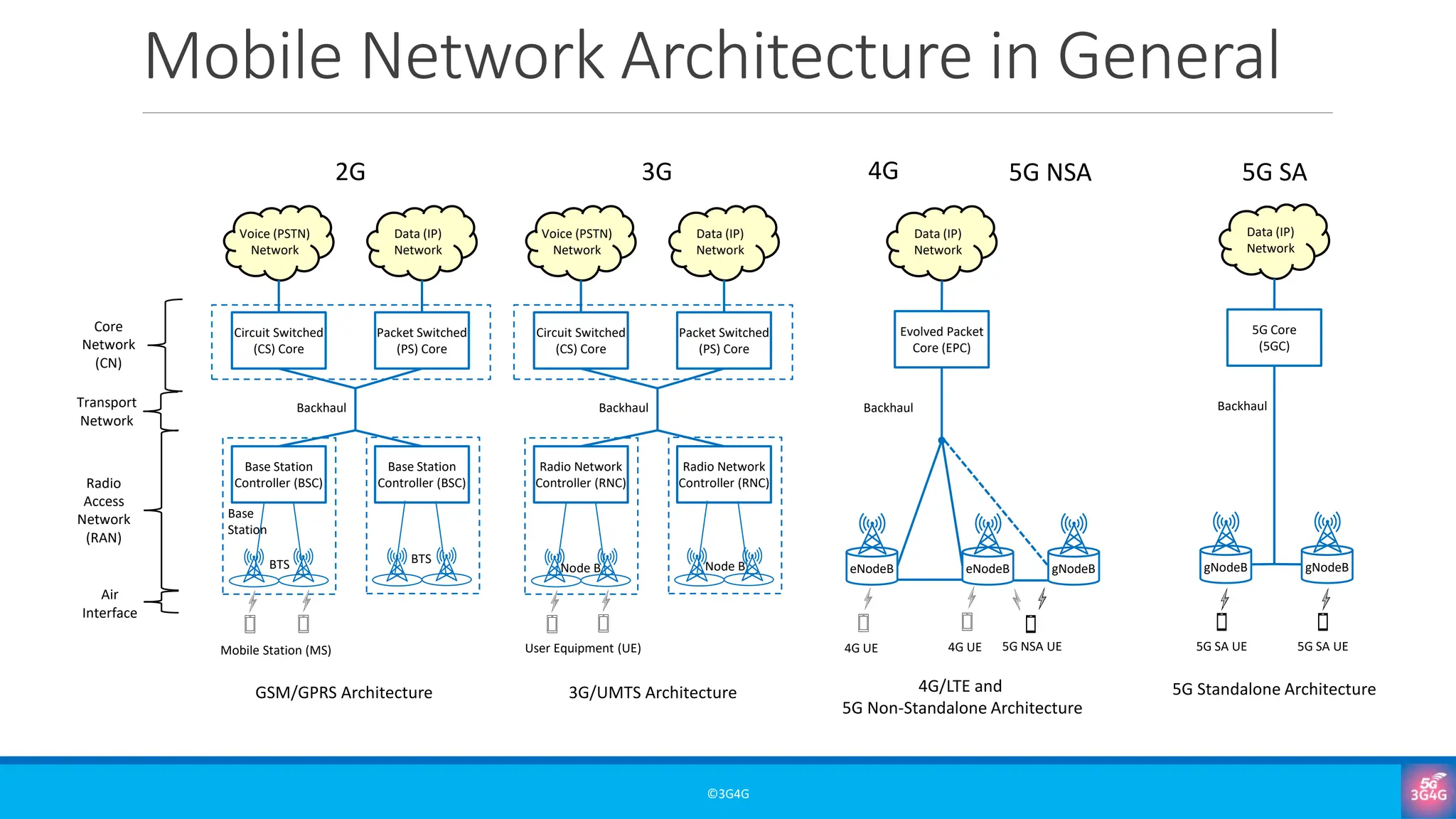
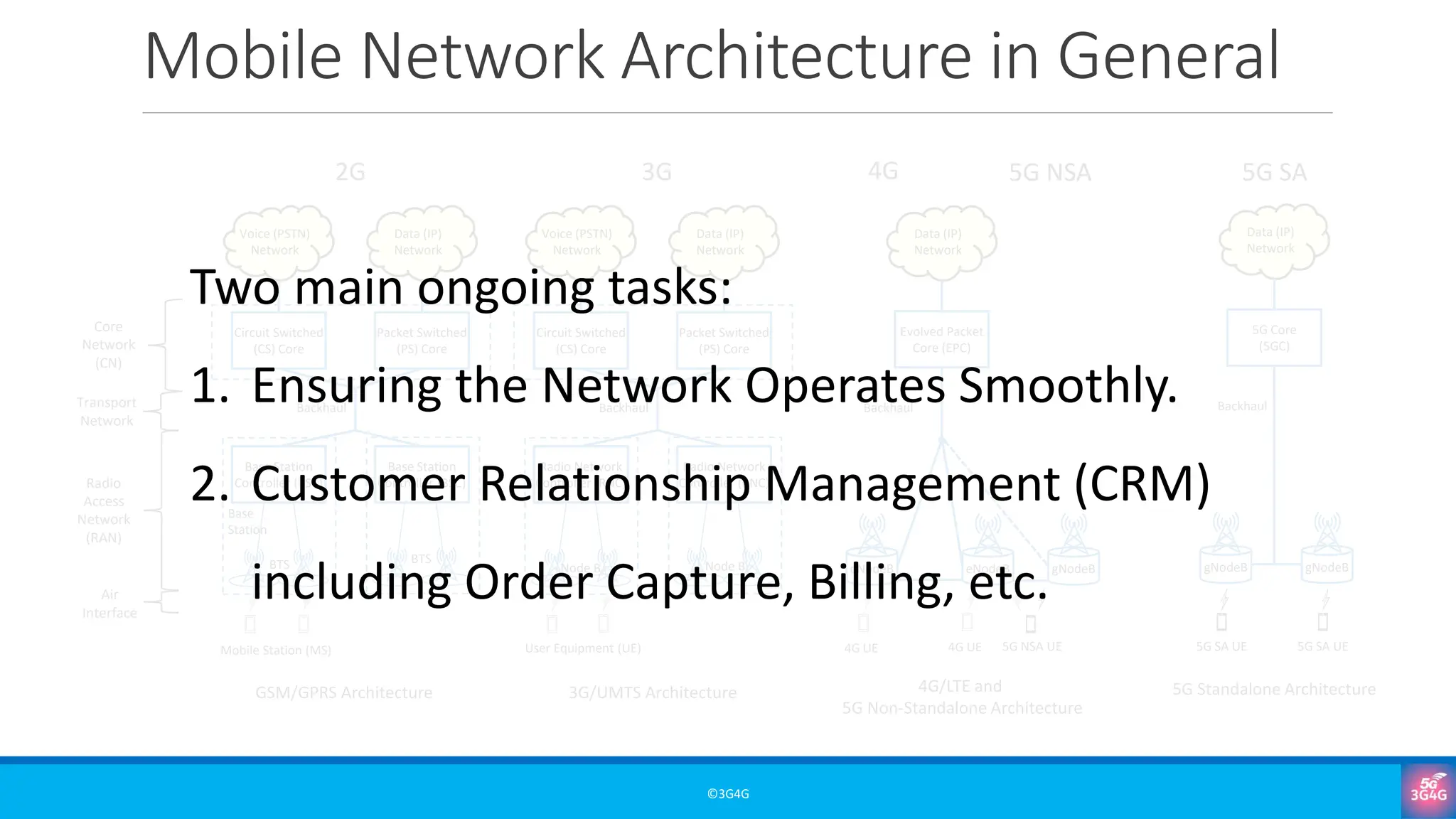
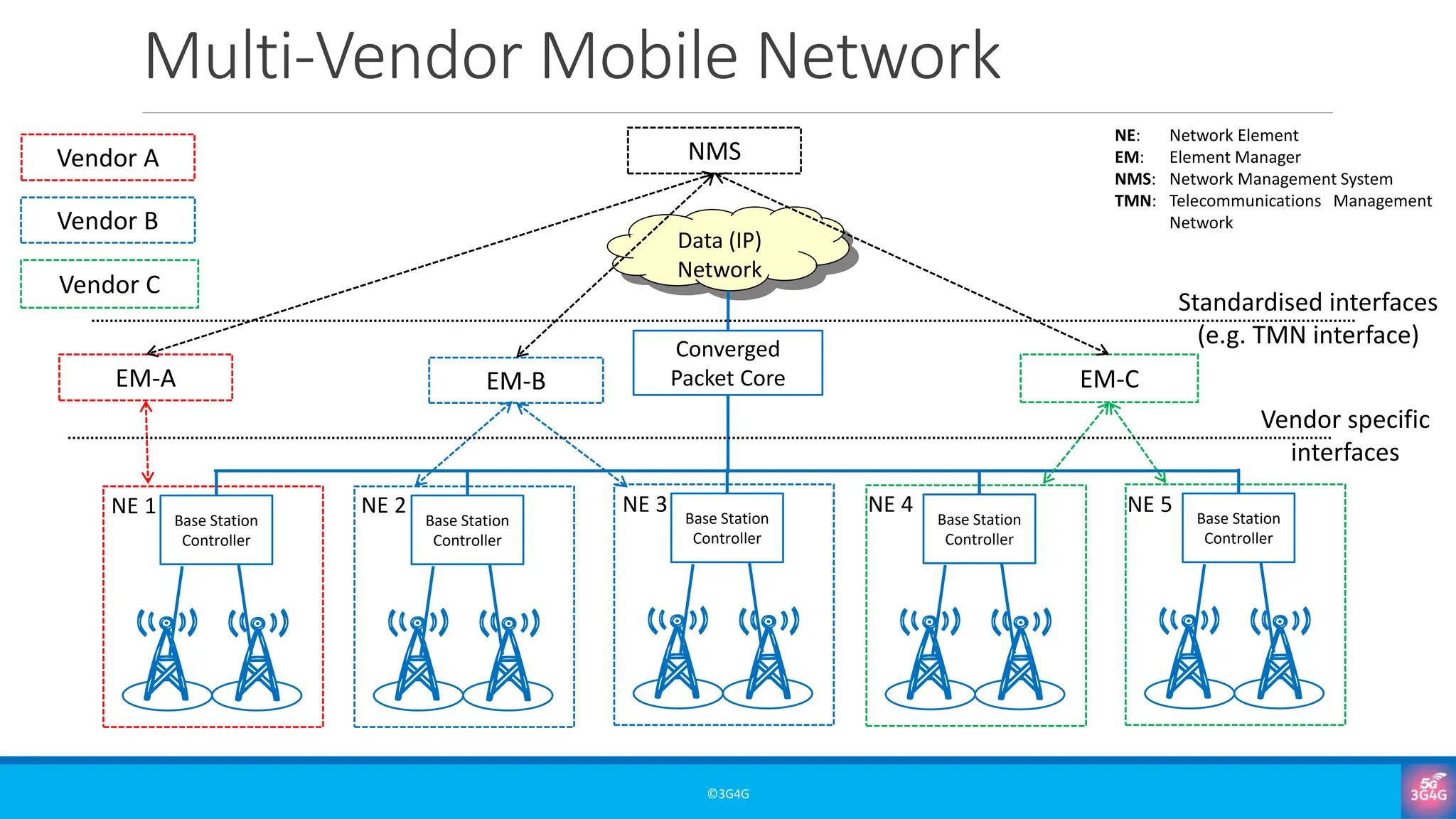
