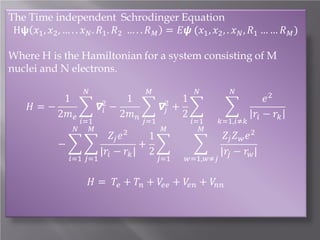
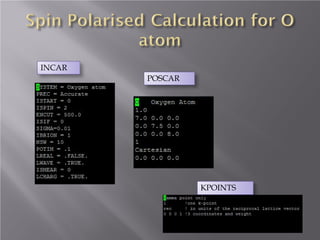
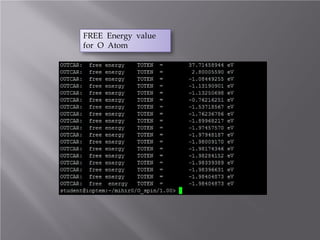
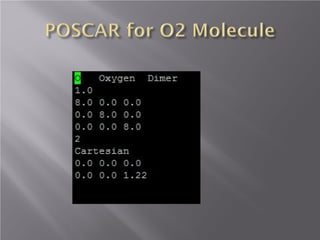
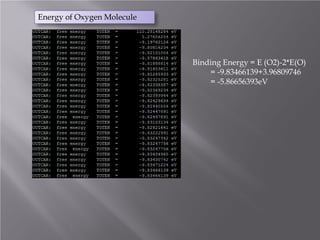
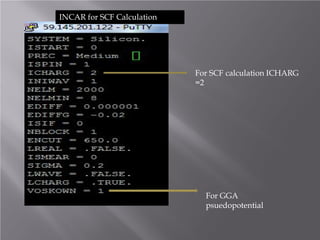
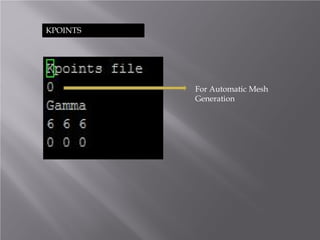
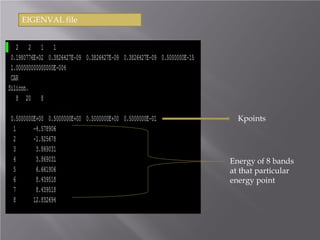
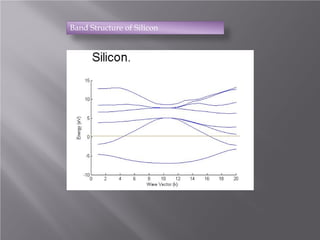
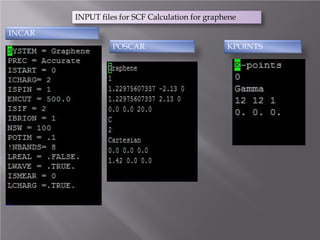
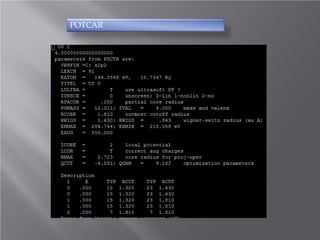
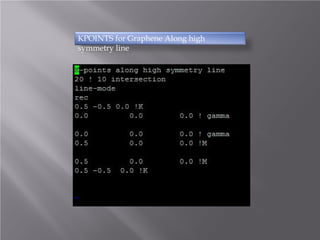
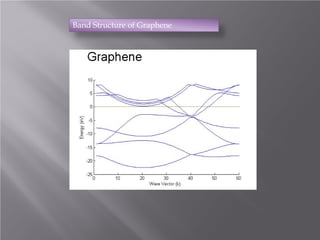
The document discusses density functional theory (DFT) and its implementation in the VASP software. It explains key concepts like the Kohn-Sham approach for approximating the many-body Schrodinger equation and the use of pseudopotentials and plane wave basis sets. It also summarizes some example calculations done in VASP like determining the binding energy of O2, equilibrium lattice constant of Cu, and band structures of Si and graphene. Key input and output files of VASP are also outlined.