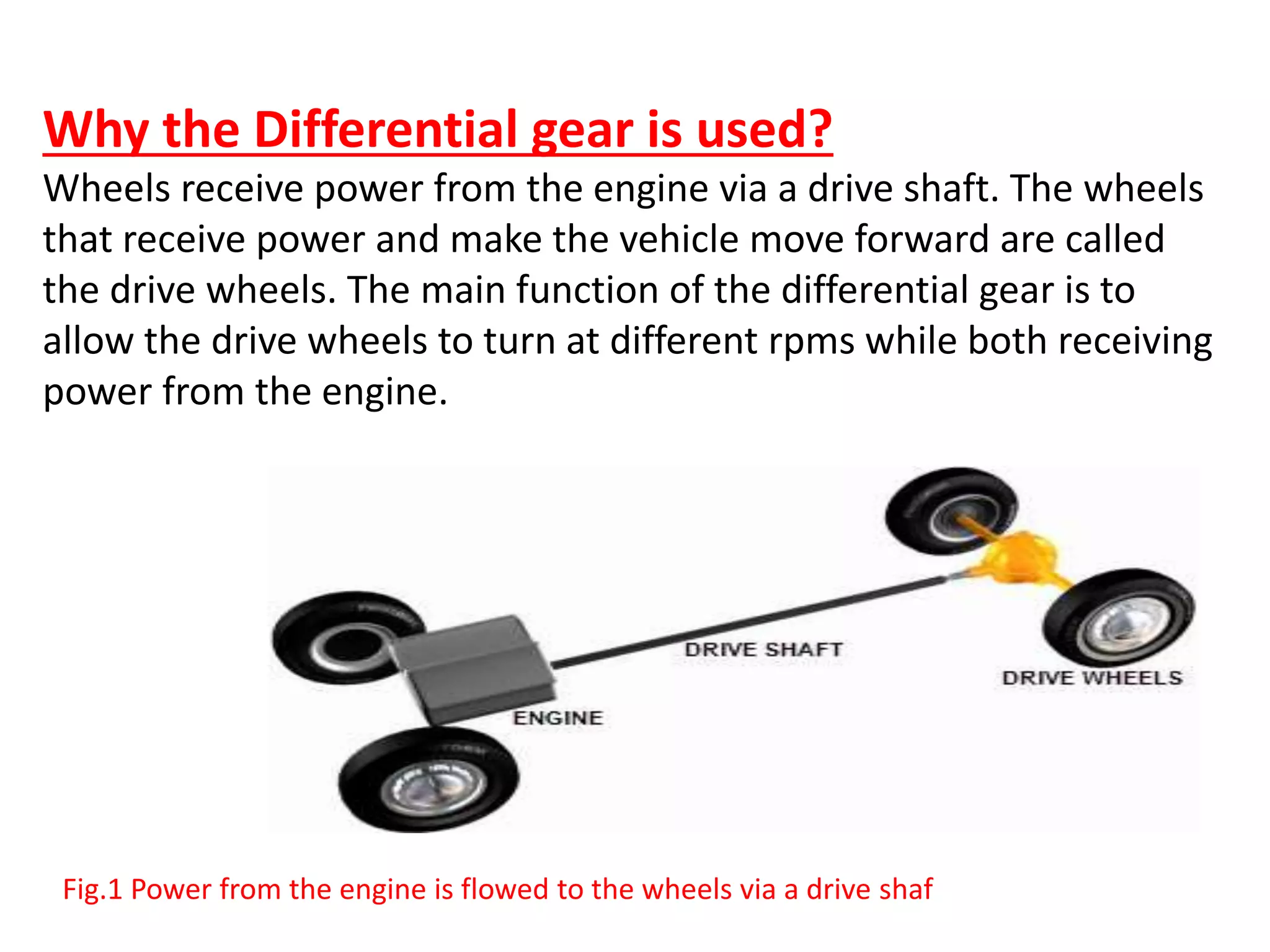
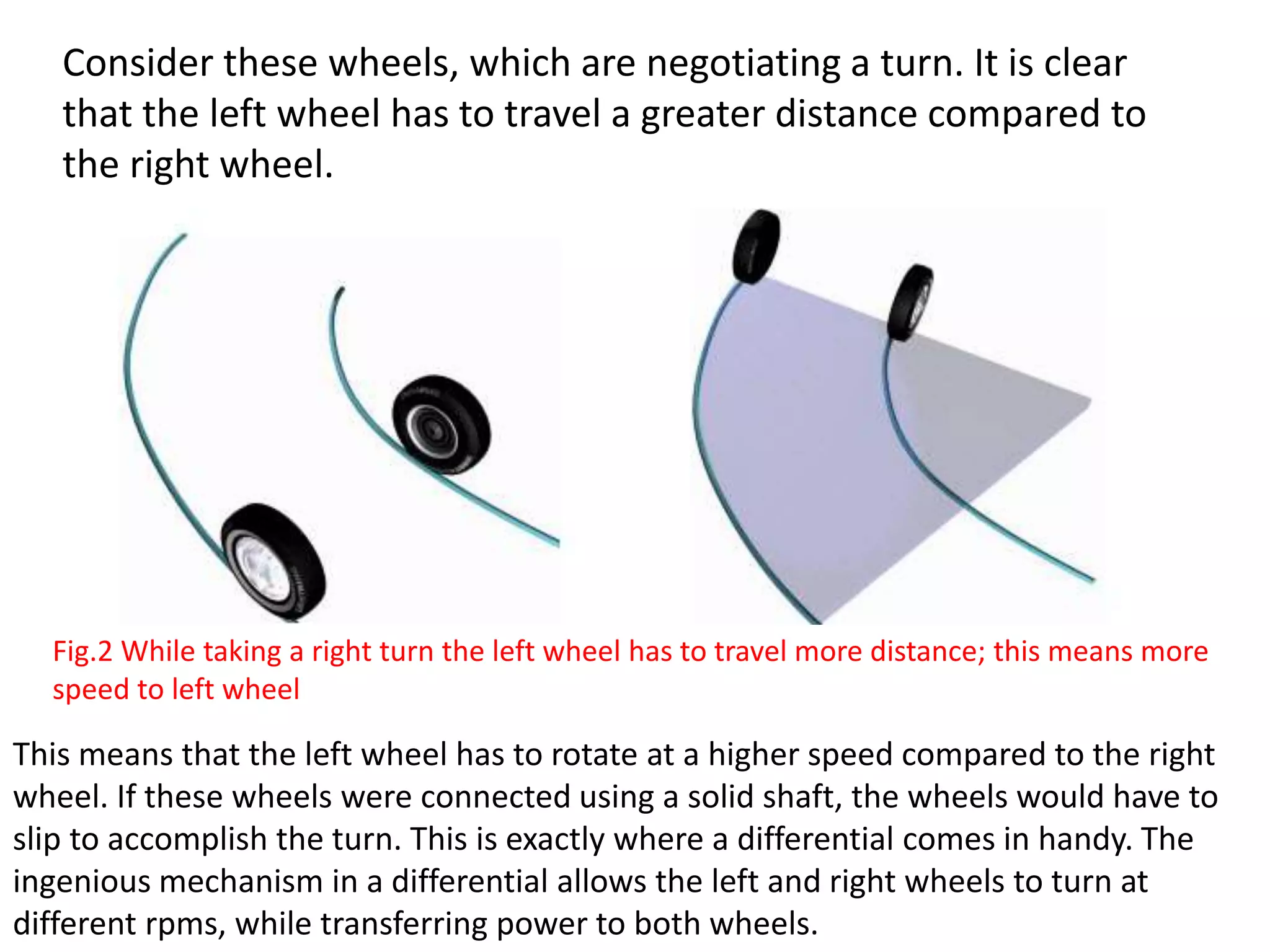
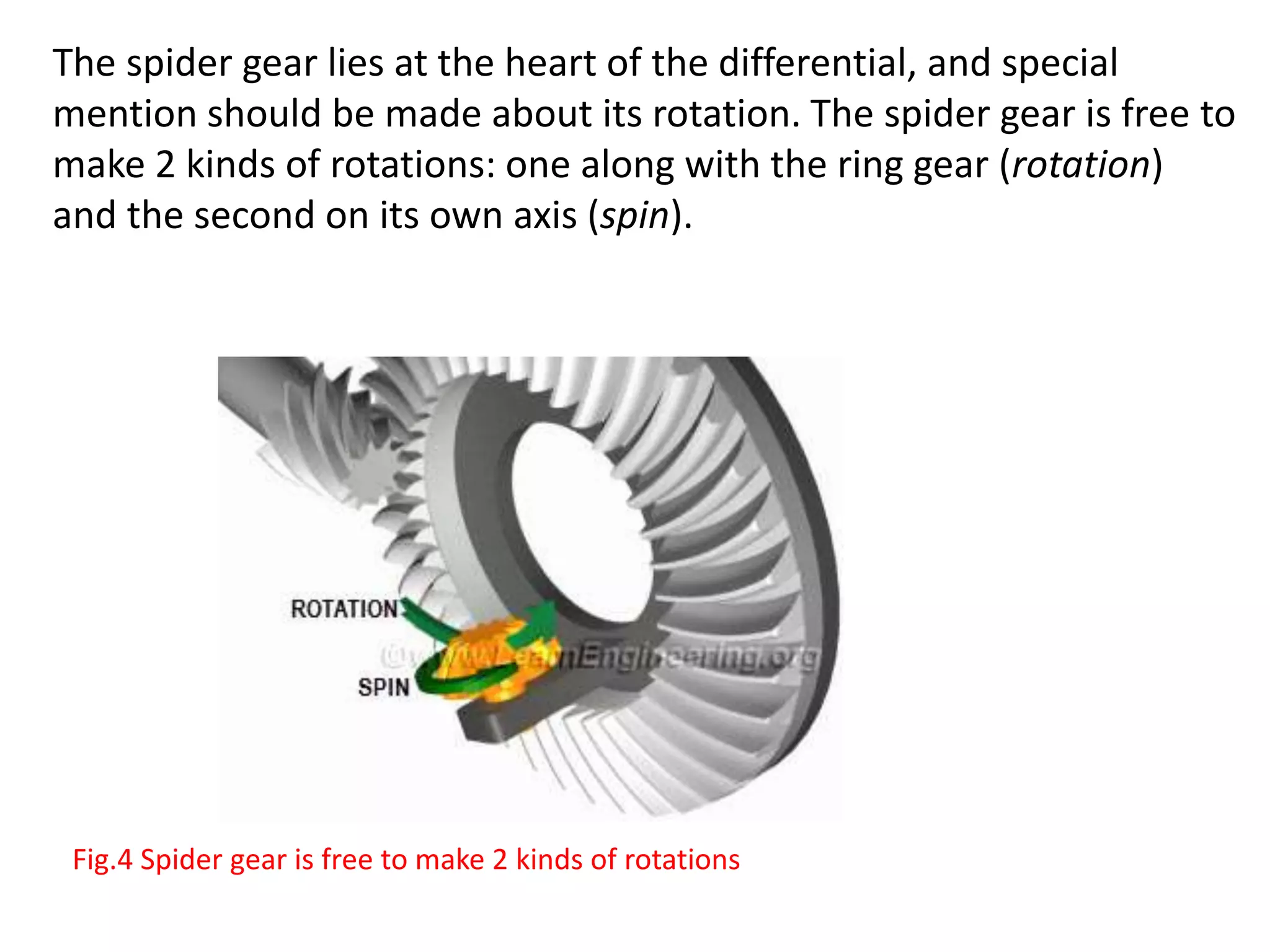
