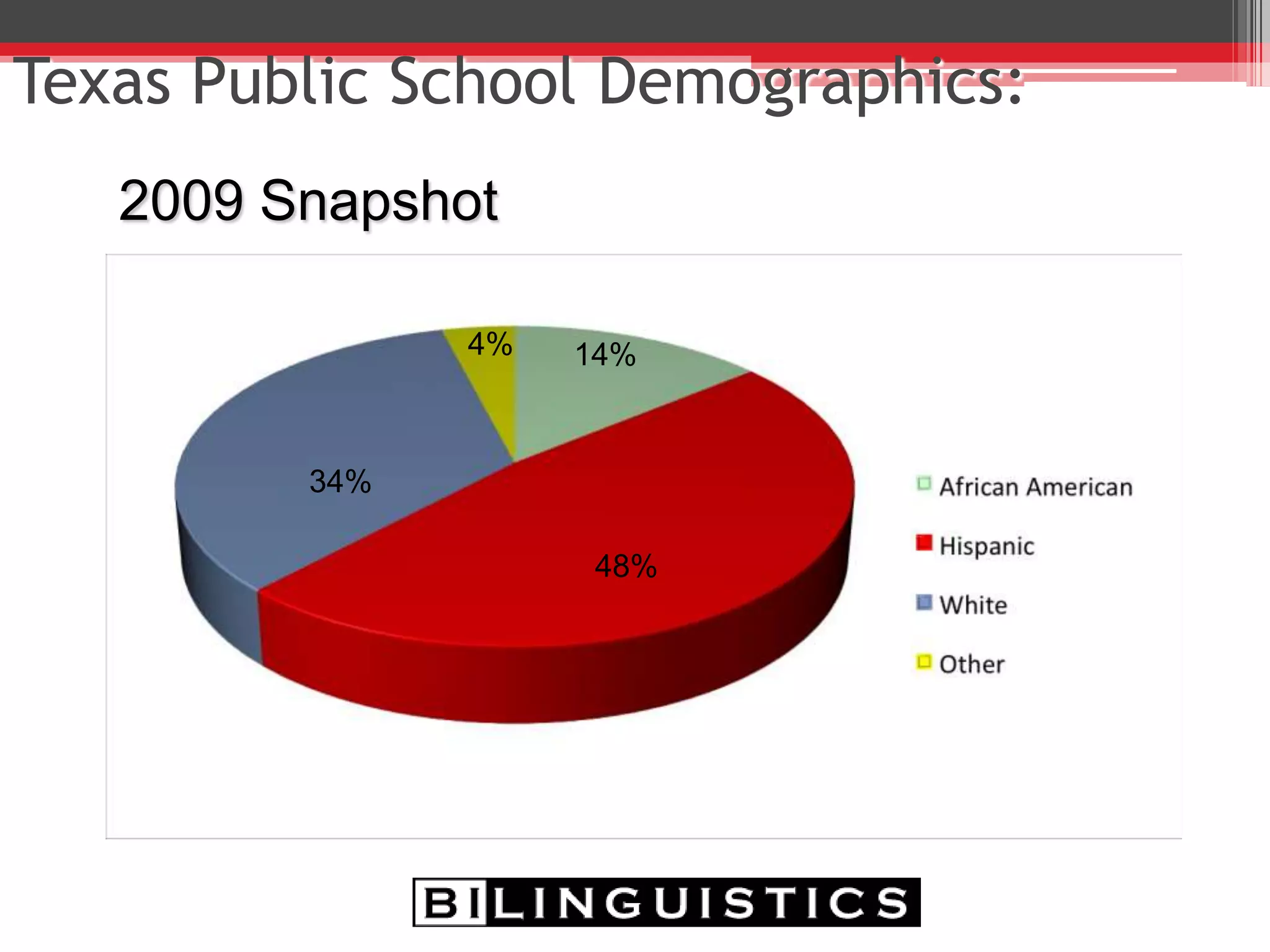
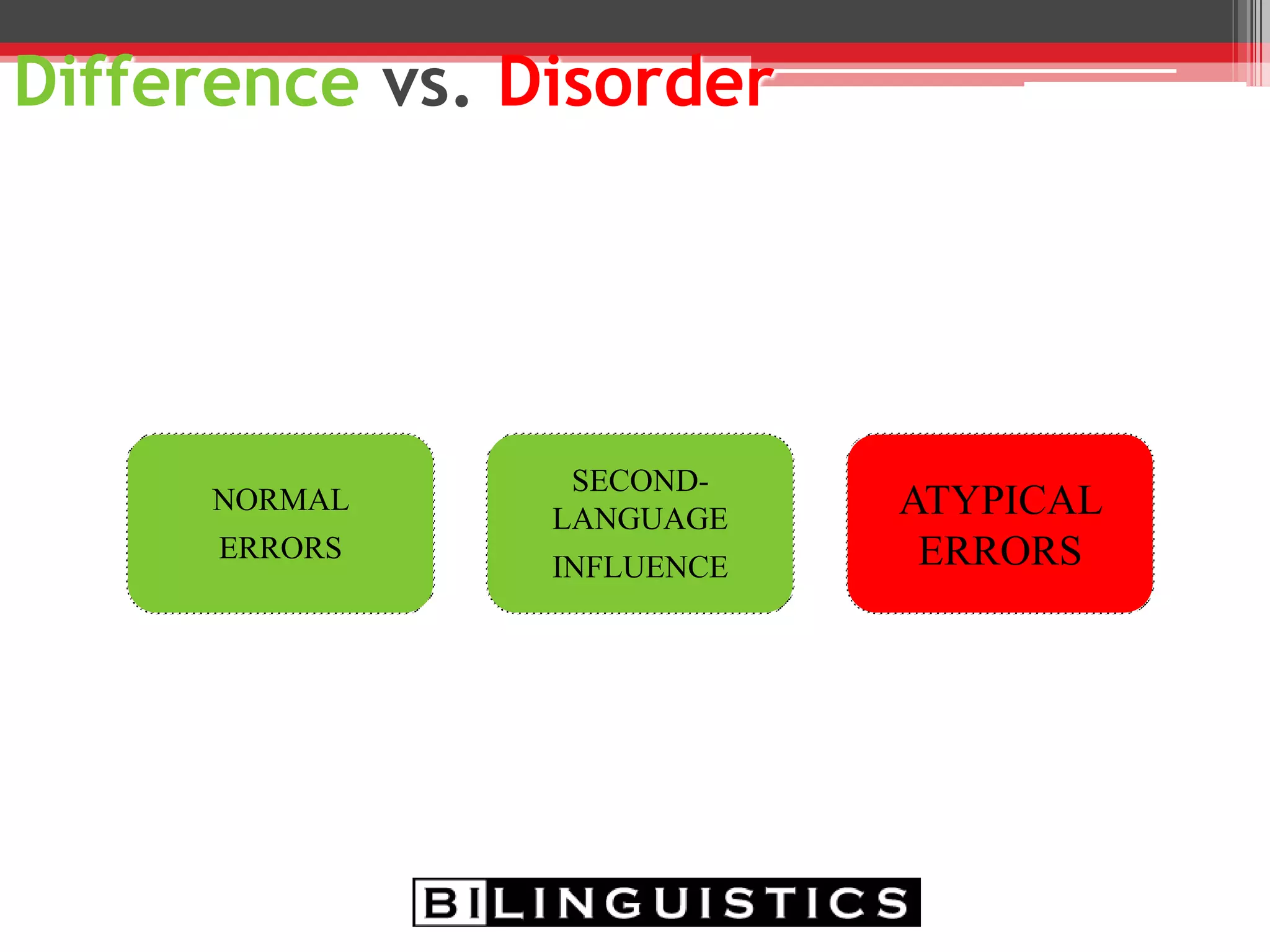
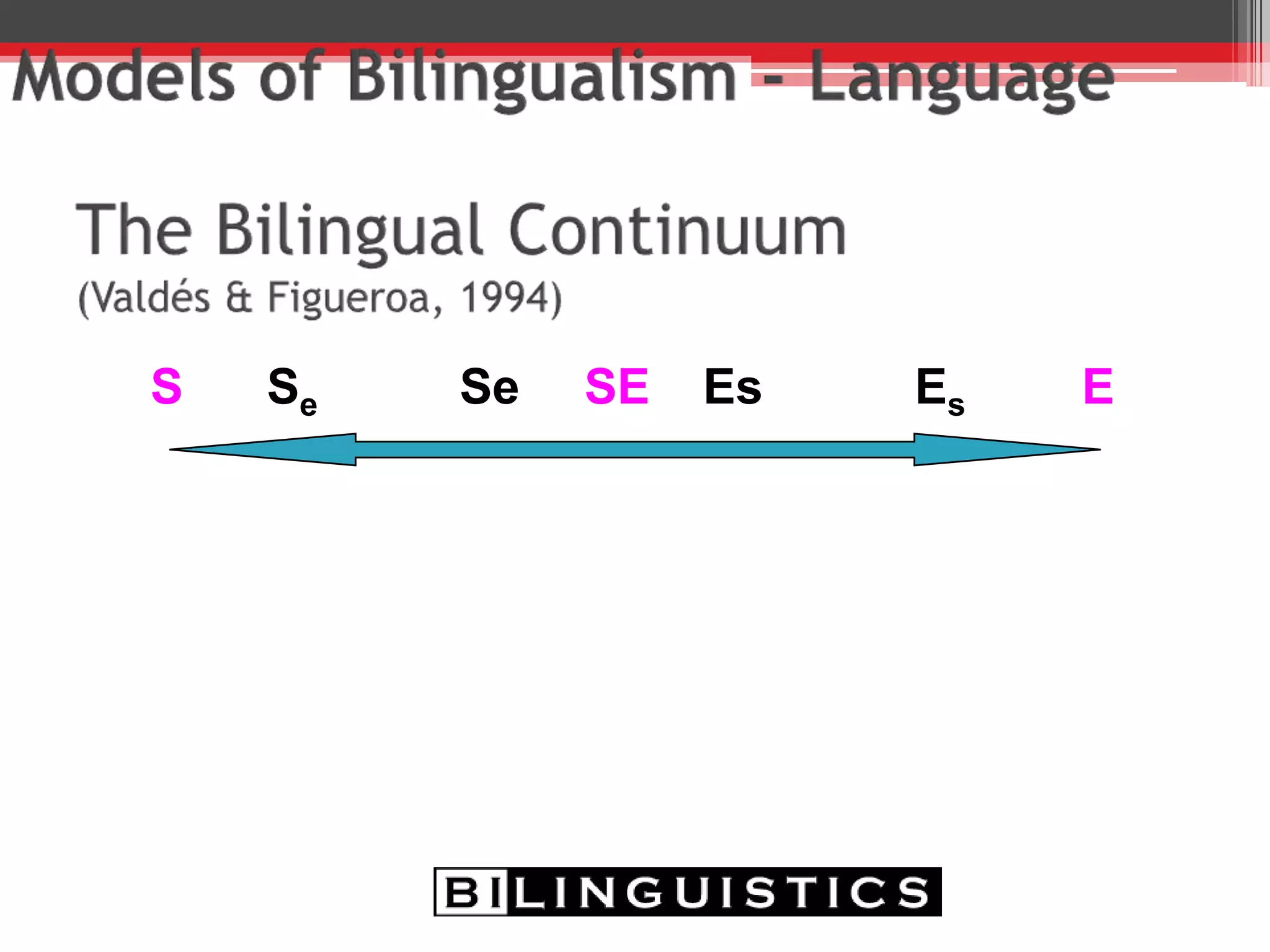
