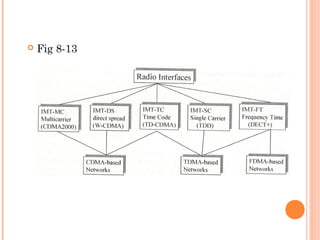
Cellular networks have evolved from 0G to 5G over several generations of technology. 1G networks in the early 1980s used analog transmission for primarily voice calls. 2G digital networks in the late 1980s enabled services like text messages. 3G networks in the 2000s supported broadband multimedia with speeds up to 2Mbps. 4G networks since 2010 provide faster "anytime, anywhere" services using IP. Research into 5G beyond 2020 aims for speeds over 10Gbps and connectivity of billions of devices. Each generation brought major improvements in speed and capabilities.