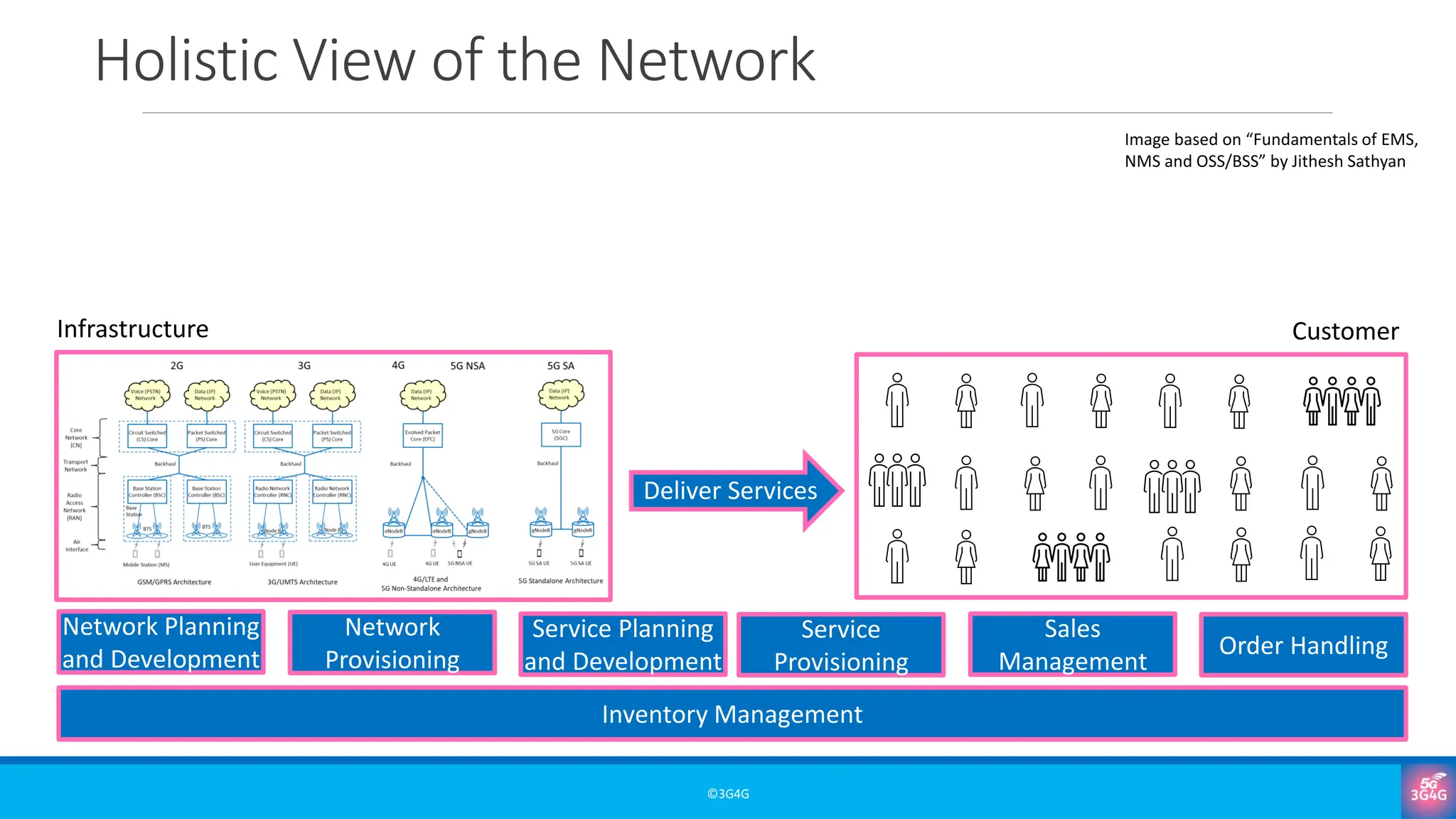
What are OSS and BSS, and why are they essential in mobile networks?
In this beginner-friendly video, we break down the basics of Operations Support Systems (OSS) and Business Support Systems (BSS) — the often overlooked yet critical components that keep telecom networks running smoothly and efficiently.