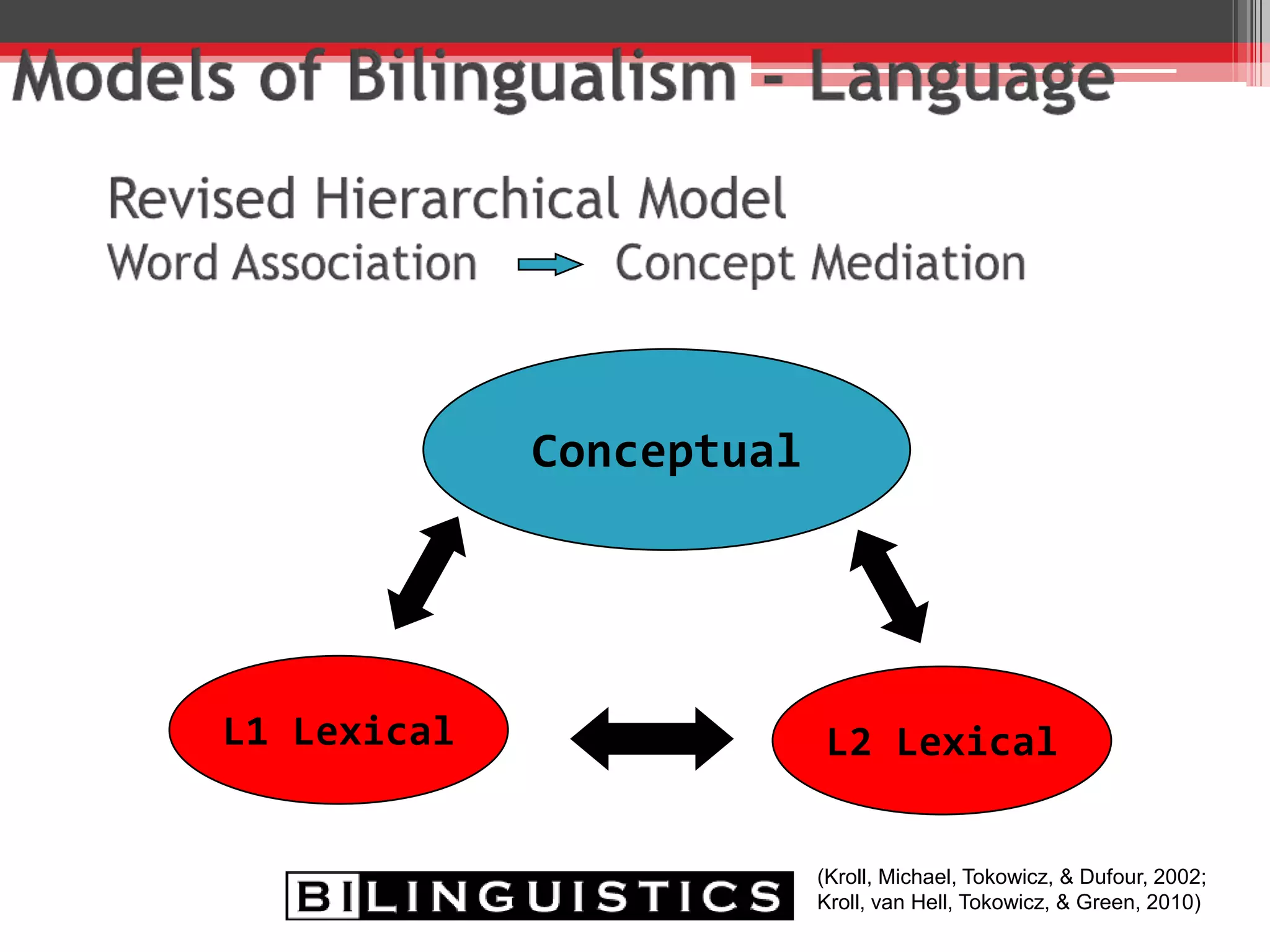
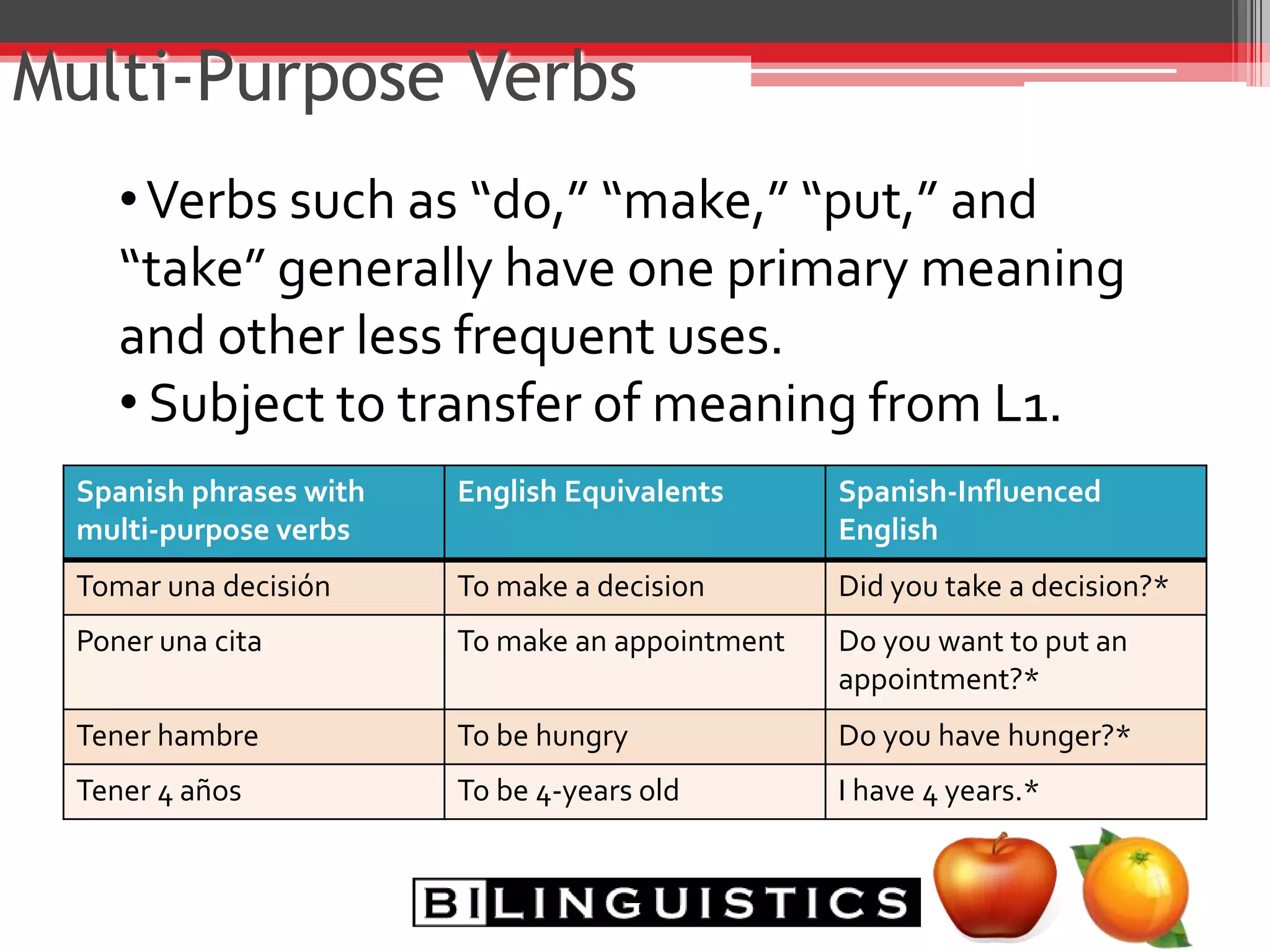
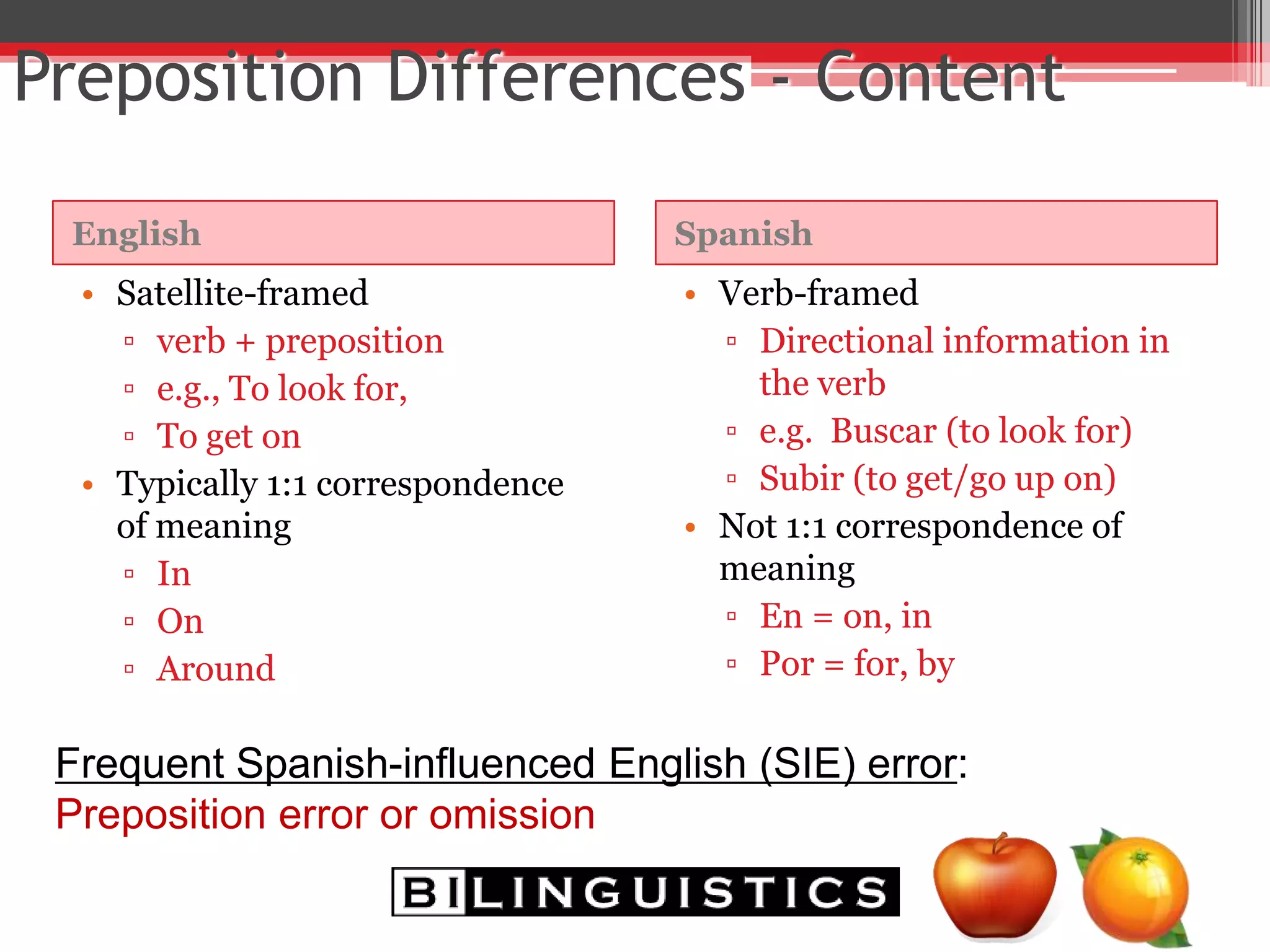
