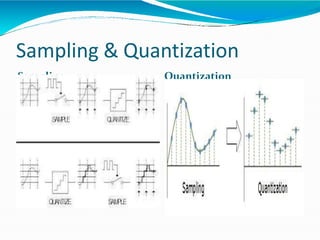
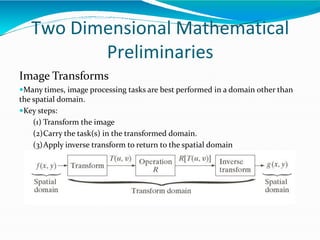
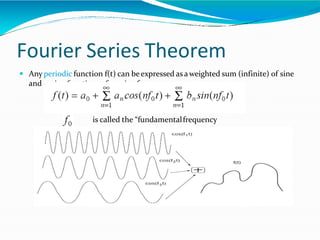
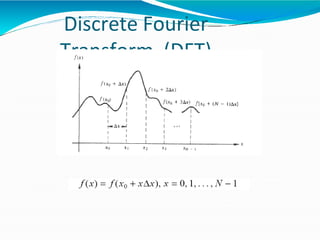
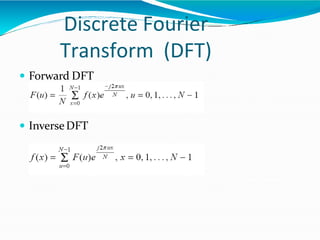
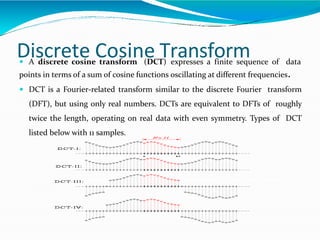
The document covers the fundamentals of digital image processing, including key components, applications, and mathematical principles involved in the field. It highlights the differences between digital and analog image processing, discusses visual perception, and explains key concepts like sampling and quantization, as well as color models such as RGB and HSI. Additionally, the uses of digital image processing in various industries, such as medical imaging and machine vision, are summarized.