📌 What you’ll learn in this video:
• The role of OSS and BSS in mobile network operations
• Real-world examples and simplified architectures
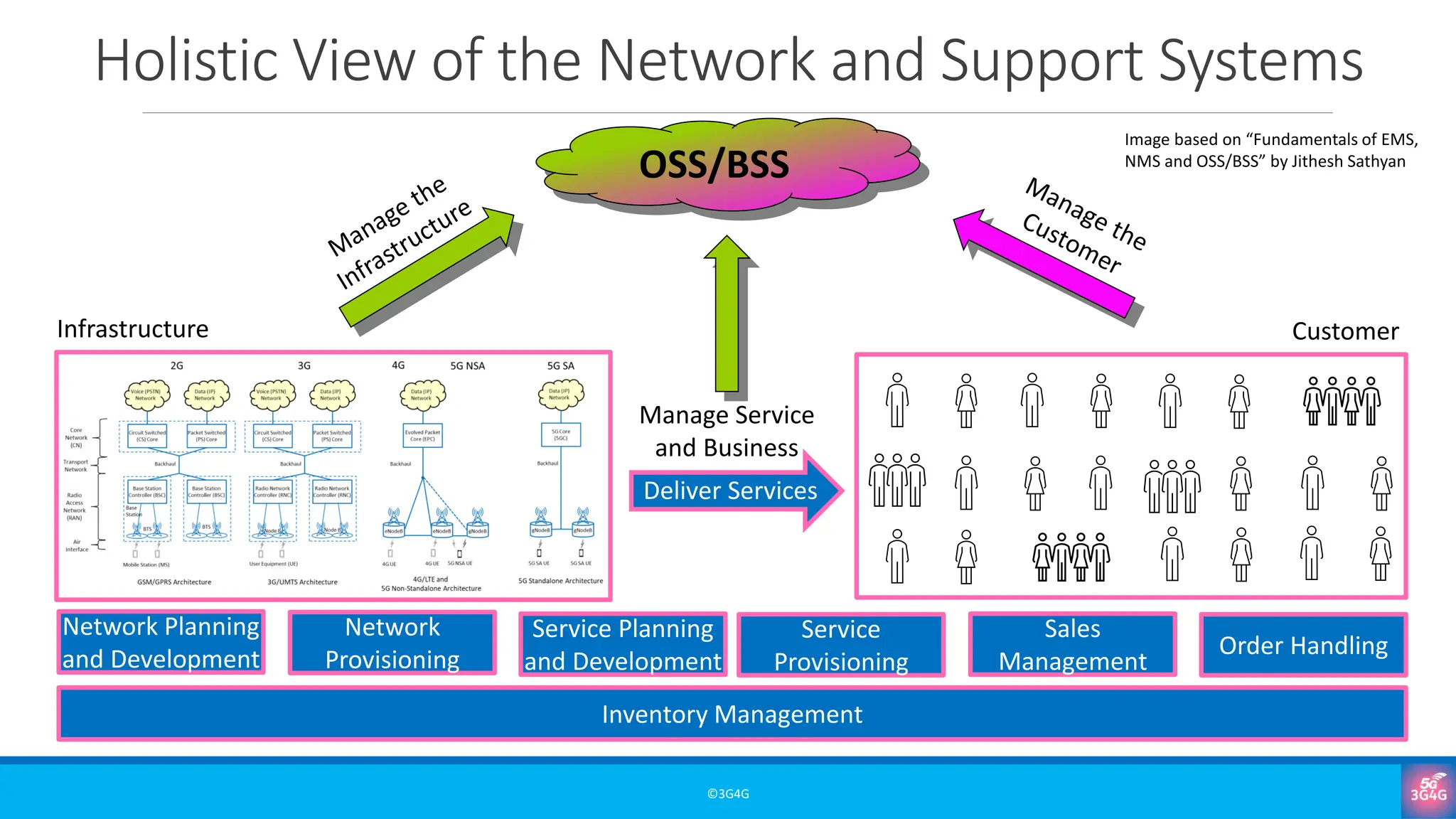
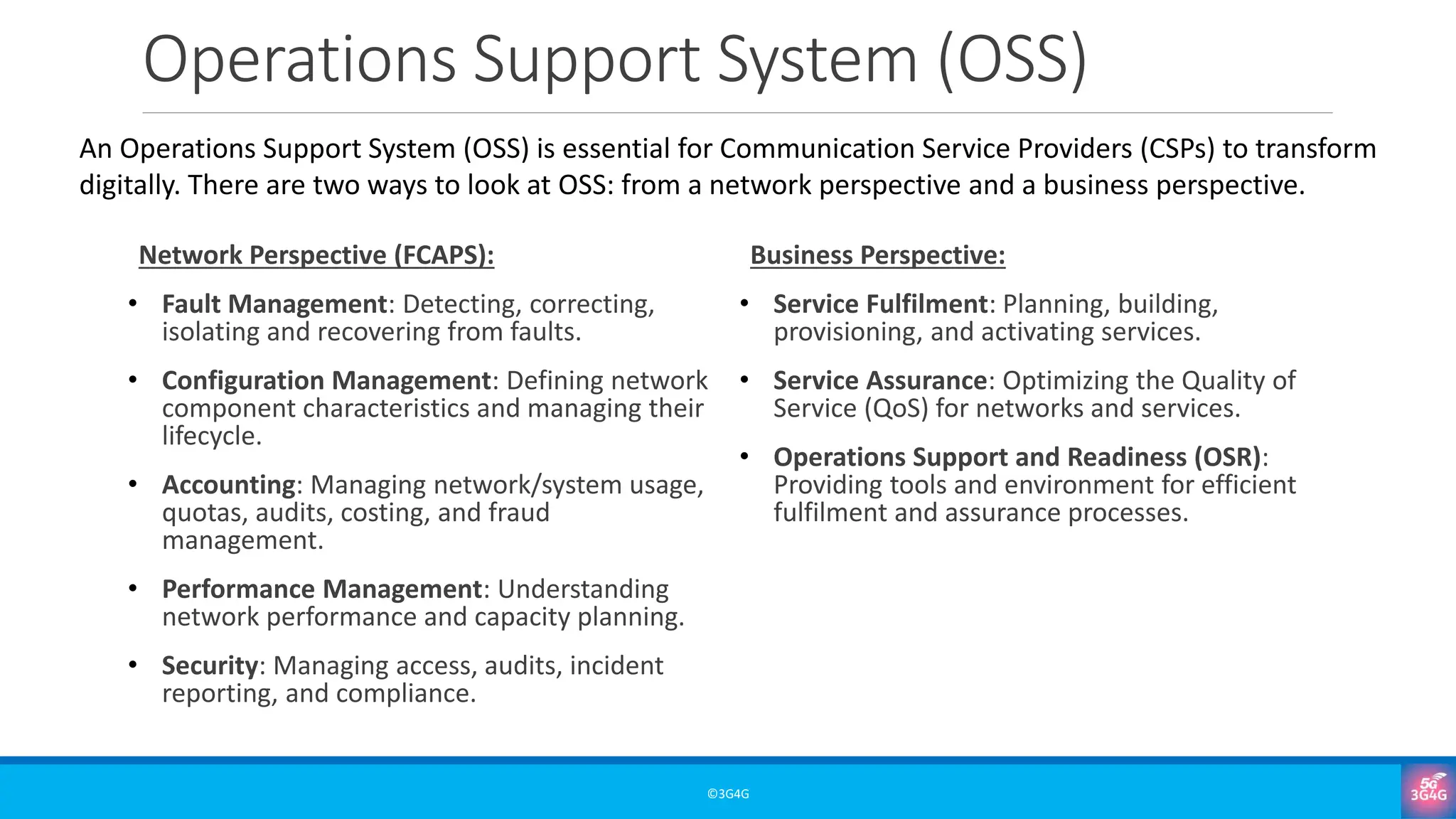
• FCAPS and the network/business perspectives of OSS
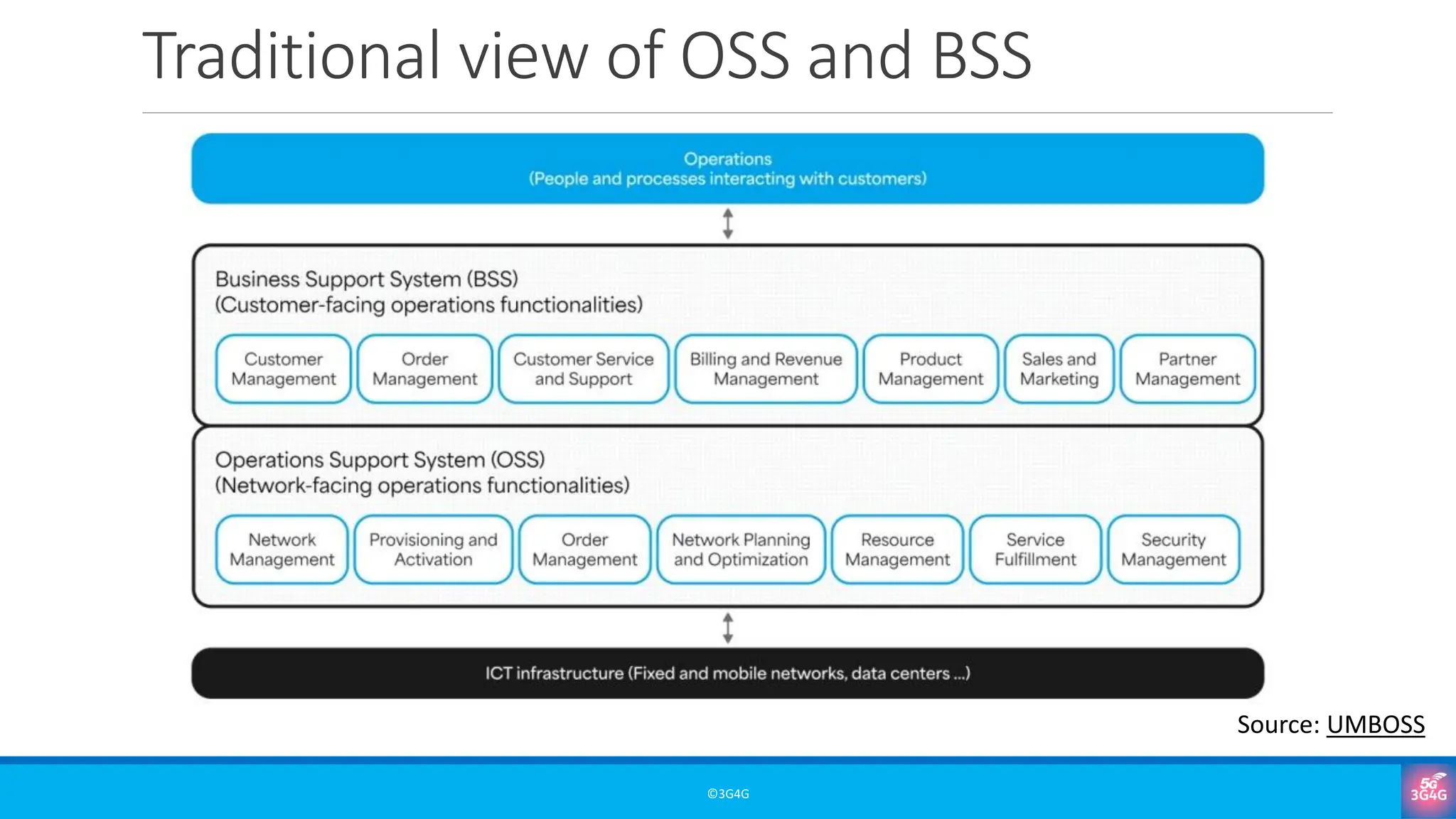
• The customer-facing importance of BSS
• Why OSS/BSS matter for service delivery, customer experience, and revenue assurance
💬 Got questions or insights? Drop them in the comments—we’d love to hear from you!
🔔 Subscribe for more: For more explainer videos on mobile and wireless technologies, don’t forget to like, subscribe, and hit the bell icon.
All our #3G4G5G slides, videos, blogs and tutorials are available at:
Tutorials: https://www.3g4g.co.uk/Training/
Videos: https://www.youtube.com/3G4G5G
Slides: https://www.slideshare.net/3G4GLtd
Our channels:
3G4G Website – https://www.3g4g.co.uk/
The 3G4G Blog – https://blog.3g4g.co.uk/
Telecoms Infrastructure Blog – https://www.telecomsinfrastructure.com/
Operator Watch Blog – https://www.operatorwatch.com/
Connectivity Technology Blog – https://www.connectivity.technology/
Free 5G Training – https://www.free5gtraining.com/
Free 6G Training – https://www.free6gtraining.com/
Private Networks Technology Blog - https://blog.privatenetworks.technology/