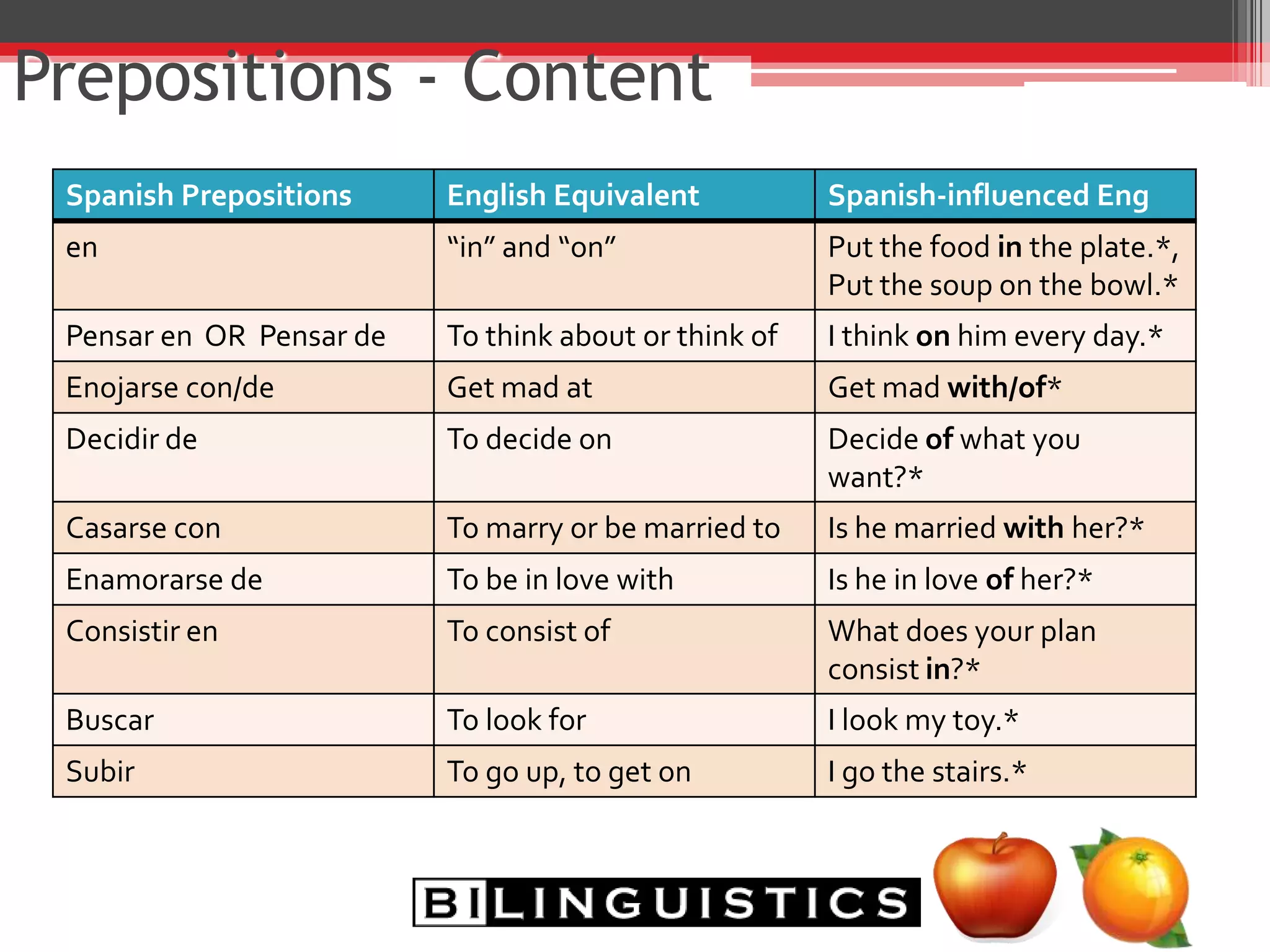
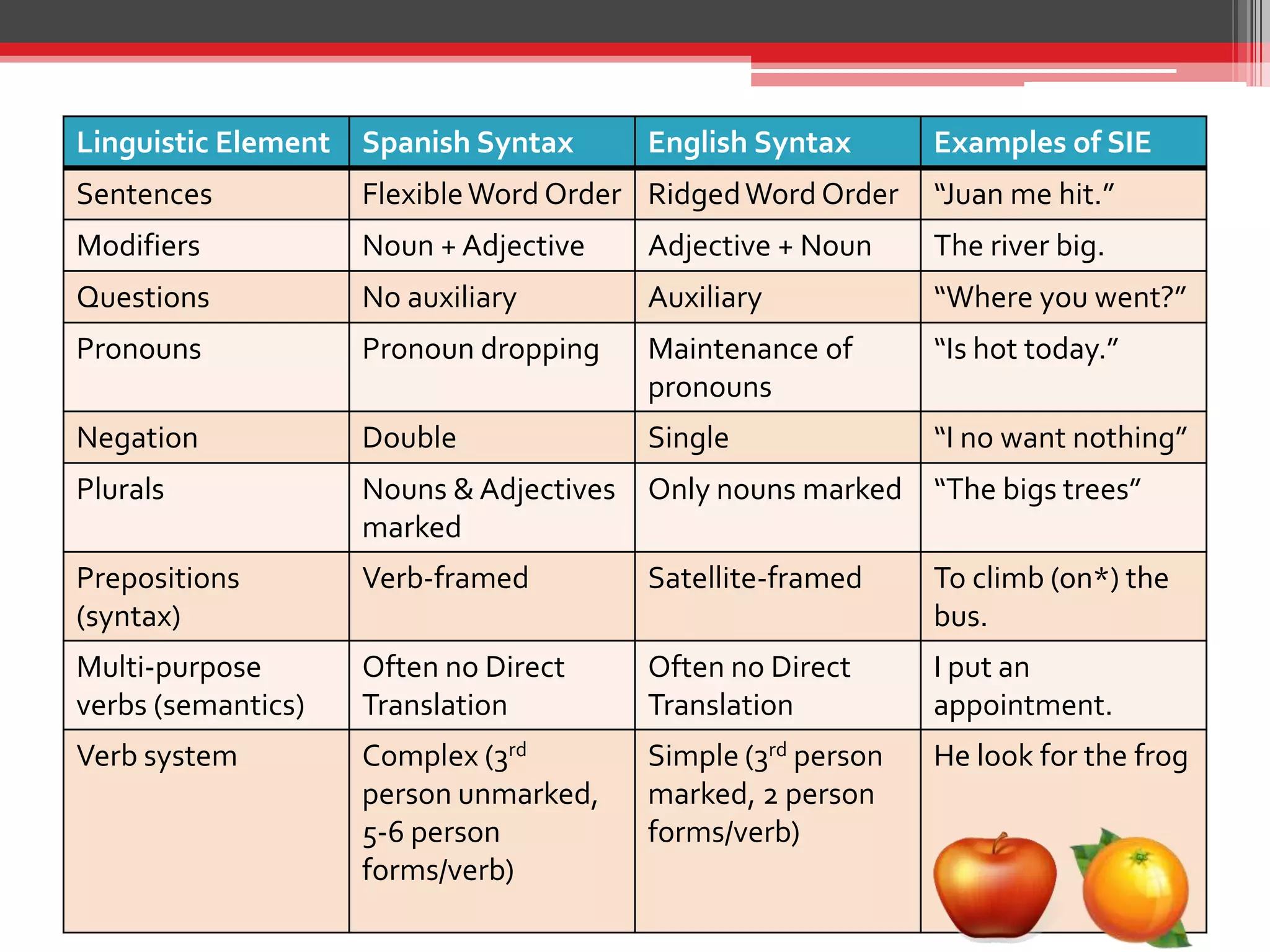
