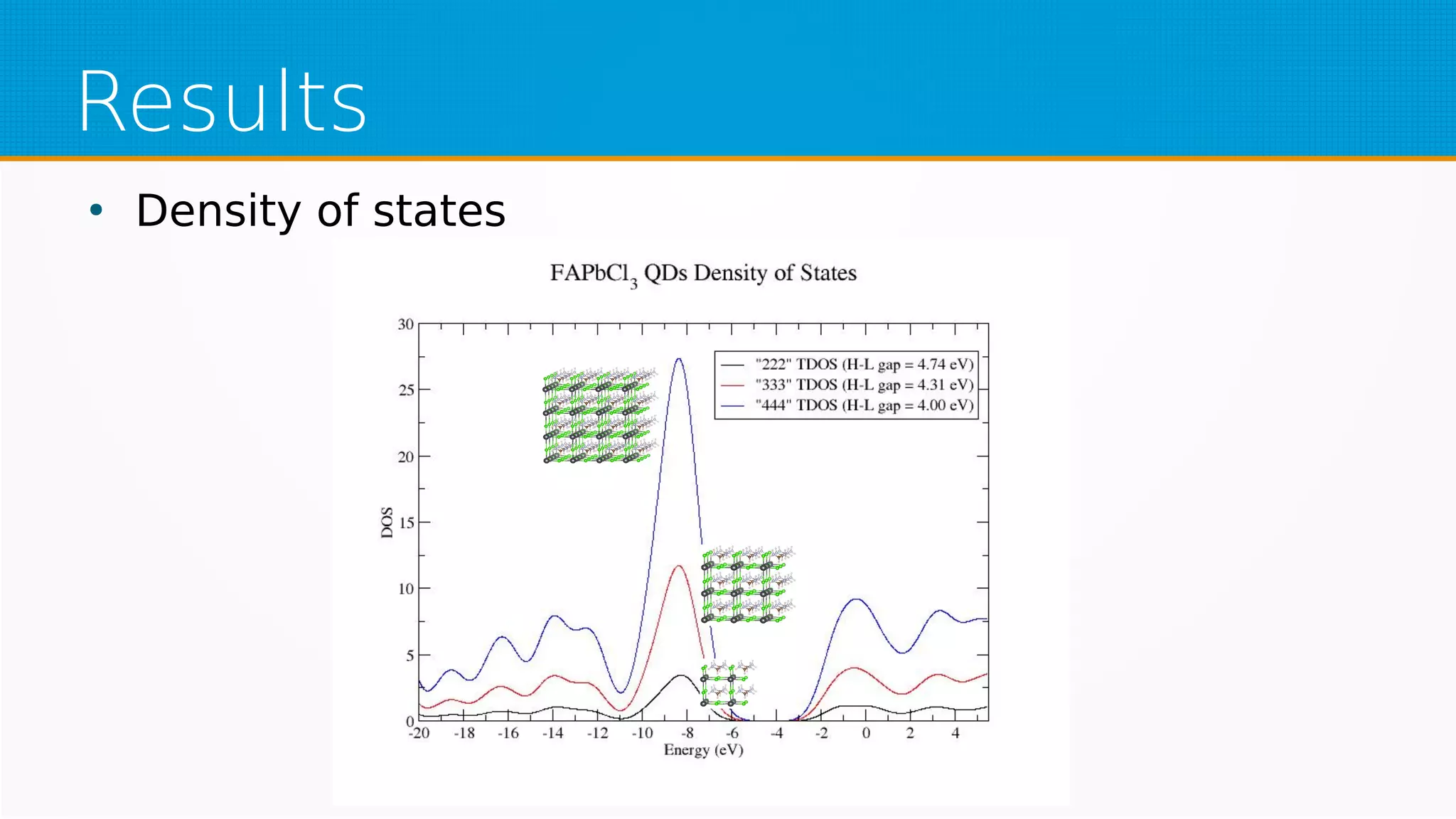
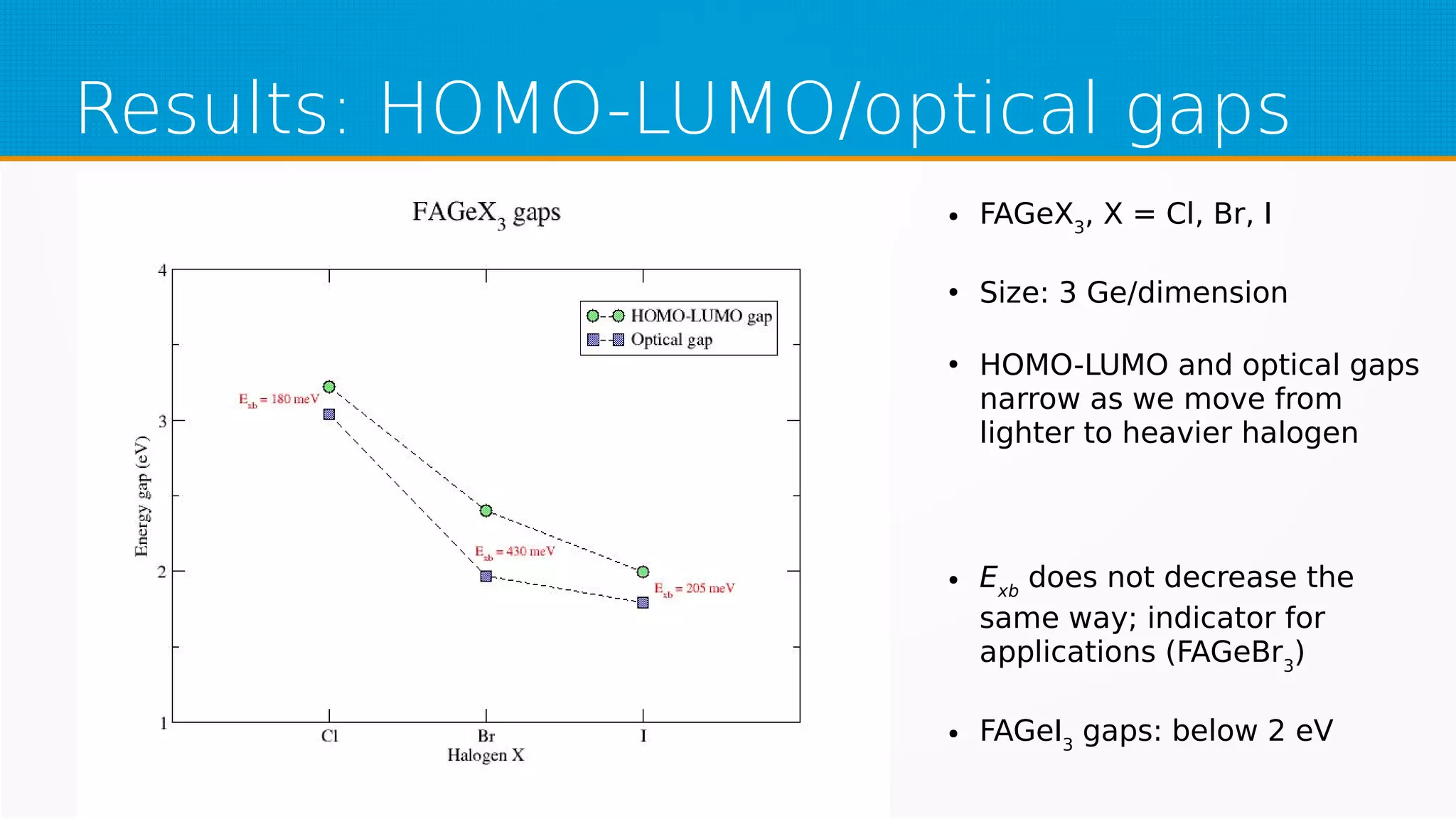
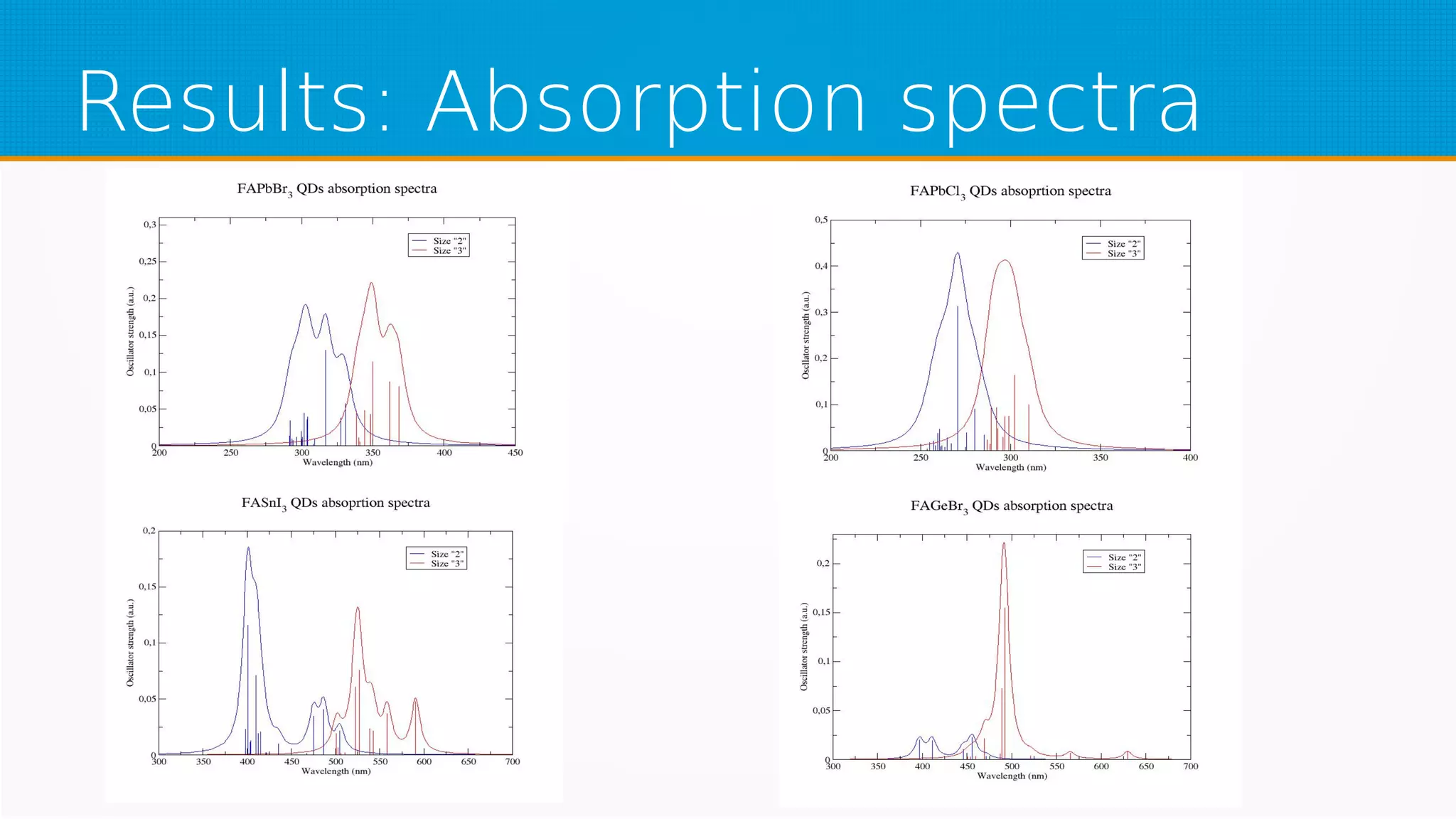
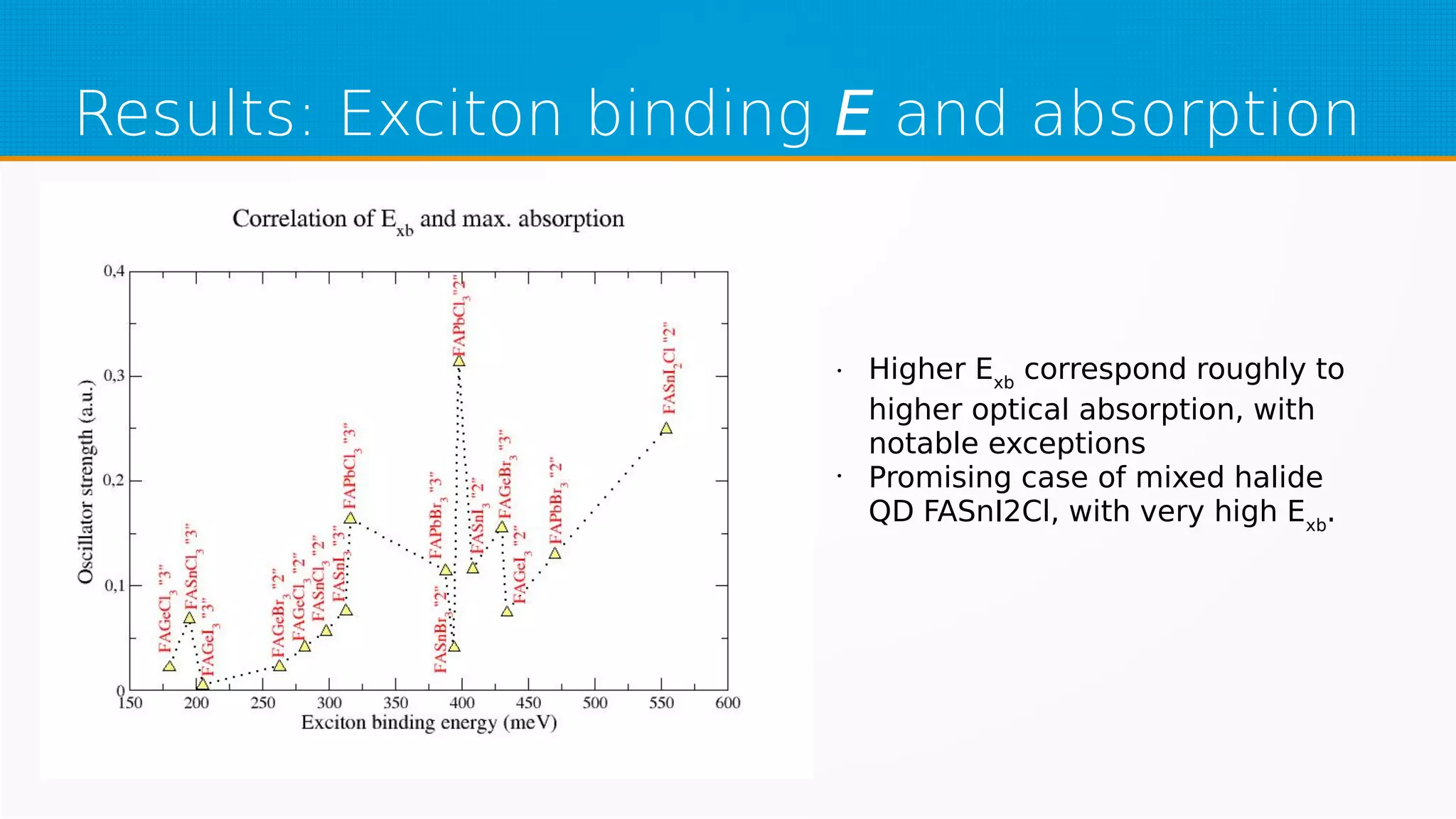
The study investigates hybrid halide perovskite quantum dots using DFT and TDDFT methods, focusing on structural and electronic properties. It reveals that gaps narrow with increasing sizes of quantum dots and heavier halogens, while exciton binding energies decrease with increased size. The results indicate a promising pathway for applications in optical absorption, particularly highlighting the performance of specific mixed halide quantum dots.