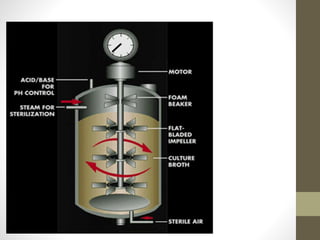
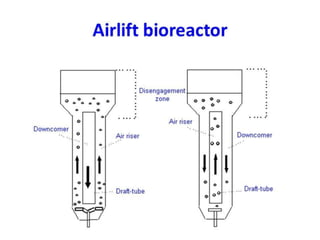
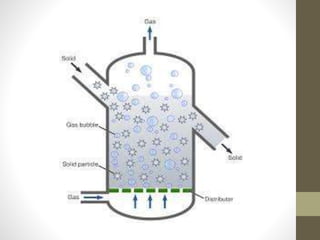
This document discusses four main types of bioreactors: stirred tank bioreactors, air lift bioreactors, bubble column bioreactors, and fluidized bed bioreactors. Stirred tank bioreactors can carefully control temperature, pH, oxygen, and nutrients using mechanical agitation. Air lift bioreactors are well-suited for large-scale plant cell cultivation using compressed air for aeration and mixing without moving parts. Bubble column bioreactors are simple cylindrical vessels aerated from below, providing high heat and mass transfer without mechanical energy input. Fluidized bed bioreactors are similar to bubble columns but have an expanded top to reduce fluid velocity and retain solids while liquid exits.