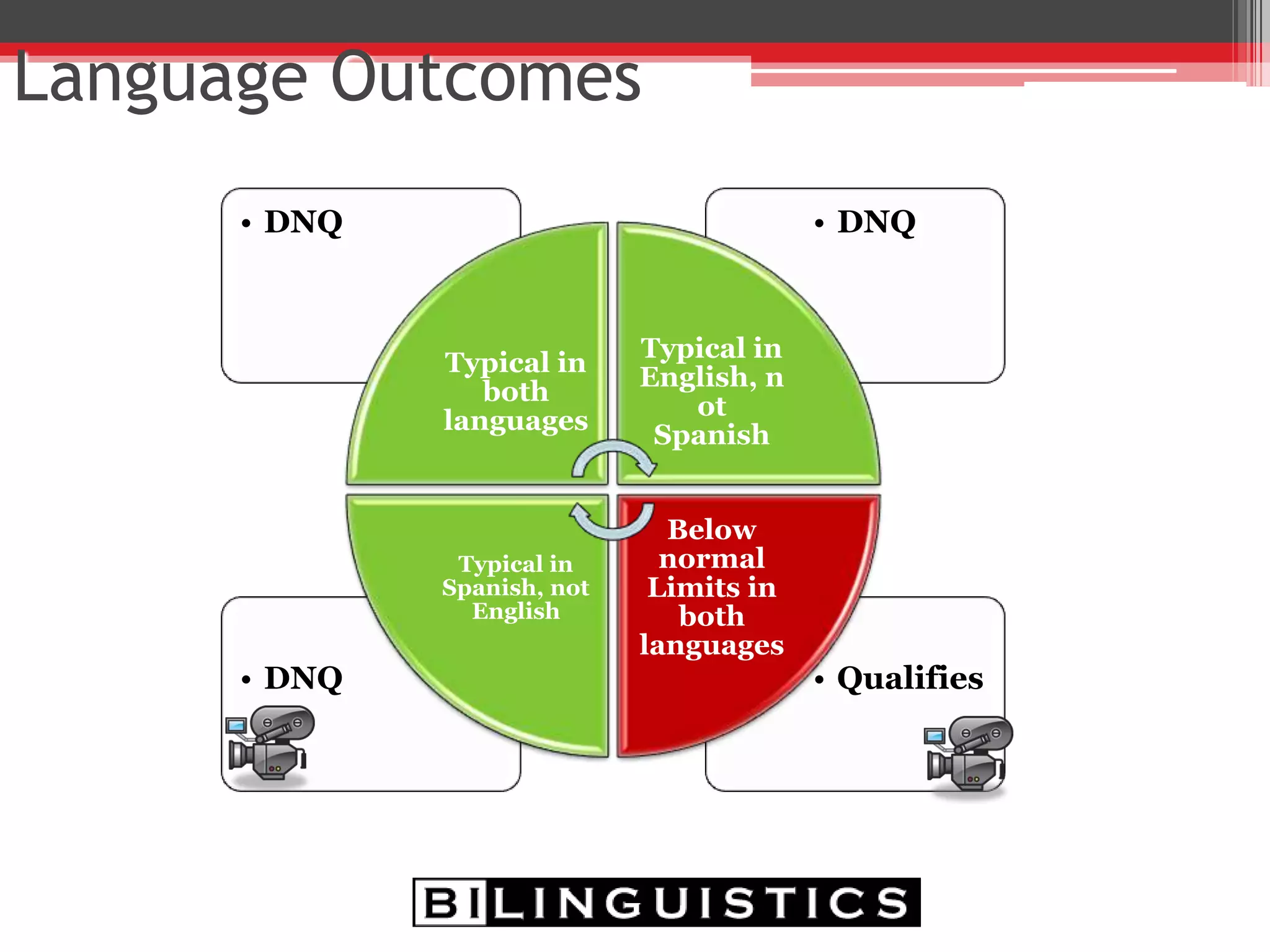
The document discusses the impact of bilingualism on language development, focusing on challenges in assessing and addressing the needs of bilingual populations in educational settings. It highlights typical language development milestones, language transfer errors, and the differences between English and Spanish in syntax, vocabulary, and semantics. Additionally, it explores practical strategies for intervention while emphasizing the importance of understanding linguistic differences and the role of continuing education for professionals.