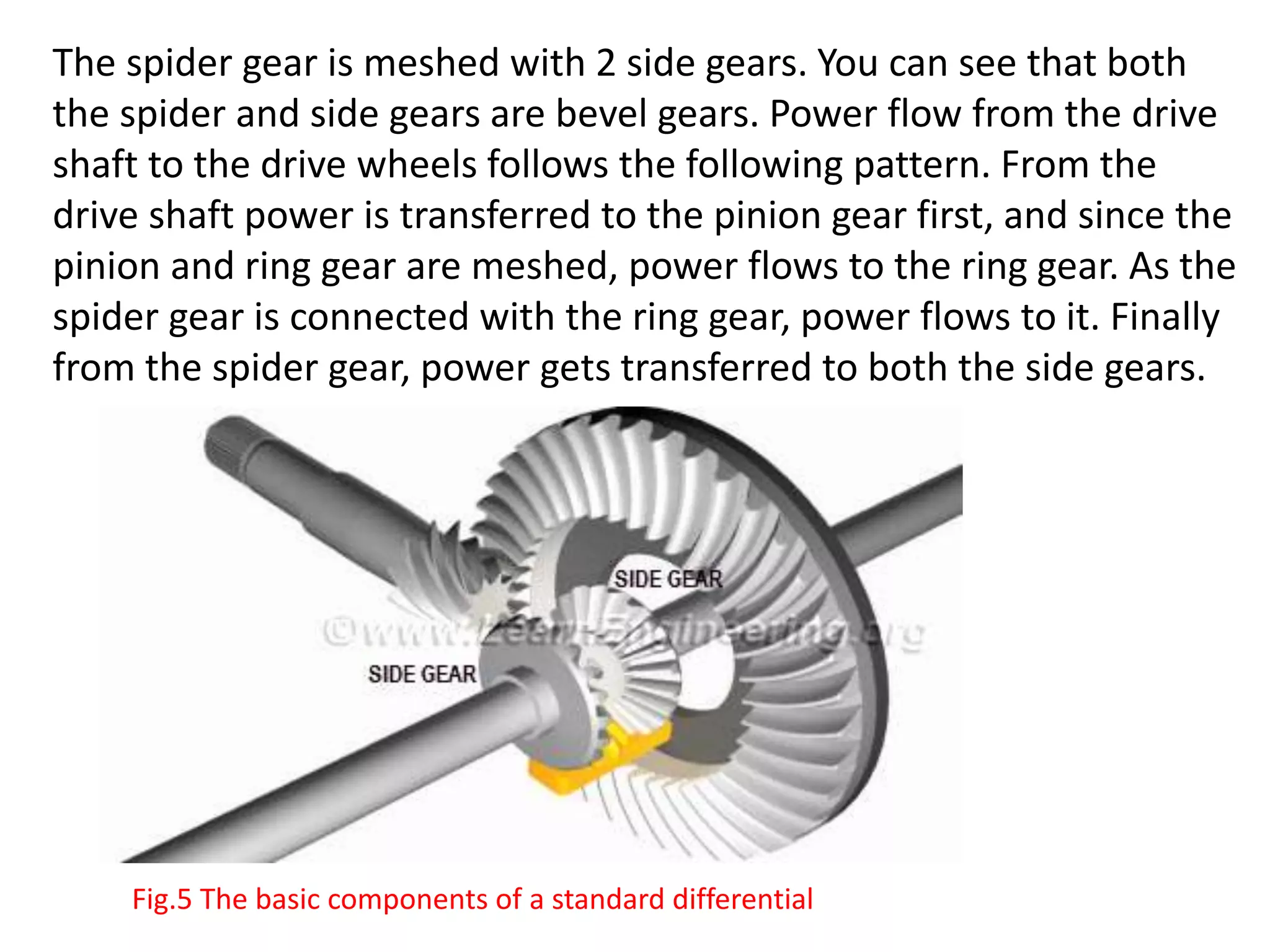
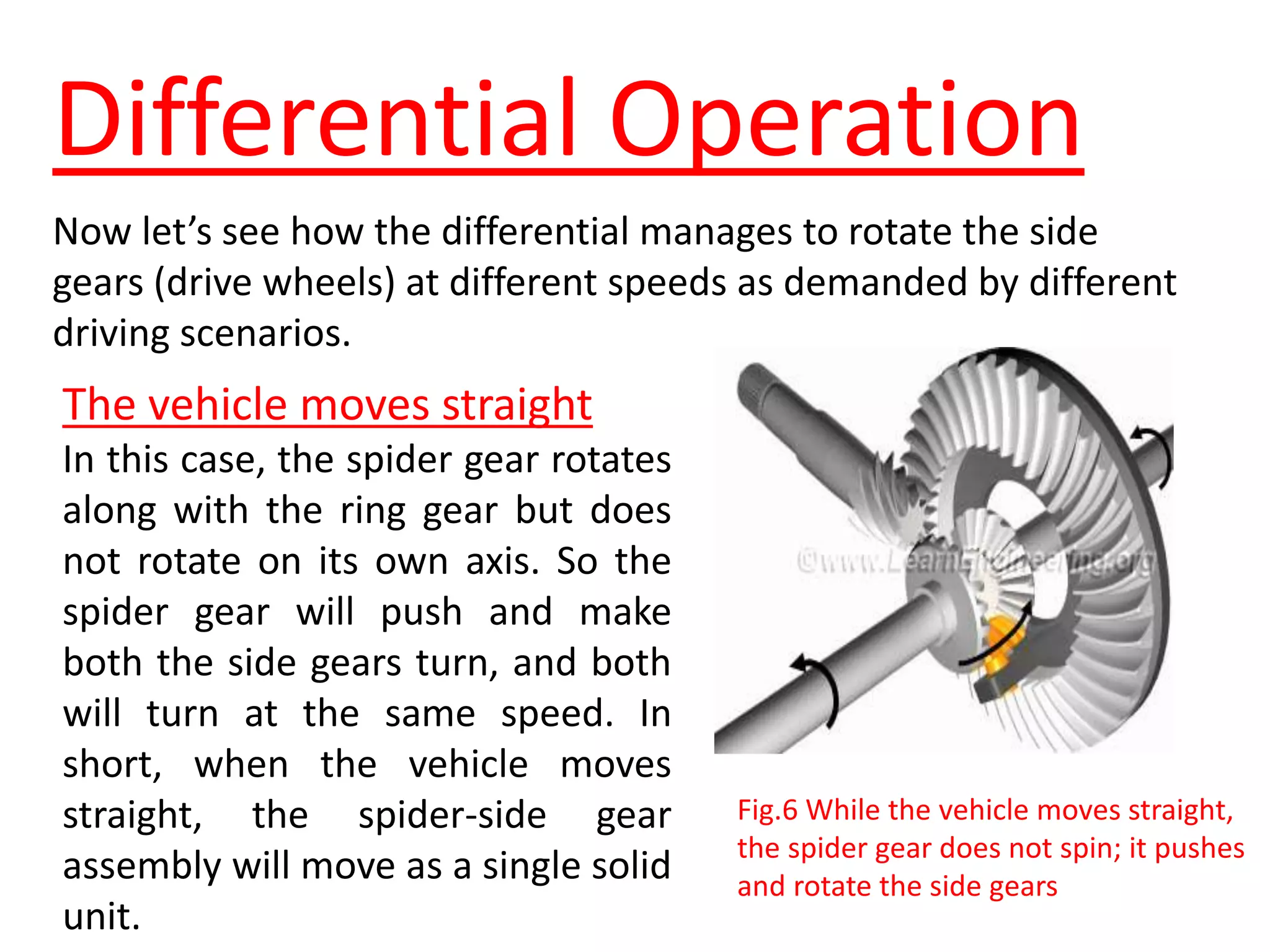
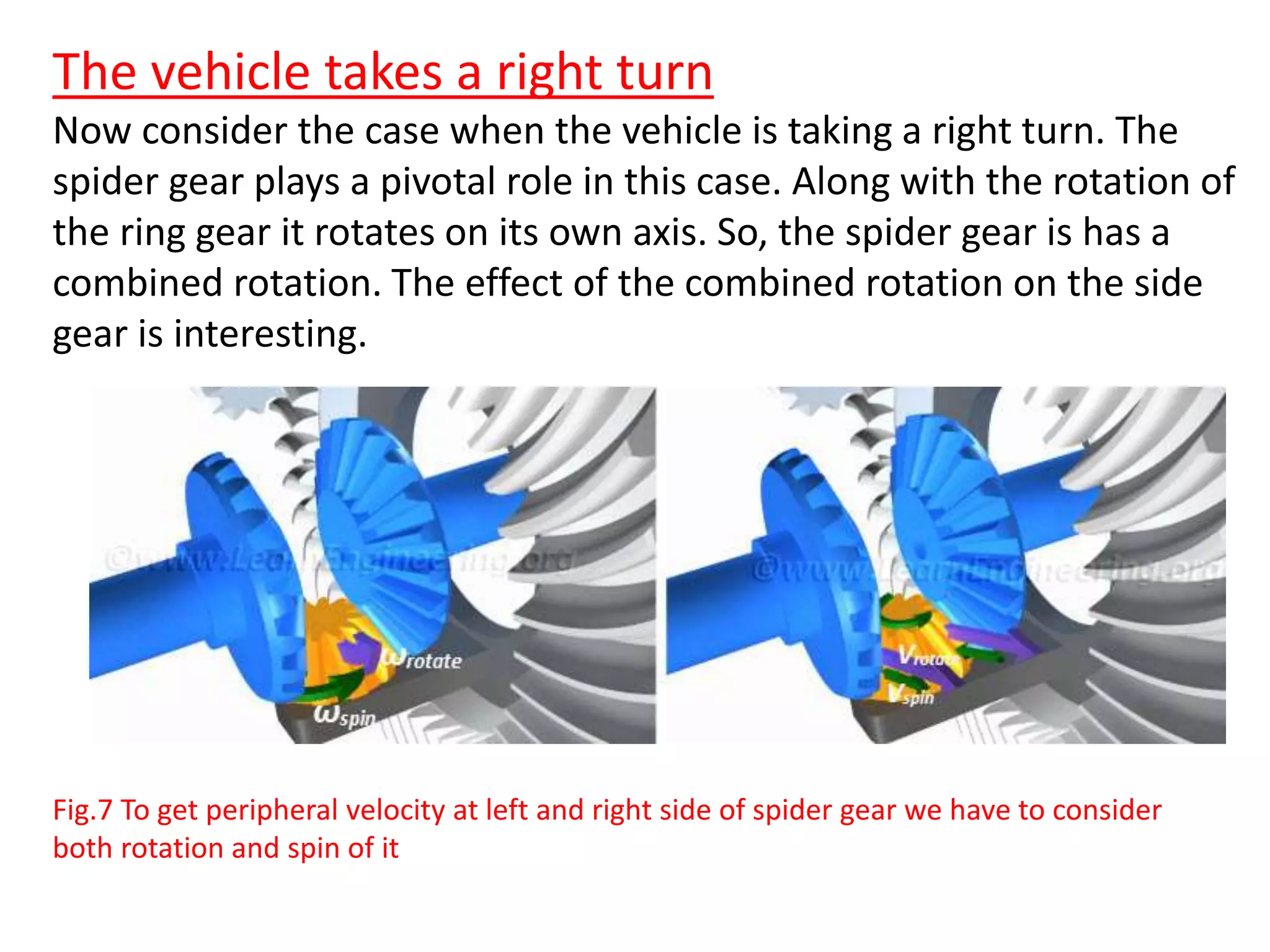
