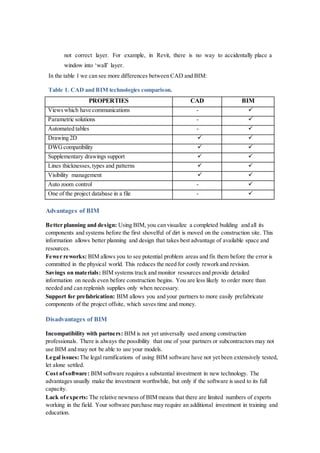
Computer-aided design (CAD) uses 2D technology to create drawings composed of lines and text without inherent meaning, while building information modeling (BIM) creates an intelligent 3D model where elements contain embedded data. BIM allows for better coordination and planning across disciplines by bringing all project information into a single, centralized database. Key differences between CAD and BIM include that BIM uses a task-oriented methodology where elements like walls are modeled as objects with properties, ensures consistency across views, and supports data-driven design and analysis using element classifications rather than layers. While BIM enables benefits like reduced rework, prefabrication support, and material savings, its adoption faces challenges including partner incompatibility, legal issues, and