Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times
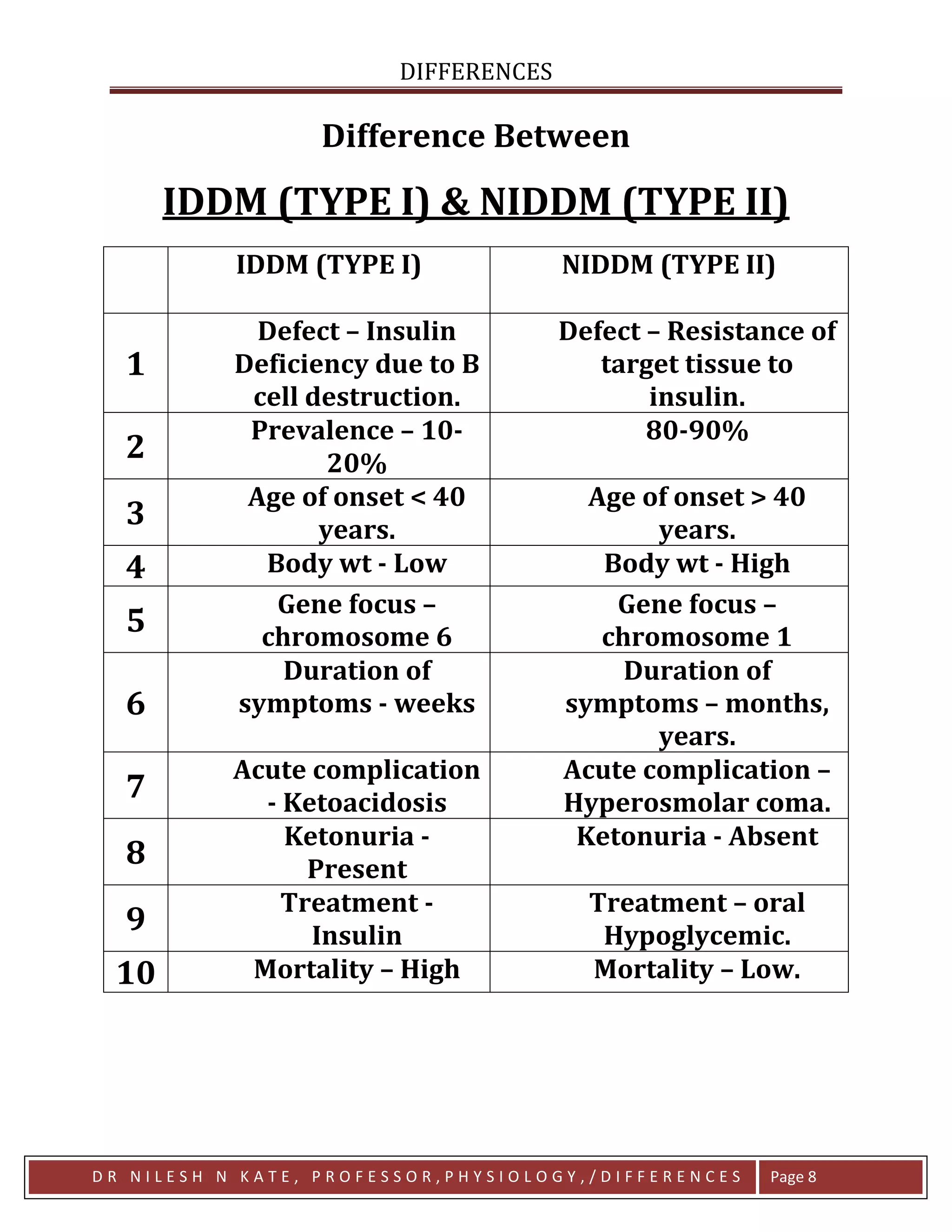

There are key differences between type I diabetes (IDDM) and type II diabetes (NIDDM). Type I is characterized by an insulin deficiency due to destruction of the beta cells and commonly occurs in younger, leaner patients. In contrast, type II involves resistance of tissues to insulin and generally affects older, overweight individuals. While type I requires lifelong insulin treatment and carries a higher mortality risk, type II can often be managed with oral medications and has a lower risk of death.