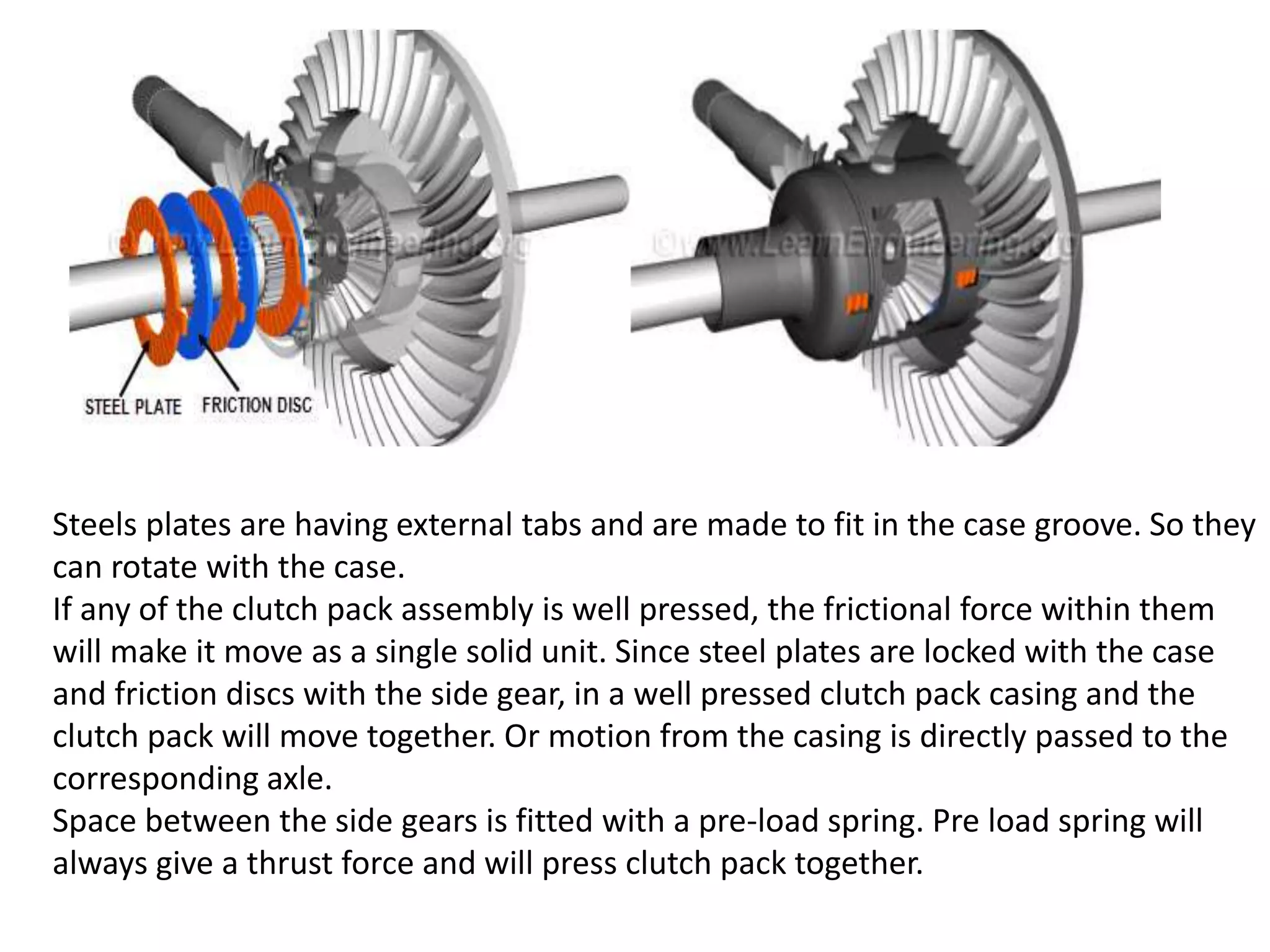
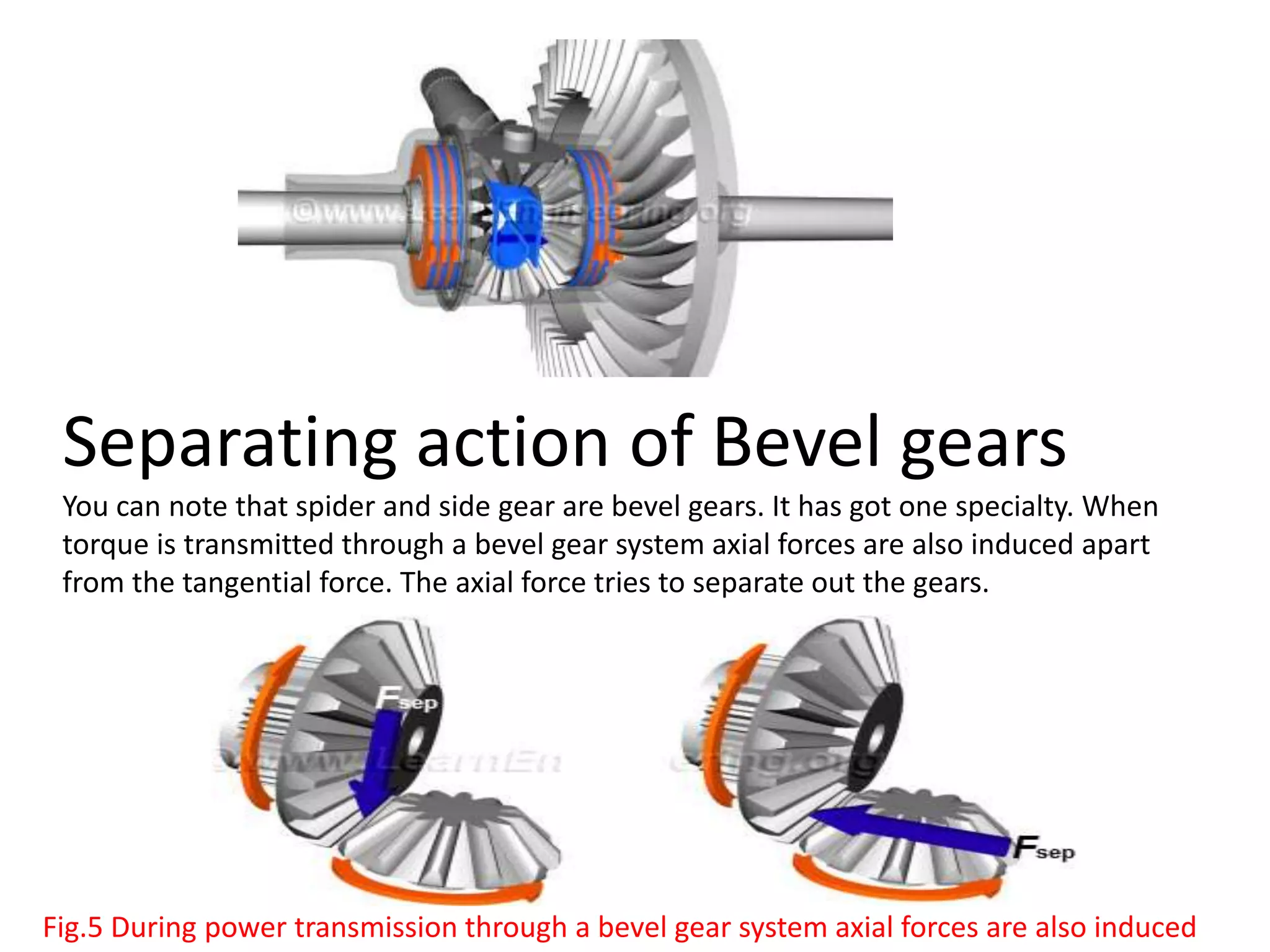
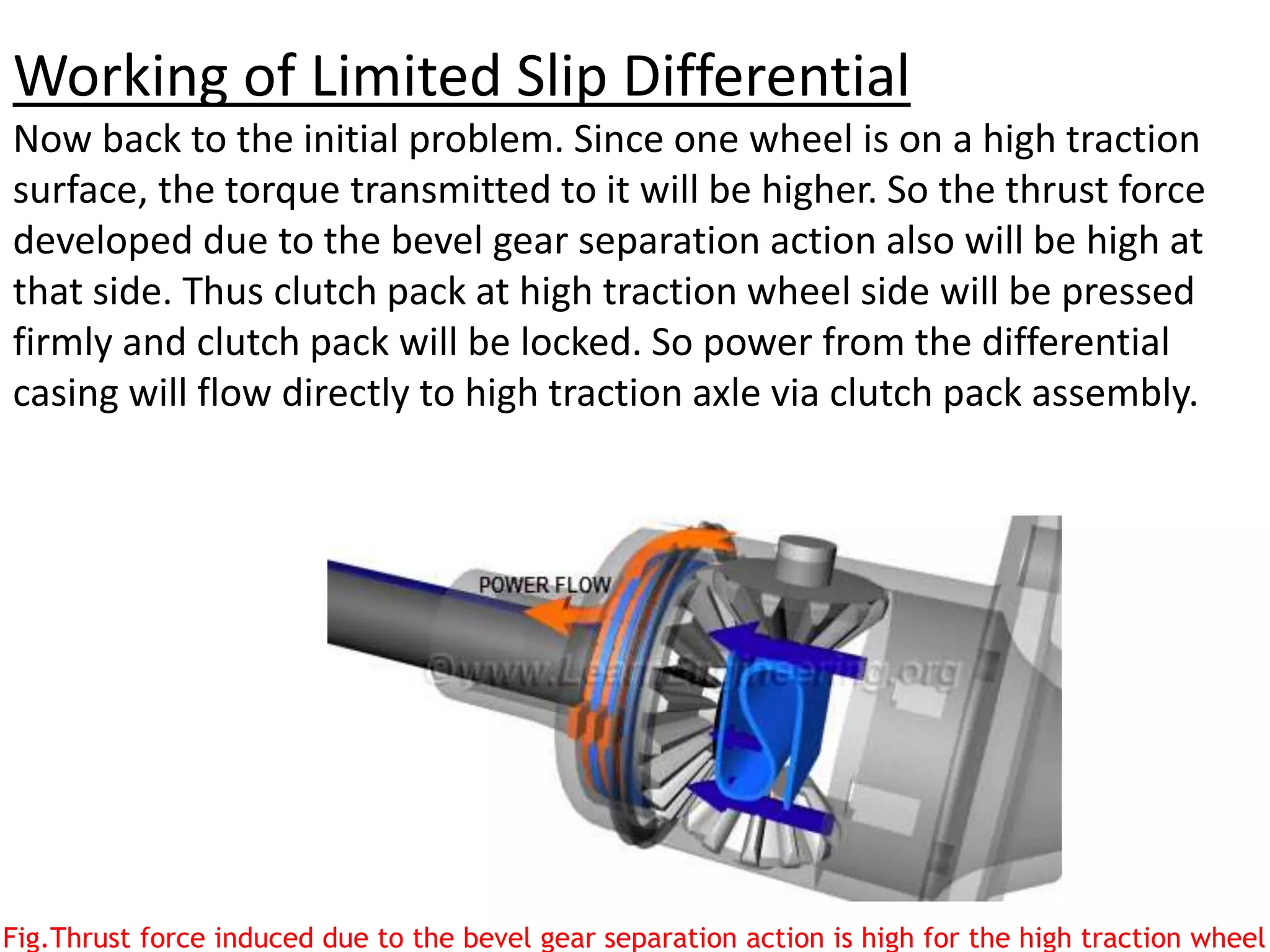
The document explains the function and mechanics of differential gears, which enable drive wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns while receiving power from the engine. It details the operation of both standard differentials and limited slip differentials (LSDs), emphasizing how LSDs address traction issues by managing power distribution to ensure better performance on varying surfaces. Additionally, it describes the components and operational principles that facilitate this function, including the roles of spider gears, friction discs, and the effects of torque transmission in bevel gear systems.