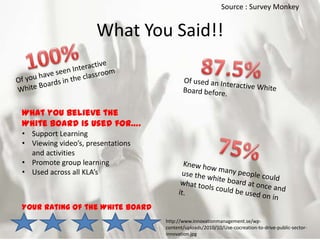
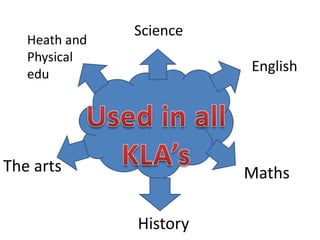
The interactive whiteboard takes the traditional classroom whiteboard and integrates information and communication technologies. It has the potential to both enhance and replace some of the teacher's role in exciting students about learning. The document discusses the progression from blackboards to interactive whiteboards and whether this represents a positive step for education. It also provides examples of how interactive whiteboards can be used to support learning across different subject areas through viewing videos, presentations, group work and internet research. Legal and ethical considerations around issues like plagiarism, privacy and appropriate student use are also addressed.